Developmental Biology
Anti-PAX4 Antibody (CAB5414)
- SKU:
- CAB5414
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Developmental Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-PAX4 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB5414 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
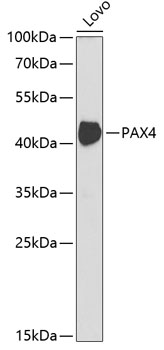
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 50-200 of human PAX4 (NP_006184.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | Lovo |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 50-200 of human PAX4 (NP_006184.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | LGRY YRTG VLEP KGIG GSKP RLAT PPVV ARIA QLKG ECPA LFAW EIQR QLCA EGLC TQDK TPSV SSIN RVLR ALQE DQGL PCTR LRSP AVLA PAVL TPHS GSET PRGT HPGT GHRN RTIF SPSQ AEAL EKEF QRGQ YPDS VARG KLAT ATS |
| Gene ID: | 5078 |
| Uniprot: | O43316 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 29kDa/37kDa |
| Observed MW: | 43kDa |
| Synonyms: | PAX4, KPD, MODY9 |
| Background: | This gene is a member of the paired box (PAX) family of transcription factors. Members of this gene family typically contain a paired box domain, an octapeptide, and a paired-type homeodomain. These genes play critical roles during fetal development and cancer growth. The paired box 4 gene is involved in pancreatic islet development and mouse studies have demonstrated a role for this gene in differentiation of insulin-producing beta cells. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PAX4: Plays an important role in the differentiation and development of pancreatic islet beta cells. Transcriptional repressor that binds to a common element in the glucagon, insulin and somatostatin promoters. Competes with PAX6 for this same promoter binding site. Isoform 2 appears to be a dominant negative form antagonizing PAX4 transcriptional activity. Defects in PAX4 are a cause of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM); also known as diabetes mellitus type 2 or maturity-onset diabetes. NIDDM is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset during adulthood and insulin resistance. Genetic variations in PAX4 are associated with susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). IDDM normally starts in childhood or adolescence and is caused by the body's own immune system which destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Classical features are polydipsia, polyphagia and polyuria, due to hyperglycemia- induced osmotic diuresis. Defects in PAX4 are a cause of susceptibility to diabetes mellitus ketosis-prone (KPD). KPD is an atypical form of diabetes mellitus characterized by an acute initial presentation with severe hyperglycemia and ketosis, as seen in classic type 1 diabetes, but after initiation of insulin therapy, prolonged remission is often possible with cessation of insulin therapy and maintenance of appropriate metabolic control. Metabolic studies show a markedly blunted insulin secretory response to glucose, partially reversible with the improvement of blood glucose control. Variable levels of insulin resistance are observed, especially in obese patients. Pancreatic beta-cell autoimmunity is a rare finding. Defects in PAX4 are the cause of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 9 (MODY9). MODY is a form of diabetes that is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset in childhood or early adulthood (usually before 25 years of age), a primary defect in insulin secretion and frequent insulin-independence at the beginning of the disease. Belongs to the paired homeobox family. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 7q32 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm Molecular Function:DNA binding Biological Process: endocrine pancreas development; organ morphogenesis Disease: Diabetes Mellitus, Ketosis-prone; Diabetes Mellitus, Noninsulin-dependent; Maturity-onset Diabetes Of The Young, Type 9 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a member of the paired box (PAX) family of transcription factors. Members of this gene family typically contain a paired box domain, an octapeptide, and a paired-type homeodomain. These genes play critical roles during fetal development and cancer growth. The paired box 4 gene is involved in pancreatic islet development and mouse studies have demonstrated a role for this gene in differentiation of insulin-producing beta cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O43316 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 3914276 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5078 |
| NCBI Accession: | O43316.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O43316,O95161, Q6B0H0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O43316 |
| Molecular Weight: | 37,061 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Paired box protein Pax-4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | paired box 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PAX4 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | KPD; MODY9 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | paired box protein Pax-4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Paired box protein Pax-4 |
| Protein Family: | Paired box protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PAX4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PAX4_HUMAN |
View AllClose