Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 5
Anti-SOX9 Antibody (CAB19710)
- SKU:
- CAB19710
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-SOX9 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB19710 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
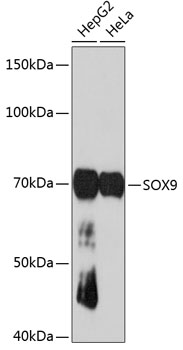
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human SOX9. |
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 IP 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HepG2, HeLa |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human SOX9. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 6662 |
| Uniprot: | P48436 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 70kDa |
| Observed MW: | 70KDa |
| Synonyms: | CMD1, CMPD1, SRA1, SRXX2, SRXY10, SOX9, SRY-box 9 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene recognizes the sequence CCTTGAG along with other members of the HMG-box class DNA-binding proteins. It acts during chondrocyte differentiation and, with steroidogenic factor 1, regulates transcription of the anti-Muellerian hormone (AMH) gene. Deficiencies lead to the skeletal malformation syndrome campomelic dysplasia, frequently with sex reversal. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SOX9: Plays an important role in the normal skeletal development. May regulate the expression of other genes involved in chondrogenesis by acting as a transcription factor for these genes. Defects in SOX9 are the cause of campomelic dysplasia (CMD1). CMD1 is a rare, often lethal, dominantly inherited, congenital osteochondrodysplasia, associated with male- to-female autosomal sex reversal in two-thirds of the affected karyotypic males. A disease of the newborn characterized by congenital bowing and angulation of long bones, unusually small scapulae, deformed pelvis and spine and a missing pair of ribs. Craniofacial defects such as cleft palate, micrognatia, flat face and hypertelorism are common. Various defects of the ear are often evident, affecting the cochlea, malleus incus, stapes and tympanum. Most patients die soon after birth due to respiratory distress which has been attributed to hypoplasia of the tracheobronchial cartilage and small thoracic cage. Defects in SOX9 are the cause of 46,XX sex reversal type 2 (SRXX2). SRXX2 is a condition in which male gonads develop in a genetic female (female to male sex reversal). |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q24.3 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; nucleus; protein complex Molecular Function:chromatin binding; protein binding; protein kinase activity; RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, enhancer binding; transcription factor activity Biological Process: cAMP-mediated signaling; cartilage condensation; cartilage development; cell fate specification; chromatin remodeling; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; hair follicle development; male germ-line sex determination; male gonad development; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of chondrocyte differentiation; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; negative regulation of immune system process; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation; negative regulation of ossification; negative regulation of photoreceptor cell differentiation; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; nucleosome assembly; otic vesicle formation; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of chondrocyte differentiation; positive regulation of epithelial cell differentiation; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; prostate gland development; protein complex assembly; regulation of apoptosis; regulation of cell proliferation; retina development in camera-type eye; Sertoli cell differentiation; signal transduction; skeletal development; somatic stem cell maintenance; spermatogenesis; tissue homeostasis Disease: 46,xy Sex Reversal 10; Campomelic Dysplasia |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene recognizes the sequence CCTTGAG along with other members of the HMG-box class DNA-binding proteins. It acts during chondrocyte differentiation and, with steroidogenic factor 1, regulates transcription of the anti-Muellerian hormone (AMH) gene. Deficiencies lead to the skeletal malformation syndrome campomelic dysplasia, frequently with sex reversal. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P48436 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1351096 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6662 |
| NCBI Accession: | P48436.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P48436,Q53Y80, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P48436 |
| Molecular Weight: | 56,137 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Transcription factor SOX-9 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | SRY-box 9 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SOX9 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CMD1; SRA1; CMPD1; SRXX2; SRXY10 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | transcription factor SOX-9 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Transcription factor SOX-9 |
| Protein Family: | Transcription factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SOX9 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SOX9_HUMAN |