Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 3
Anti-SNIP1 Antibody (CAB16747)
- SKU:
- CAB16747
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-SNIP1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16747 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
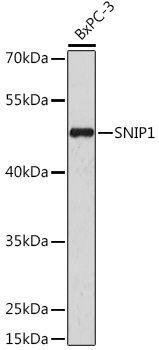
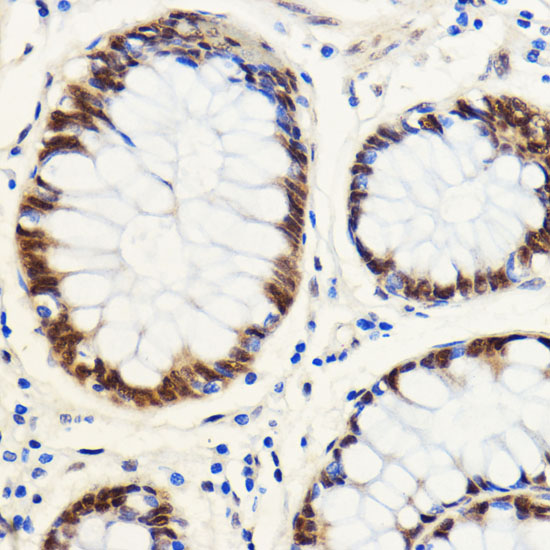
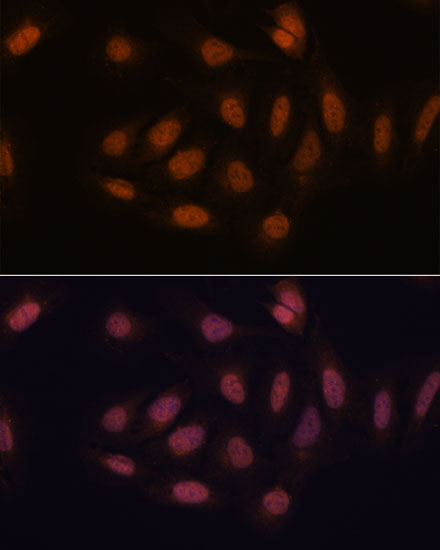
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human SNIP1. |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | BxPC-3 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human SNIP1. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 79753 |
| Uniprot: | Q8TAD8 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 45kDa |
| Observed MW: | 46kDa |
| Synonyms: | SNIP1, PML1, PMRED |
| Background: | This gene encodes a protein that contains a coiled-coil motif and C-terminal forkhead-associated (FHA) domain. The encoded protein functions as a transcriptional coactivator that increases c-Myc activity and inhibits transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kB) signaling. The encoded protein also regulates the stability of cyclin D1 mRNA, and may play a role in cell proliferation and cancer progression. Mutations in this gene are a cause of psychomotor retardation, epilepsy, and craniofacial dysmorphism (PMRED). |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SNIP1: Down-regulates NF-kappa-B signaling by competing with RELA for CREBBP/EP300 binding. Involved in the microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis. Defects in SNIP1 are the cause of psychomotor retardation, epilepsy, and craniofacial dysmorphism (PMRED). A disease characterized by severe psychomotor retardation, intractable seizures, dysmorphic features, and a lumpy skull surface. Patients are hypotonic and have poor feeding in the neonatal period. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Inhibitor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p34.3 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; cytoplasm Molecular Function:protein binding Biological Process: miRNA-mediated gene silencing, production of miRNAs; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent Disease: Psychomotor Retardation, Epilepsy, And Craniofacial Dysmorphism |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a protein that contains a coiled-coil motif and C-terminal forkhead-associated (FHA) domain. The encoded protein functions as a transcriptional coactivator that increases c-Myc activity and inhibits transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kB) signaling. The encoded protein also regulates the stability of cyclin D1 mRNA, and may play a role in cell proliferation and cancer progression. Mutations in this gene are a cause of psychomotor retardation, epilepsy, and craniofacial dysmorphism (PMRED). [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012] |
| UniProt Code: | Q8TAD8 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 48428655 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 79753 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q8TAD8.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q8TAD8 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46 kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Smad nuclear-interacting protein 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | Smad nuclear interacting protein 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SNIP1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PML1; PMRED |
| NCBI Protein Information: | smad nuclear-interacting protein 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Smad nuclear-interacting protein 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | FHA domain-containing protein SNIP1 |
| Protein Family: | Smad nuclear interacting protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SNIP1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SNIP1_HUMAN |
View AllClose