Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 4
Anti-Phospho-MYC-T358 Antibody (CABP0411)
- SKU:
- CABP0411
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-MYC-T358 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0411 |
| Antibody Size: | 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding T358 of human c-Myc |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
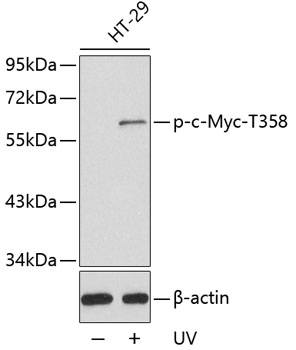
| Positive Samples: | HT-29 |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding T358 of human c-Myc |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 4609 |
| Uniprot: | P01106 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus, nucleolus, nucleoplasm |
| Calculated MW: | 48kDa/50kDa |
| Observed MW: | 65kDa |
| Synonyms: | MRTL, MYCC, bHLHe39, c-Myc, MYC |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a multifunctional, nuclear phosphoprotein that plays a role in cell cycle progression, apoptosis and cellular transformation. It functions as a transcription factor that regulates transcription of specific target genes. Mutations, overexpression, rearrangement and translocation of this gene have been associated with a variety of hematopoietic tumors, leukemias and lymphomas, including Burkitt lymphoma. There is evidence to show that alternative translation initiations from an upstream, in-frame non-AUG (CUG) and a downstream AUG start site result in the production of two isoforms with distinct N-termini. The synthesis of non-AUG initiated protein is suppressed in Burkitt's lymphomas, suggesting its importance in the normal function of this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Myc: a proto-oncogenic transcription factor that plays a role in cell proliferation, apoptosis and in the development of human tumors. Seems to activate the transcription of growth-related genes. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Nucleolus; Oncoprotein; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8q24.21 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; protein complex; nucleolus; nucleus; cytosol Molecular Function:protein dimerization activity; protein binding; DNA binding; protein complex binding; transcription factor binding; transcription factor activity Biological Process: oxygen transport; cellular iron ion homeostasis; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of caspase activity; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; Wnt receptor signaling pathway through beta-catenin; chromosome organization and biogenesis; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation; response to gamma radiation; cell cycle arrest; response to drug; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; Notch signaling pathway; regulation of telomere maintenance; transcription, DNA-dependent; MAPKKK cascade; negative regulation of cell division; negative regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade; negative regulation of monocyte differentiation; chromatin remodeling; ureteric bud branching; regulation of gene expression; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation; energy reserve metabolic process; gene expression; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; response to DNA damage stimulus; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; negative regulation of apoptosis Disease: Burkitt Lymphoma |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a multifunctional, nuclear phosphoprotein that plays a role in cell cycle progression, apoptosis and cellular transformation. It functions as a transcription factor that regulates transcription of specific target genes. Mutations, overexpression, rearrangement and translocation of this gene have been associated with a variety of hematopoietic tumors, leukemias and lymphomas, including Burkitt lymphoma. There is evidence to show that alternative translation initiations from an upstream, in-frame non-AUG (CUG) and a downstream AUG start site result in the production of two isoforms with distinct N-termini. The synthesis of non-AUG initiated protein is suppressed in Burkitt's lymphomas, suggesting its importance in the normal function of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P01106 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 127619 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4609 |
| NCBI Accession: | P01106.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P01106,P01107, Q14026, A8WFE7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P01106 |
| Molecular Weight: | 439 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Myc proto-oncogene protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | v-myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MYC |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | MRTL; MYCC; c-Myc; bHLHe39 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | myc proto-oncogene protein; proto-oncogene c-Myc; transcription factor p64; class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 39; avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog; v-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog; myc-related translation/localization regulatory factor |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Myc proto-oncogene protein |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 39; bHLHe39; Proto-oncogene c-Myc; Transcription factor p64 |
| Protein Family: | Myc protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MYC |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MYC_HUMAN |