Cell Biology Antibodies 13
Anti-RGCC Antibody (CAB17689)
- SKU:
- CAB17689
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-RGCC Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB17689 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
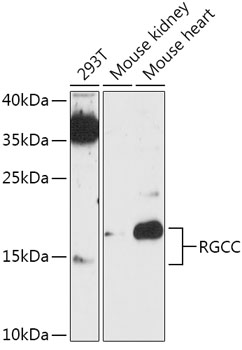
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of Human RGCC. |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | 293T, Mouse kidney, Mouse heart |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of Human RGCC. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 28984 |
| Uniprot: | Q9H4X1 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | |
| Observed MW: | 15KD/20kDa |
| Synonyms: | C13orf15, RGC-32, RGC32, bA157L14.2, RGCC |
| Background: | This gene is thought to regulate cell cycle progression. It is induced by p53 in response to DNA damage, or by sublytic levels of complement system proteins that result in activation of the cell cycle. The encoded protein localizes to the cytoplasm during interphase and to centrosomes during mitosis. The protein forms a complex with polo-like kinase 1. The protein also translocates to the nucleus in response to treatment with complement system proteins, and can associate with and increase the kinase activity of cell division cycle 2 protein. In different assays and cell types, overexpression of this protein has been shown to activate or suppress cell cycle progression. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | RGC32: modulates the activity of cell cycle-specific kinases. Interacts with CDK1 and PLK1. Enhances CDK1 activity and contribute to the regulation of the cell cycle. May inhibit growth of glioma cells by promoting arrest of mitotic progression at the G2/M transition. Fibrogenic factor contributing to the pathogenesis of renal fibrosis through fibroblast activation. Interacts with SMAD3. Cytoplasmic in unstimulated cells; translocates to the nucleus following activation by complement. Associated with the centrosome during prometaphase and metaphase. Induced by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Up-regulated in aorta endothelial cells in response to complement activation. Important in vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) differentiation following transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) induction. Its expression is greatly induced by TGF-beta in neural crest cells, leading to the induction of VSMC gene promoters. Smad and RhoA signaling are important for RGC-32 activation in neural crest cells. Forms a complex with hnRNP A/B that regulates the transcription of VSMC differentiation genes. Two isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, regulatory subunit; Cell cycle regulation Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 13q14.11 Cellular Component: centrosome; cytoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding; protein kinase activator activity; protein kinase binding Biological Process: positive regulation of mitosis; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process; negative regulation of cytokine secretion; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration; G1/S-specific positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; complement activation; negative regulation of cell proliferation; negative regulation of angiogenesis; negative regulation of exit from mitosis; positive regulation of stress fiber formation; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription factor activity; positive regulation of cytokine secretion |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is thought to regulate cell cycle progression. It is induced by p53 in response to DNA damage, or by sublytic levels of complement system proteins that result in activation of the cell cycle. The encoded protein localizes to the cytoplasm during interphase and to centrosomes during mitosis. The protein forms a complex with polo-like kinase 1. The protein also translocates to the nucleus in response to treatment with complement system proteins, and can associate with and increase the kinase activity of cell division cycle 2 protein. In different assays and cell types, overexpression of this protein has been shown to activate or suppress cell cycle progression. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9H4X1 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 132626811 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 28984 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_054778.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9H4X1,Q6NZ48, Q9UL69, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9H4X1 |
| Molecular Weight: | 12,924 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | regulator of cell cycle RGCC |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | regulator of cell cycle |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | RGCC |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | RGC32; RGC-32; C13orf15; bA157L14.2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | regulator of cell cycle RGCC |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Regulator of cell cycle RGCC |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Response gene to complement 32 protein; RGC-32 |
| Protein Family: | Regulator of cell cycle |
| UniProt Gene Name: | RGCC |
| UniProt Entry Name: | RGCC_HUMAN |