Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 3
Anti-OGG1 Antibody (CAB2268)
- SKU:
- CAB2268
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-OGG1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB2268 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human OGG1 |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:200 - 1:1000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
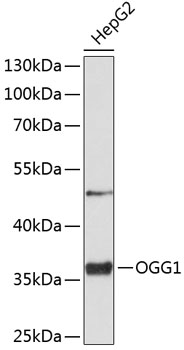
| Positive Samples: | HepG2 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human OGG1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 4968 |
| Uniprot: | O15527 |
| Cellular Location: | Mitochondrion, Nucleus, Nucleus matrix, Nucleus speckle, nucleoplasm |
| Calculated MW: | 22kDa/36kDa/38kDa/39kDa/40kDa/45kDa/47kDa |
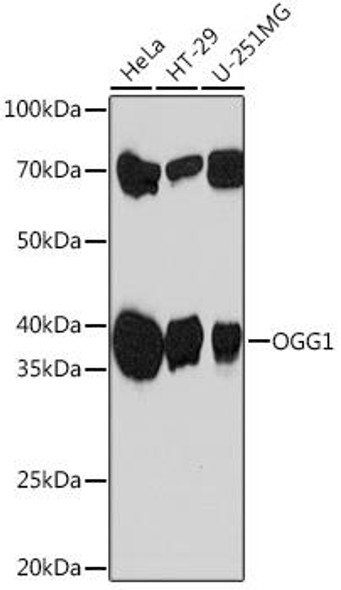
| Observed MW: | 36kDa |
| Synonyms: | OGG1, HMMH, HOGG1, MUTM, OGH1 |
| Background: | This gene encodes the enzyme responsible for the excision of 8-oxoguanine, a mutagenic base byproduct which occurs as a result of exposure to reactive oxygen. The action of this enzyme includes lyase activity for chain cleavage. Alternative splicing of the C-terminal region of this gene classifies splice variants into two major groups, type 1 and type 2, depending on the last exon of the sequence. Type 1 alternative splice variants end with exon 7 and type 2 end with exon 8. All variants share the N-terminal region in common, which contains a mitochondrial targeting signal that is essential for mitochondrial localization. Many alternative splice variants for this gene have been described, but the full-length nature for every variant has not been determined. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | OGG1: DNA repair enzyme that incises DNA at 8-oxoG residues. Excises 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine and 2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5-N- methylformamidopyrimidine (FAPY) from damaged DNA. Has a beta- lyase activity that nicks DNA 3' to the lesion. Defects in OGG1 may be a cause of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). It is a heterogeneous group of sporadic or hereditary carcinoma derived from cells of the proximal renal tubular epithelium. It is subclassified into clear cell renal carcinoma (non-papillary carcinoma), papillary renal cell carcinoma, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, collecting duct carcinoma with medullary carcinoma of the kidney, and unclassified renal cell carcinoma. Belongs to the type-1 OGG1 family. 8 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 4.2.99.18; Lyase; DNA repair, damage; Deoxyribonuclease Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 3p26.2 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; nuclear matrix; mitochondrion; nuclear speck Molecular Function:protein binding; microtubule binding; endonuclease activity; DNA N-glycosylase activity; oxidized purine base lesion DNA N-glycosylase activity; damaged DNA binding; 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine DNA N-glycosylase activity Biological Process: response to drug; depurination; DNA repair; DNA catabolic process, endonucleolytic; response to estradiol stimulus; response to radiation; response to ethanol; base-excision repair, AP site formation; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; nucleotide-excision repair; base-excision repair; response to folic acid; regulation of protein import into nucleus, translocation; response to oxidative stress; acute inflammatory response; negative regulation of apoptosis; aging Disease: Renal Cell Carcinoma, Nonpapillary |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes the enzyme responsible for the excision of 8-oxoguanine, a mutagenic base byproduct which occurs as a result of exposure to reactive oxygen. The action of this enzyme includes lyase activity for chain cleavage. Alternative splicing of the C-terminal region of this gene classifies splice variants into two major groups, type 1 and type 2, depending on the last exon of the sequence. Type 1 alternative splice variants end with exon 7 and type 2 end with exon 8. All variants share the N-terminal region in common, which contains a mitochondrial targeting signal that is essential for mitochondrial localization. Many alternative splice variants for this gene have been described, but the full-length nature for every variant has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O15527 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 12643548 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4968 |
| NCBI Accession: | O15527.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O15527,O00390, O00670, O00705, O14876, O95488, P78554 Q9BW42, Q9UIK0, Q9UIK1, Q9UIK2, A8K1E3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O15527 |
| Molecular Weight: | 345 |
| NCBI Full Name: | N-glycosylase/DNA lyase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | OGG1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HMMH; MUTM; OGH1; HOGG1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | N-glycosylase/DNA lyase; AP lyase; OGG1 type 1f; 8-hydroxyguanine DNA glycosylase; DNA-apurinic or apyrimidinic site lyase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | N-glycosylase/DNA lyase |
| Protein Family: | N-glycosylase/DNA lyase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | OGG1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | OGG1_HUMAN |