Signal Transduction Antibodies 3
Anti-Phospho-TBC1D4-T642 pAb Antibody (CABP0791)
- SKU:
- CABP0791
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-TBC1D4-T642 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0791 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
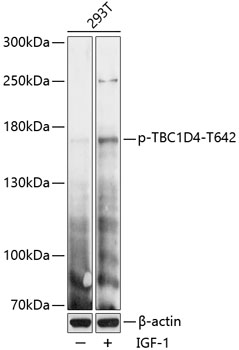
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around T642 of human TBC1D4 (NP_055647.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | 293T |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around T642 of human TBC1D4 (NP_055647.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | AHTF S |
| Gene ID: | 9882 |
| Uniprot: | O60343 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm |
| Calculated MW: | 53kDa/60kDa/139kDa/145kDa/146kDa |
| Observed MW: | 160kDa |
| Synonyms: | AS160, NIDDM5, TBC1D4 |
| Background: | This gene is a member of the Tre-2/BUB2/CDC16 domain family. The protein encoded by this gene is a Rab-GTPase-activating protein, and contains two phopshotyrosine-binding domains (PTB1 and PTB2), a calmodulin-binding domain (CBD), a Rab-GTPase domain, and multiple AKT phosphomotifs. This protein is thought to play an important role in glucose homeostasis by regulating the insulin-dependent trafficking of the glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4), important for removing glucose from the bloodstream into skeletal muscle and fat tissues. Reduced expression of this gene results in an increase in GLUT4 levels at the plasma membrane, suggesting that this protein is important in intracellular retention of GLUT4 under basal conditions. When exposed to insulin, this protein is phosphorylated, dissociates from GLUT4 vesicles, resulting in increased GLUT4 at the cell surface, and enhanced glucose transport. Phosphorylation of this protein by AKT is required for proper translocation of GLUT4 to the cell surface. Individuals homozygous for a mutation in this gene are at higher risk for type 2 diabetes and have higher levels of circulating glucose and insulin levels after glucose ingestion. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | AS160: a widely-expressed Rab GTPase-activating protein which apparently plays a role in mediating insulin action. Phosphorylated by the Ser/Thr protein kinase Akt in response to insulin. Is redistributed from low-density microsomes to the cytosol upon insulin treatment. Insulin stimulation of GLUT4 exocytosis is dependent on AS160. The translocation of GLUT4 from intracellular storage sites to the cell surface functions to stimulate insulin uptake by adipose and muscle tissue. Its expression is decreased by twofold in pancreatic islets in type 2 diabetes patients compared to control subjects; its phosphorylation is impaired in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetics. The protein is expressed in pancreatic Langerhans islets, including beta cells. Up-regulated in T cells from patients with atopic dermatitis. Two alternatively spliced isoforms have been described. Isoform 2, which promotes GLUT4 translocation at the plasma membrane, is the highest overexpressed in most tissues. Isoform 2 shows a cytoplasmic perinuclear localization in a myoblastic cell line in resting and insulin-stimulated cells Isoform 2 is strongly expressed in adrenal and thyroid gland, and also in lung, kidney, colon, brain and adipose tissue. Isoform 2 is moderately expressed in skeletal muscle. Isoform 1 is highly expressed in skeletal muscle and heart, but was not detectable in the liver or adipose tissue. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:GAPs; GAPs, Rab Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 13q22.2 Cellular Component: cytoplasmic vesicle membrane; cytoplasm Biological Process: vesicle-mediated transport; negative regulation of vesicle fusion; cellular response to insulin stimulus Disease: Diabetes Mellitus, Noninsulin-dependent, 5 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a member of the Tre-2/BUB2/CDC16 domain family. The protein encoded by this gene is a Rab-GTPase-activating protein, and contains two phopshotyrosine-binding domains (PTB1 and PTB2), a calmodulin-binding domain (CBD), a Rab-GTPase domain, and multiple AKT phosphomotifs. This protein is thought to play an important role in glucose homeostasis by regulating the insulin-dependent trafficking of the glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4), important for removing glucose from the bloodstream into skeletal muscle and fat tissues. Reduced expression of this gene results in an increase in GLUT4 levels at the plasma membrane, suggesting that this protein is important in intracellular retention of GLUT4 under basal conditions. When exposed to insulin, this protein is phosphorylated, dissociates from GLUT4 vesicles, resulting in increased GLUT4 at the cell surface, and enhanced glucose transport. Phosphorylation of this protein by AKT is required for proper translocation of GLUT4 to the cell surface. Individuals homozygous for a mutation in this gene are at higher risk for type 2 diabetes and have higher levels of circulating glucose and insulin levels after glucose ingestion. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | O60343 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 67473227 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 9882 |
| NCBI Accession: | O60343.2 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O60343 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | TBC1 domain family member 4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | TBC1 domain family member 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TBC1D4 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AS160; NIDDM5 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | TBC1 domain family member 4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | TBC1 domain family member 4 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Akt substrate of 160 kDa |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TBC1D4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TBCD4_HUMAN |