Signal Transduction Antibodies 3
Anti-Phospho-GRIN2B-Y1474 Antibody (CABP0357)
- SKU:
- CABP0357
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Applications:
- IF
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-GRIN2B-Y1474 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0357 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
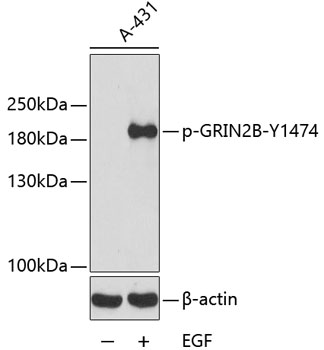
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Y1474 of human GRIN2B |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | A-431 |
| Immunogen: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Y1474 of human GRIN2B |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 2904 |
| Uniprot: | Q13224 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell junction, Cell membrane, Multi-pass membrane protein, postsynaptic cell membrane, synapse |
| Calculated MW: | 166kDa |
| Observed MW: | 200kDa |
| Synonyms: | GRIN2B, EIEE27, GluN2B, MRD6, NMDAR2B, NR2B, hNR3 |
| Background: | N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are a class of ionotropic glutamate receptors. NMDA receptor channel has been shown to be involved in long-term potentiation, an activity-dependent increase in the efficiency of synaptic transmission thought to underlie certain kinds of memory and learning. NMDA receptor channels are heteromers composed of three different subunits: NR1 (GRIN1), NR2 (GRIN2A, GRIN2B, GRIN2C, or GRIN2D) and NR3 (GRIN3A or GRIN3B). The NR2 subunit acts as the agonist binding site for glutamate. This receptor is the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter receptor in the mammalian brain. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NMDAR2B: an NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. Plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. Mediates neuronal functions in glutamate neurotransmission. In concert with DAPK1 at extrasynaptic sites, acts as a central mediator for stroke damage. Its phosphorylation at Ser-1303 by DAPK1 enhances synaptic NMDA receptor channel activity inducing injurious Ca2+ influx through them, resulting in an irreversible neuronal death. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Channel, ligand-gated; Channel, calcium; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12p12 Cellular Component: postsynaptic membrane; synaptic vesicle; neuron projection; cell surface; integral to plasma membrane; dendrite; plasma membrane; cell junction; N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor complex Molecular Function:protein binding; extracellular-glutamate-gated ion channel activity; zinc ion binding; glycine binding; N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor activity; calcium channel activity Biological Process: synaptic transmission, glutamatergic; axon guidance; startle response; behavioral fear response; in utero embryonic development; glutamate signaling pathway; regulation of synaptic plasticity; learning; memory; synaptic transmission; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain; behavioral response to pain; sensory organ development; learning and/or memory; response to ethanol; suckling behavior; transport; ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway; ephrin receptor signaling pathway; regulation of excitatory postsynaptic membrane potential Disease: Mental Retardation, Autosomal Dominant 6; Epileptic Encephalopathy, Early Infantile, 27 |
| NCBI Summary: | N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are a class of ionotropic glutamate receptors. NMDA receptor channel has been shown to be involved in long-term potentiation, an activity-dependent increase in the efficiency of synaptic transmission thought to underlie certain kinds of memory and learning. NMDA receptor channels are heteromers composed of three different subunits: NR1 (GRIN1), NR2 (GRIN2A, GRIN2B, GRIN2C, or GRIN2D) and NR3 (GRIN3A or GRIN3B). The NR2 subunit acts as the agonist binding site for glutamate. This receptor is the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter receptor in the mammalian brain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q13224 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 14548162 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2904 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q13224.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q13224,Q12919, Q13220, Q13225, Q14CU4, Q9UM56, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q13224 |
| Molecular Weight: | 1484 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2B |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GRIN2B |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | MRD6; NR2B; hNR3; EIEE27; GluN2B; NMDAR2B |
| NCBI Protein Information: | glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B; NR3; glutamate receptor subunit epsilon-2; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 3; N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-2; N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; NMDAR2B; NR2B; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 3; NR3; hNR3 |
| Protein Family: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GRIN2B |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NMDE2_HUMAN |