Cell Biology Antibodies 14
Anti-Phospho-AKT1-S473+AKT2-S474+AKT3-S472 Antibody (CABP1068)
- SKU:
- CABP1068
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-AKT1-S473+AKT2-S474+AKT3-S472 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP1068 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A phospho synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S473/S474/S472 of human AKT1/AKT2/AKT3. |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
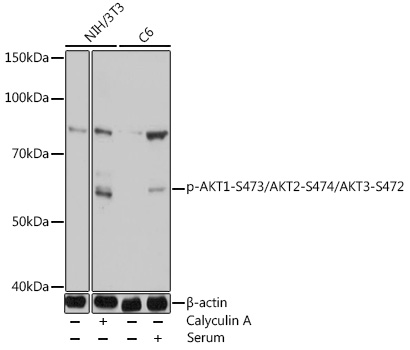
| Positive Samples: | NIH/3T3, C6 |
| Immunogen: | A phospho synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S473/S474/S472 of human AKT1/AKT2/AKT3. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 207/208/10000 |
| Uniprot: | P31749/P31751/Q9Y243 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 48kDa/55kDa/51kDa/54kDa |
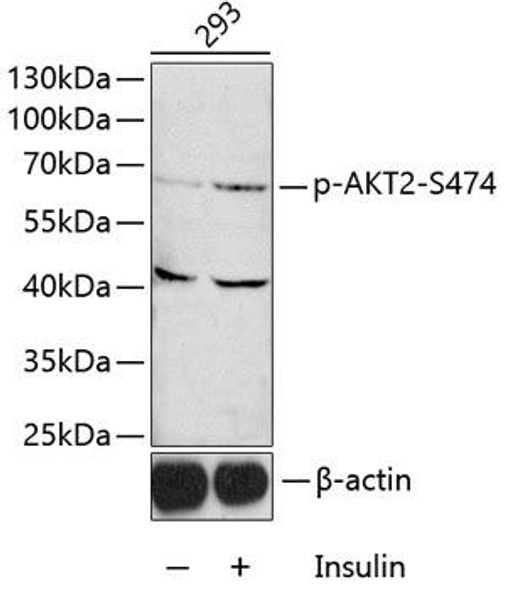
| Observed MW: | 60kDa |
| Synonyms: | AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 |
| Background: | The serine-threonine protein kinase encoded by the AKT1 gene is catalytically inactive in serum-starved primary and immortalized fibroblasts. AKT1 and the related AKT2 are activated by platelet-derived growth factor. The activation is rapid and specific, and it is abrogated by mutations in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1. It was shown that the activation occurs through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. In the developing nervous system AKT is a critical mediator of growth factor-induced neuronal survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating the serine/threonine kinase AKT1, which then phosphorylates and inactivates components of the apoptotic machinery. Mutations in this gene have been associated with the Proteus syndrome. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011] |