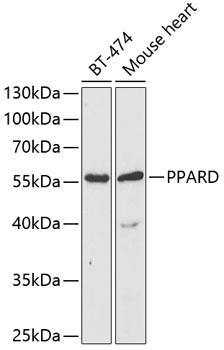
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) family. PPARs are nuclear hormone receptors that bind peroxisome proliferators and control the size and number of peroxisomes produced by cells. PPARs mediate a variety of biological processes, and may be involved in the development of several chronic diseases, including diabetes, obesity, atherosclerosis, and cancer. This protein is a potent inhibitor of ligand-induced transcription activity of PPAR alpha and PPAR gamma. It may function as an integrator of transcription repression and nuclear receptor signaling. The expression of this gene is found to be elevated in colorectal cancer cells. The elevated expression can be repressed by adenomatosis polyposis coli (APC), a tumor suppressor protein related to APC/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Knockout studies in mice suggested the role of this protein in myelination of the corpus callosum, lipid metabolism, and epidermal cell proliferation. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Ligand-activated transcription factor. Receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Has a preference for poly-unsaturated fatty acids, such as gamma-linoleic acid and eicosapentanoic acid. Once activated by a ligand, the receptor binds to promoter elements of target genes. Regulates the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Functions as transcription activator for the acyl-CoA oxidase gene. Decreases expression of NPC1L1 once activated by a ligand. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) family. PPARs are nuclear hormone receptors that bind peroxisome proliferators and control the size and number of peroxisomes produced by cells. PPARs mediate a variety of biological processes, and may be involved in the development of several chronic diseases, including diabetes, obesity, atherosclerosis, and cancer. This protein is a potent inhibitor of ligand-induced transcription activity of PPAR alpha and PPAR gamma. It may function as an integrator of transcription repression and nuclear receptor signaling. The expression of this gene is found to be elevated in colorectal cancer cells. The elevated expression can be repressed by adenomatosis polyposis coli (APC), a tumor suppressor protein related to APC/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Knockout studies in mice suggested the role of this protein in myelination of the corpus callosum, lipid metabolism, and epidermal cell proliferation. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | Q03181 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 417522 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5467 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q03181.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q03181,Q5D1P0, Q7Z5K0, Q9BUD4, A8K6J6, B4E3V3, B6ZGS1 B7Z3W1, E9PE18, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q03181 |
| Molecular Weight: | 38,855 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | peroxisome proliferator activated receptor delta |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PPARD |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FAAR; NUC1; NUCI; NR1C2; NUCII; PPARB |
| NCBI Protein Information: | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | NUCI; Nuclear hormone receptor 1; NUC1; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 2; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta; PPAR-beta |
| Protein Family: | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PPARD |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PPARD_HUMAN |