Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 5
Anti-Retinoic Acid Receptor beta Antibody (CAB4535)
- SKU:
- CAB4535
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Retinoic Acid Receptor beta Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB4535 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
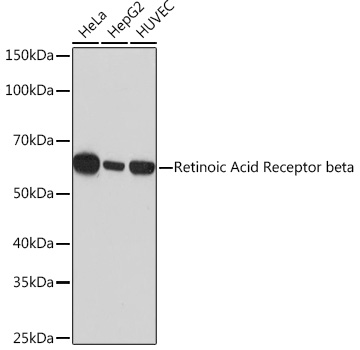
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Retinoic Acid Receptor beta |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, HepG2, HUVEC |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Retinoic Acid Receptor beta |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 5915 |
| Uniprot: | P10826 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 55kDa |
| Observed MW: | 55KDa |
| Synonyms: | HAP, MCOPS12, NR1B2, RARbeta1, RRB2 |
| Background: | This gene encodes retinoic acid receptor beta, a member of the thyroid-steroid hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear transcriptional regulators. This receptor localizes to the cytoplasm and to subnuclear compartments. It binds retinoic acid, the biologically active form of vitamin A which mediates cellular signalling in embryonic morphogenesis, cell growth and differentiation. It is thought that this protein limits growth of many cell types by regulating gene expression. The gene was first identified in a hepatocellular carcinoma where it flanks a hepatitis B virus integration site. Alternate promoter usage and differential splicing result in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | RARB: is a receptor for retinoic acid, a potent mammalian morphogen and teratogen that has profound effects on vertebrate development. RARB is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Controls cell function by directly regulating gene expression. Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal steroid-binding domain. Four splice-variant isoforms have been described. Isoform beta-1 and beta-2 are nuclear and isoform beta-4 cytoplasmic. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Oncoprotein; Nuclear receptor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 3p24.2 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; cytoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:retinoid X receptor binding; protein binding; DNA binding; zinc ion binding; protein complex binding; steroid hormone receptor activity; drug binding; retinoic acid receptor activity Biological Process: retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; regulation of myelination; glandular epithelial cell development; striatum development; positive regulation of apoptosis; embryonic eye morphogenesis; multicellular organism growth; negative regulation of chondrocyte differentiation; ventricular cardiac muscle cell differentiation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; signal transduction; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis; negative regulation of cell proliferation; ureteric bud development; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; gene expression; steroid hormone mediated signaling; positive regulation of neuron differentiation; embryonic gut development; transmembrane transport; negative regulation of apoptosis Disease: Microphthalmia, Syndromic 12 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes retinoic acid receptor beta, a member of the thyroid-steroid hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear transcriptional regulators. This receptor localizes to the cytoplasm and to subnuclear compartments. It binds retinoic acid, the biologically active form of vitamin A which mediates cellular signalling in embryonic morphogenesis, cell growth and differentiation. It is thought that this protein limits growth of many cell types by regulating gene expression. The gene was first identified in a hepatocellular carcinoma where it flanks a hepatitis B virus integration site. Alternate promoter usage and differential splicing result in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | P10826 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 17380507 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5915 |
| NCBI Accession: | P10826.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P10826,P12891, Q00989, Q15298, Q9UN48, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P10826 |
| Molecular Weight: | Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Retinoic acid receptor beta |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | retinoic acid receptor, beta |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | RARB |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HAP; RRB2; NR1B2; MCOPS12 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | retinoic acid receptor beta; RAR-beta; RAR-epsilon; HBV-activated protein; hepatitis B virus activated protein; retinoic acid receptor, beta polypeptide; nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Retinoic acid receptor beta |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | HBV-activated protein; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 2; RAR-epsilon |
| Protein Family: | Retinoic acid receptor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | RARB |
| UniProt Entry Name: | RARB_HUMAN |