Description
| Product Name: | NUP62 Rabbit mAb |
| Product Code: | CAB19271 |
| Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Synonyms: | NUP62, IBSN, SNDI, p62, nucleoporin 62 |
| Applications: | WB, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human NUP62. |
| Applications: | WB, IP |
| Recommended Dilutions: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IP 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
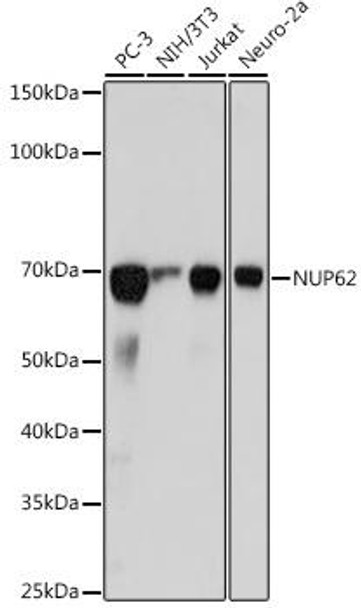
| Positive Samples: | PC-3, NIH/3T3, Jurkat, Neuro-2a, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human NUP62. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 23636 |
| Uniprot: | P37198 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus, cytoskeleton, nuclear pore complex, spindle pole |
| Calculated MW: | 70kDa |
| Observed MW: | 70KDa |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NUP62: Essential component of the nuclear pore complex. The N- terminal is probably involved in nucleocytoplasmic transport. The C-terminal is probably involved in protein-protein interaction via coiled-coil formation and may function in anchorage of p62 to the pore complex. Defects in NUP62 are the cause of infantile striatonigral degeneration (SNDI); also known as infantile bilateral striatal necrosis (IBSN) or familial striatal degeneration. SNDI is a neurological disorder characterized by symmetrical degeneration of the caudate nucleus, putamen and occasionally the globus pallidus, with little involvement of the rest of the brain. The clinical features include developmental regression, choreoathetosis, dystonia, spasticity, dysphagia, failure to thrive, nystagmus, optic atrophy and mental retardation. Belongs to the nucleoporin NSP1/NUP62 family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Nucleoporin; Adaptor/scaffold Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 19q13.33 Cellular Component: pore complex; spindle pole; nucleocytoplasmic shuttling complex; nuclear membrane; intracellular membrane-bound organelle; cytoplasm; nuclear envelope; nuclear pore; ribonucleoprotein complex Molecular Function:ubiquitin binding; protein binding; receptor signaling complex scaffold activity; structural constituent of nuclear pore; PTB domain binding; chromatin binding; SH2 domain binding; thyroid hormone receptor binding; nucleocytoplasmic transporter activity Biological Process: cell death; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity; mRNA transport; viral reproduction; hormone-mediated signaling; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; mitotic nuclear envelope disassembly; regulation of signal transduction; nucleocytoplasmic transport; pathogenesis; viral infectious cycle; glucose transport; negative regulation of cell proliferation; protein transport; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of programmed cell death; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction; viral transcription; transmembrane transport; regulation of Ras protein signal transduction; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; transcription, DNA-dependent; cytokine and chemokine mediated signaling pathway; cell aging; hexose transport; carbohydrate metabolic process; gene expression; mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of apoptosis Disease: Striatonigral Degeneration, Infantile |
| NCBI Summary: | The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure that extends across the nuclear envelope, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nucleoporins are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the FG-repeat containing nucleoporins and is localized to the nuclear pore central plug. This protein associates with the importin alpha/beta complex which is involved in the import of proteins containing nuclear localization signals. Multiple transcript variants of this gene encode a single protein isoform. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P37198 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 134047855 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 23636 |
| NCBI Accession: | P37198.3 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P37198 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Nuclear pore glycoprotein p62 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | nucleoporin 62 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | NUP62 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | p62; IBSN; SNDI |
| NCBI Protein Information: | nuclear pore glycoprotein p62 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Nuclear pore glycoprotein p62 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | 62 kDa nucleoporin; Nucleoporin Nup62 |
| Protein Family: | Nuclear pore glycoprotein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | NUP62 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NUP62_HUMAN |