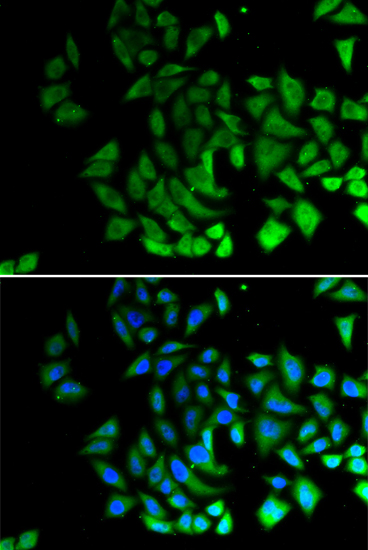
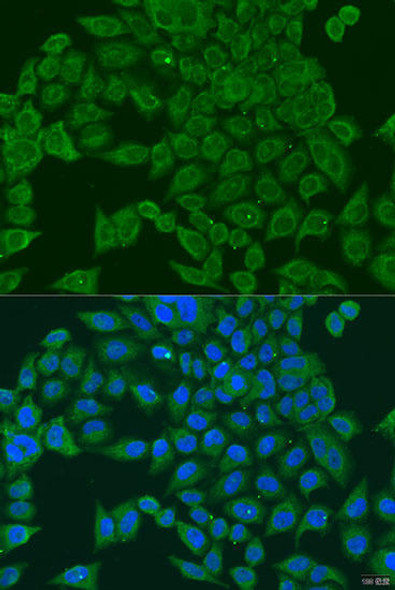
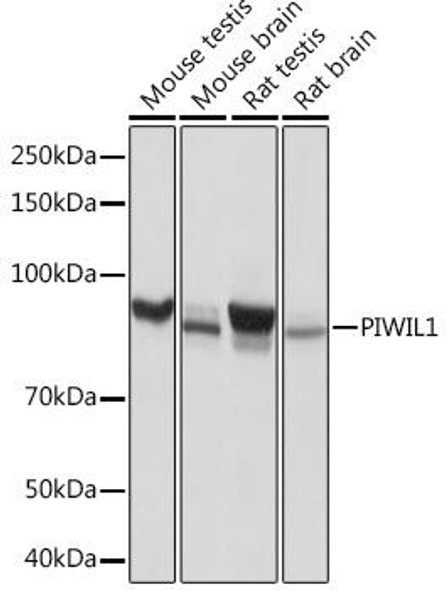
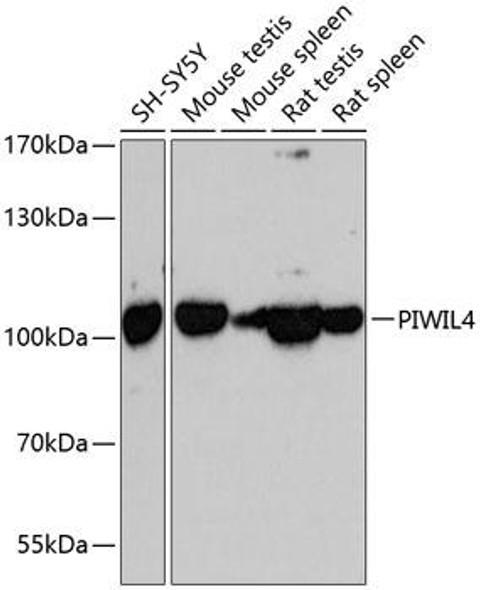
| UniProt Protein Function: | PIWIL1: Plays a central role during spermatogenesis by repressing transposable elements and prevent their mobilization, which is essential for the germline integrity. Acts via the piRNA metabolic process, which mediates the repression of transposable elements during meiosis by forming complexes composed of piRNAs and Piwi proteins and govern the methylation and subsequent repression of transposons. Directly binds methylated piRNAs, a class of 24 to 30 nucleotide RNAs that are generated by a Dicer- independent mechanism and are primarily derived from transposons and other repeated sequence elements. Besides their function in transposable elements repression, piRNAs are probably involved in other processes during meiosis such as translation regulation. Probable component of some RISC complex, which mediates RNA cleavage and translational silencing. Also plays a role in the formation of chromatoid bodies and is required for some miRNAs stability. Isoform 3 may be a negative developmental regulator. Interacts (via Piwi domain) with DICER1, suggesting that it forms ribonucleoprotein RISC complexes. This interaction is regulated by HSP90AB1 activity. Interacts with MAEL, KIF17, PABPC1, PRMT5 and WDR77. Interacts (when methylated on arginine residues) with TDRD1, TDRKH/TDRD2, RNF17/TDRD4, TDRD6, TDRD7 and TDRD9. Isoform 3 is down-regulated in CD34(+) hematopoietic cells during differentiation. Detected in most fetal and adult tissues. Expressed in testes, specifically in germline cells; detected in spermatocytes and spermatids during spermatogenesis. Increased expression in testicular tumors originating from embryonic germ cells with retention of germ cells phenotype. No expression in testicular tumors of somatic origin, such as Sertoli cell and Leydig cell tumors. Overexpressed in gastric cancer cells. Isoform 3 is ubiquitously expressed, and specifically in CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells but not in more differentiated cells. Belongs to the argonaute family. Piwi subfamily. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing.Protein type: Membrane protein, peripheralCellular Component: polysome; mRNA cap complex; cytoplasmMolecular Function: mRNA binding; protein binding; single-stranded RNA binding; nucleic acid binding; RNA binding; protein kinase bindingBiological Process: regulation of translation; meiotic cell cycle; multicellular organismal development; RNA-mediated gene silencing; spermatogenesis; cell differentiation; spermatid development |