Metabolism Antibodies 3
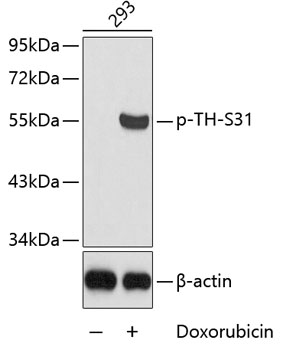
Anti-Phospho-TH-S31 Antibody (CABP0210)
- SKU:
- CABP0210
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-TH-S31 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0210 |
| Antibody Size: | 100 uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S31 of human TH |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | 293 |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S31 of human TH |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 7054 |
| Uniprot: | P07101 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 44kDa/45kDa/55kDa/56kDa/58kDa |
| Observed MW: | 55kDa |
| Synonyms: | DYT14, DYT5b, TYH, TH |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is involved in the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine. It is the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of catecholamines, hence plays a key role in the physiology of adrenergic neurons. Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal recessive Segawa syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | TH: an enzyme involved in the conversion of phenylalanine to dopamine. As the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of catecholamines, tyrosine hydroxylase has a key role in the physiology of adrenergic neurons. Four splice variant isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 1.14.16.2; Vesicle; Endoplasmic reticulum; Mitochondrial; Amino Acid Metabolism - tyrosine; Oxidoreductase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 11p15.5 Cellular Component: synaptic vesicle; internal side of plasma membrane; neuron projection; smooth endoplasmic reticulum; mitochondrion; dendrite; melanosome membrane; cytoplasm; terminal button; perikaryon; cytoplasmic vesicle; cytosol; nucleus Molecular Function:amino acid binding; protein domain specific binding; protein binding; enzyme binding; ferric iron binding; ferrous iron binding; dopamine binding; oxygen binding; tyrosine 3-monooxygenase activity Biological Process: heart morphogenesis; heart development; response to lipopolysaccharide; dopamine biosynthetic process; phytoalexin metabolic process; norepinephrine biosynthetic process; dopamine biosynthetic process from tyrosine; catecholamine biosynthetic process; response to electrical stimulus; epinephrine biosynthetic process; neurotransmitter biosynthetic process; response to pyrethroid; response to corticosterone stimulus; response to light stimulus; anatomical structure morphogenesis; phthalate metabolic process; mating behavior; social behavior; eye photoreceptor cell development; organ morphogenesis; circadian sleep/wake cycle; response to ethanol; response to zinc ion; cerebral cortex development; response to activity; response to water deprivation; synaptic transmission, dopaminergic; response to peptide hormone stimulus; locomotory behavior; fatty acid metabolic process; response to salt stress; regulation of heart contraction; response to estradiol stimulus; sensory perception of sound; visual perception; glycoside metabolic process; response to nutrient levels; terpene metabolic process; sphingolipid metabolic process; eating behavior; response to amphetamine; multicellular organismal aging; isoquinoline alkaloid metabolic process; response to herbicide; learning; response to ether; memory; synaptic vesicle amine transport; pigmentation; response to hypoxia; embryonic camera-type eye morphogenesis Disease: Segawa Syndrome, Autosomal Recessive |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is involved in the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine. It is the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of catecholamines, hence plays a key role in the physiology of adrenergic neurons. Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal recessive Segawa syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P07101 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 239938945 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7054 |
| NCBI Accession: | P07101.5 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P07101,Q0PWM2, Q0PWM3, Q15585, Q15588, Q15589, Q2M3B4 B7ZL70, B7ZL73, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P07101 |
| Molecular Weight: | 528 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | tyrosine hydroxylase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TH |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | TYH; DYT14; DYT5b |
| NCBI Protein Information: | tyrosine 3-monooxygenase; dystonia 14; tyrosine 3-hydroxylase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Tyrosine 3-hydroxylase; TH |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TH |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TY3H_HUMAN |