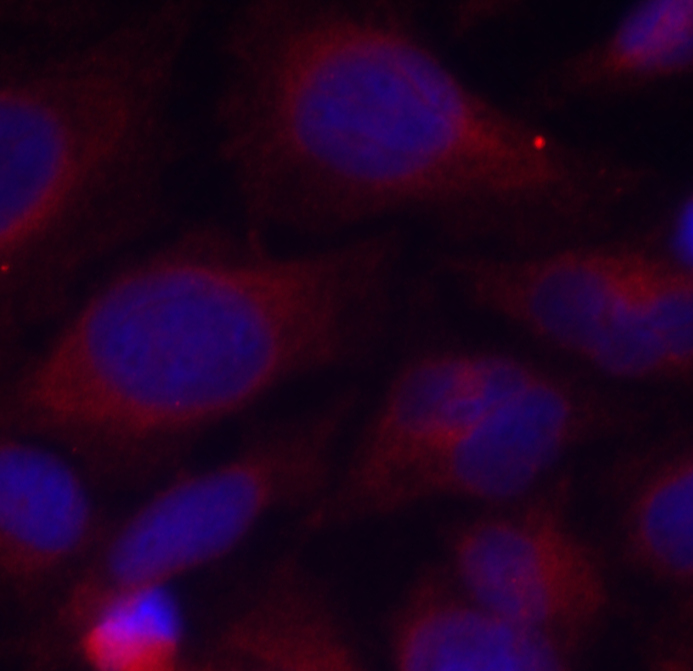
Cell Death Antibodies 2
Anti-Phospho-NFKB1-S893 Antibody (CABP0415)
- SKU:
- CABP0415
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- IHC
- Applications:
- IF
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Death
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-NFKB1-S893 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0415 |
| Antibody Size: | 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S893 of human NFKB1 |
| Application: | IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:100 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S893 of human NFKB1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 4790 |
| Uniprot: | P19838 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 85kDa/105kDa |
| Observed MW: |
| Synonyms: | NFKB1, CVID12, EBP-1, KBF1, NF-kB1, NF-kappa-B, NF-kappaB, NFKB-p105, NFKB-p50, NFkappaB, p105, p50 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a 105 kD protein which can undergo cotranslational processing by the 26S proteasome to produce a 50 kD protein. The 105 kD protein is a Rel protein-specific transcription inhibitor and the 50 kD protein is a DNA binding subunit of the NF-kappa-B (NFKB) protein complex. NFKB is a transcription regulator that is activated by various intra- and extra-cellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant-free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. Activated NFKB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions. Inappropriate activation of NFKB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NFKB leads to inappropriate immune cell development or delayed cell growth. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms, at least one of which is proteolytically processed. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NFkB-p105: a transcription factor of the nuclear factor-kappaB ( NFkB) group. Undergoes cotranslational processing by the 26S proteasome to produce a 50 kD protein. The 105 kD protein is a Rel protein-specific transcription inhibitor and the 50 kD protein is a DNA binding subunit of NFkB. NFkB is a transcription regulator that is activated by various intra- and extra-cellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant-free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. Activated NFkB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions. Inappropriate activation of NFkB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NFkB leads to inappropriate immune cell development or delayed cell growth. There are five NFkB proteins in mammals (RelA/NFkB-p65, RelB, c-Rel, NF-_B1/NFkB-p105, and NF-_B2/NFkB-p100). They form a variety of homodimers and heterodimers, each of which activates its own characteristic set of genes. Two alternatively spliced isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 4q24 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; cytosol; mitochondrion; neuron projection; nucleoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:actinin binding; chromatin binding; heat shock protein binding; identical protein binding; protein binding; protein heterodimerization activity; protein homodimerization activity; transcription factor activity; transcription factor binding Biological Process: activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; apoptosis; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; inflammatory response; innate immune response; membrane protein intracellular domain proteolysis; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of cellular protein metabolic process; negative regulation of cholesterol transport; negative regulation of inflammatory response; negative regulation of interleukin-12 biosynthetic process; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of interferon type I production; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; response to copper ion; response to oxidative stress; stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway; stress-activated MAPK cascade; T cell receptor signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 10 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 5 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor signaling pathway; transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter Disease: Immunodeficiency, Common Variable, 12 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a 105 kD protein which can undergo cotranslational processing by the 26S proteasome to produce a 50 kD protein. The 105 kD protein is a Rel protein-specific transcription inhibitor and the 50 kD protein is a DNA binding subunit of the NF-kappa-B (NFKB) protein complex. NFKB is a transcription regulator that is activated by various intra- and extra-cellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant-free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. Activated NFKB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions. Inappropriate activation of NFKB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NFKB leads to inappropriate immune cell development or delayed cell growth. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms, at least one of which is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016] |
| UniProt Code: | P19838 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 21542418 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4790 |
| NCBI Accession: | P19838.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P19838,Q68D84, Q86V43, Q8N4X7, Q9NZC0, A8K5Y5, B3KVE8 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P19838 |
| Molecular Weight: | 85,520 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | NFKB1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | p50; KBF1; p105; EBP-1; CVID12; NF-kB1; NFKB-p50; NFkappaB; NF-kappaB; NFKB-p105; NF-kappa-B |
| NCBI Protein Information: | nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | DNA-binding factor KBF1; EBP-1; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | NFKB1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NFKB1_HUMAN |