Cell Biology Antibodies 17
Anti-Phospho-mTOR-S2481 Antibody (CABP0490)
- SKU:
- CABP0490
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-mTOR-S2481 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0490 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
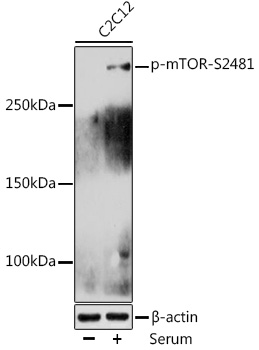
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S2481 of human mTOR (NP_004949.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, |
| Positive Samples: | C2C12 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S2481 of human mTOR (NP_004949.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | IHSF I |
| Gene ID: | 2475 |
| Uniprot: | P42345 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Cytoplasmic side, Endoplasmic reticulum membrane, Golgi apparatus membrane, Lysosome, Mitochondrion outer membrane, Nucleus, PML body, Peripheral membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 288kDa |
| Observed MW: | 289kDa |
| Synonyms: | FRAP, FRAP1, FRAP2, RAFT1, RAPT1, SKS, mTOR, MTOR |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of phosphatidylinositol kinase-related kinases. These kinases mediate cellular responses to stresses such as DNA damage and nutrient deprivation. This protein acts as the target for the cell-cycle arrest and immunosuppressive effects of the FKBP12-rapamycin complex. The ANGPTL7 gene is located in an intron of this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | mTOR: an atypical kinase belonging to the PIKK family of kinases. Is the catalytic subunit of two protein complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2. mTORC1 activates S6K and inactivates 4E-BP1, up-regulating protein synthesis. mTORC1 contains Raptor, a positive regulatory subunit and scaffold for recruiting substrates, two negative regulators, PRAS40 and DEPTOR, and mLST8; it is a target for the cell-cycle arrest and immunosuppressive effects of the FKBP12-rapamycin complex. mTORC2, a downstream effector of PI3K, is insensitive to rapamycin and activates Akt by phosphorylating a key activation site. mTORC2 contains regulatory subunits Rictor and mSIN1, PROTOR, mLST8, and the negative regulator DEPTOR. mTORC1 suppresses PI3K activity via a strong negative feedback loop that involves S6K1. Inhibiting mTORC1 ablates this negative feedback loop and potentiates PI3K signaling. Known inhibitors of mTOR include rapamycin, temsirolimus (CCI-779). |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, atypical; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); Autophagy; EC 2.7.11.1; Kinase, protein; ATYPICAL group; PIKK family; FRAP subfamily Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p36.2 Cellular Component: cell soma; cytoplasm; cytosol; dendrite; endomembrane system; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Golgi membrane; lysosomal membrane; lysosome; membrane; mitochondrial outer membrane; nucleoplasm; phosphoinositide 3-kinase complex; PML body; TORC2 complex Molecular Function:ATP binding; drug binding; kinase activity; phosphoprotein binding; protein binding; protein domain specific binding; protein kinase binding; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; ribosome binding Biological Process: 'de novo' pyrimidine base biosynthetic process; brain development; cardiac muscle cell development; cardiac muscle contraction; cell aging; cell cycle arrest; cell growth; cellular response to nutrient levels; DNA repair; energy reserve metabolic process; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; gene expression; germ cell development; growth; heart morphogenesis; innate immune response; insulin receptor signaling pathway; long-term memory; macroautophagy; maternal process involved in pregnancy; mRNA stabilization; multicellular organism growth; negative regulation of autophagy; negative regulation of cell size; negative regulation of muscle atrophy; negative regulation of NFAT protein import into nucleus; negative regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; phosphorylation; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process; positive regulation of neuron maturation; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation; positive regulation of stress fiber formation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase III promoter; positive regulation of translation; post-embryonic development; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; protein amino acid phosphorylation; protein catabolic process; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; regulation of carbohydrate utilization; regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation; regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process; regulation of GTPase activity; regulation of myelination; regulation of osteoclast differentiation; regulation of protein kinase activity; regulation of response to food; response to amino acid stimulus; response to cocaine; response to morphine; response to nutrient; response to stress; ruffle organization and biogenesis; signal transduction; social behavior; spinal cord development; T cell costimulation; TOR signaling pathway; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; visual learning; voluntary musculoskeletal movement; wound healing |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of phosphatidylinositol kinase-related kinases. These kinases mediate cellular responses to stresses such as DNA damage and nutrient deprivation. This protein acts as the target for the cell-cycle arrest and immunosuppressive effects of the FKBP12-rapamycin complex. The ANGPTL7 gene is located in an intron of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P42345 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1169735 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2475 |
| NCBI Accession: | P42345.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P42345,Q4LE76, Q5TER1, Q6LE87, Q96QG3, Q9Y4I3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P42345 |
| Molecular Weight: | 288,892 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MTOR |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SKS; FRAP; FRAP1; FRAP2; RAFT1; RAPT1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin complex-associated protein 1; FKBP12-rapamycin complex-associated protein; Mammalian target of rapamycin; mTOR; Mechanistic target of rapamycin; Rapamycin and FKBP12 target 1; Rapamycin target protein 1 |
| Protein Family: | Serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MTOR |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MTOR_HUMAN |