Signal Transduction Antibodies 3
Anti-SUMO4 Antibody (CAB9016)
- SKU:
- CAB9016
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-SUMO4 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9016 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human SUMO4 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
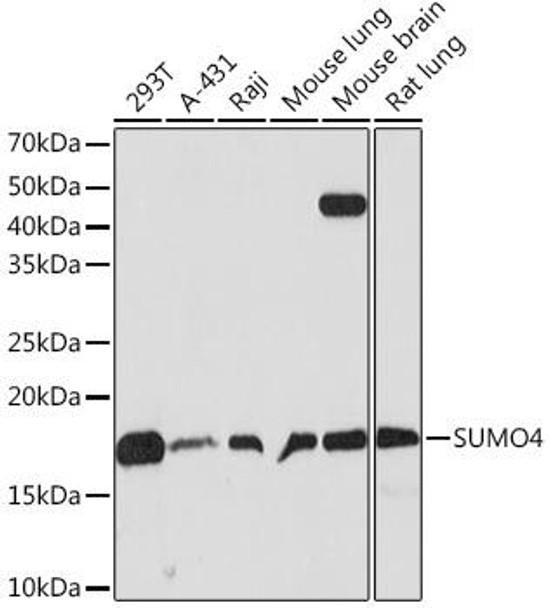
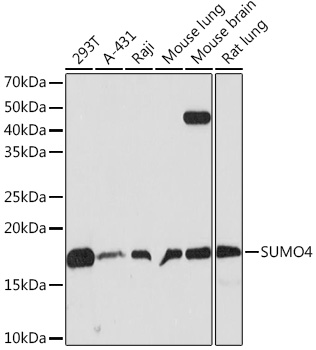
| Positive Samples: | 293T, A-431, Raji, Mouse lung, Mouse brain, Rat lung |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human SUMO4 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 387082 |
| Uniprot: | Q6EEV6 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 15kDa |
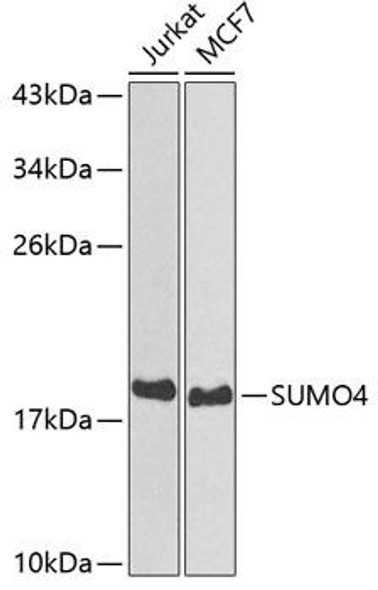
| Observed MW: | 17KDa |
| Synonyms: | IDDM5, SMT3H4, SUMO-4, dJ281H8.4 |
| Background: | This gene is a member of the SUMO gene family. This family of genes encode small ubiquitin-related modifiers that are attached to proteins and control the target proteins' subcellular localization, stability, or activity. The protein described in this record is located in the cytoplasm and specifically modifies IKBA, leading to negative regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent transcription of the IL12B gene. A specific polymorphism in this SUMO gene, which leads to the M55V substitution, has been associated with type I diabetes. The RefSeq contains this polymorphism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SUMO4: Ubiquitin-like protein which can be covalently attached to target lysines as a monomer. Does not seem to be involved in protein degradation and may modulate protein subcellular localization, stability or activity. Upon oxidative stress, conjugates to various anti-oxidant enzymes, chaperones, and stress defense proteins. May also conjugate to NFKBIA, TFAP2A and FOS, negatively regulating their transcriptional activity, and to NR3C1, positively regulating its transcriptional activity. Covalent attachment to its substrates requires prior activation by the E1 complex SAE1-SAE2 and linkage to the E2 enzyme UBE2I. Belongs to the ubiquitin family. SUMO subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Ubiquitin-like modifier Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 6q25 Cellular Component: nucleus Biological Process: protein sumoylation Disease: Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin-dependent, 5 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a member of the SUMO gene family. This family of genes encode small ubiquitin-related modifiers that are attached to proteins and control the target proteins' subcellular localization, stability, or activity. The protein described in this record is located in the cytoplasm and specifically modifies IKBA, leading to negative regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent transcription of the IL12B gene. A specific polymorphism in this SUMO gene, which leads to the M55V substitution, has been associated with type I diabetes. The RefSeq contains this polymorphism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q6EEV6 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 81175019 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 387082 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q6EEV6.2 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q6EEV6 |
| Molecular Weight: | ~18kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | small ubiquitin like modifier 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SUMO4 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | IDDM5; SMT3H4; SUMO-4; dJ281H8.4 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | small ubiquitin-related modifier 4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Small ubiquitin-related modifier 4 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Small ubiquitin-like protein 4 |
| Protein Family: | Small ubiquitin-related modifier |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SUMO4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SUMO4_HUMAN |
View AllClose