Cell Death Antibodies 2
Anti-Presenilin 1 Antibody (CAB19103)
- SKU:
- CAB19103
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Death
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Presenilin 1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB19103 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Presenilin 1 |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
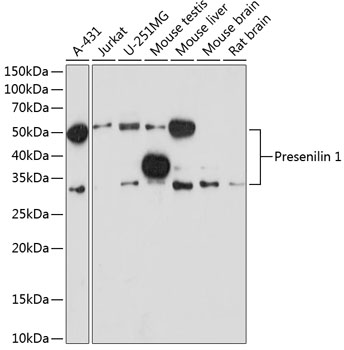
| Positive Samples: | A-431, Jurkat, U-251MG, Mouse testis, Mouse liver, Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Presenilin 1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 5663 |
| Uniprot: | P49768 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 28kDa |
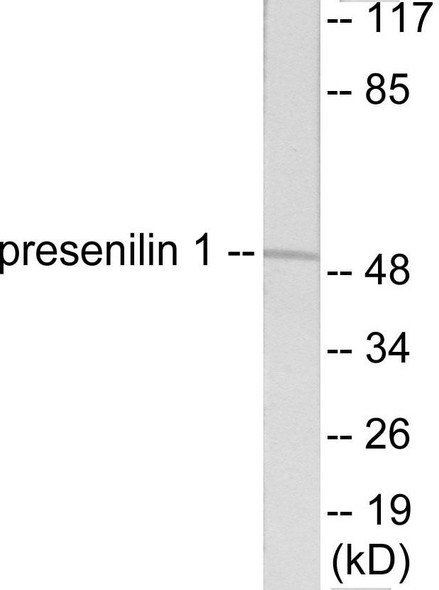
| Observed MW: | 30kDa/46kDa |
| Synonyms: | AD3, FAD, PS-1, PS1, S182, Presenilin 1, PSEN1 |
| Background: | Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients with an inherited form of the disease carry mutations in the presenilin proteins (PSEN1; PSEN2) or in the amyloid precursor protein (APP). These disease-linked mutations result in increased production of the longer form of amyloid-beta (main component of amyloid deposits found in AD brains). Presenilins are postulated to regulate APP processing through their effects on gamma-secretase, an enzyme that cleaves APP. Also, it is thought that the presenilins are involved in the cleavage of the Notch receptor, such that they either directly regulate gamma-secretase activity or themselves are protease enzymes. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene, the full-length nature of only some have been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PSEN1: probable catalytic subunit of the gamma-secretase complex, an endoprotease complex that catalyzes the intramembrane cleavage of integral membrane proteins such as Notch receptors and APP (beta-amyloid precursor protein). Requires the other members of the gamma-secretase complex to have a protease activity. May play a role in intracellular signaling and gene expression or in linking chromatin to the nuclear membrane. Regulates epithelial- cadherin function. Five alternative splice isoforms have been identified. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell surface; Protease; Mitochondrial; Membrane protein, integral; Membrane protein, multi-pass; EC 3.4.23.- Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 14q24.3 Cellular Component: Golgi apparatus; nuclear outer membrane; centrosome; cell surface; smooth endoplasmic reticulum; mitochondrion; lysosomal membrane; integral to plasma membrane; integral to membrane; lipid raft; ciliary rootlet; kinetochore; cell soma; membrane; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; mitochondrial inner membrane; apical plasma membrane; cytoplasmic vesicle; dendritic shaft; neuromuscular junction; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; nuclear membrane; rough endoplasmic reticulum; endoplasmic reticulum; cell cortex; Z disc; Golgi membrane; growth cone; axon Molecular Function:protein binding; cadherin binding; calcium channel activity; endopeptidase activity; beta-catenin binding; aspartic-type endopeptidase activity; PDZ domain binding Biological Process: positive regulation of catalytic activity; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; activation of MAPKK activity; positive regulation of apoptosis; beta-amyloid formation; regulation of synaptic plasticity; positive regulation of coagulation; Wnt receptor signaling pathway through beta-catenin; choline transport; T cell receptor signaling pathway; T cell activation during immune response; post-embryonic development; mitochondrial transport; extracellular matrix disassembly; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity; epithelial cell proliferation; cell-cell adhesion; negative regulation of axonogenesis; negative regulation of neuron apoptosis; embryonic limb morphogenesis; autophagic vacuole formation; somitogenesis; skin morphogenesis; regulation of phosphorylation; Notch receptor processing; negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity; neuron development; Cajal-Retzius cell differentiation; hemopoietic progenitor cell differentiation; response to oxidative stress; negative regulation of apoptosis; regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic; protein maturation; neuron migration; protein amino acid glycosylation; cell fate specification; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; protein transport; amyloid precursor protein catabolic process; beta-amyloid metabolic process; regulation of resting membrane potential; brain morphogenesis; heart looping; positive regulation of receptor recycling; dorsoventral neural tube patterning; blood vessel development; Notch signaling pathway; L-glutamate transport; thymus development; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis; memory; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor activity; smooth endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis; endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis; neuron apoptosis; cerebral cortex cell migration; skeletal morphogenesis; regulation of protein binding; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; protein processing; synaptic vesicle targeting; response to DNA damage stimulus Disease: Pick Disease Of Brain; Alzheimer Disease 3; Frontotemporal Dementia; Acne Inversa, Familial, 3; Cardiomyopathy, Dilated, 1u |
| NCBI Summary: | Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients with an inherited form of the disease carry mutations in the presenilin proteins (PSEN1; PSEN2) or in the amyloid precursor protein (APP). These disease-linked mutations result in increased production of the longer form of amyloid-beta (main component of amyloid deposits found in AD brains). Presenilins are postulated to regulate APP processing through their effects on gamma-secretase, an enzyme that cleaves APP. Also, it is thought that the presenilins are involved in the cleavage of the Notch receptor, such that they either directly regulate gamma-secretase activity or themselves are protease enzymes. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene, the full-length nature of only some have been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P49768 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1709856 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5663 |
| NCBI Accession: | P49768.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P49768,O95465, Q14762, Q15719, Q15720, Q96P33, Q9UIF0 B2R6D3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P49768 |
| Molecular Weight: | 48,997 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Presenilin-1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | presenilin 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PSEN1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AD3; FAD; PS1; PS-1; S182 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | presenilin-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Presenilin-1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Protein S182Cleaved into the following 3 chains:Presenilin-1 NTF subunit; Presenilin-1 CTF subunit; Presenilin-1 CTF12; PS1-CTF12 |
| Protein Family: | FHA domain-containing protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PSEN1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PSN1_HUMAN |