Immunology Antibodies 2
Anti-NOD2 Antibody (CAB15992)
- SKU:
- CAB15992
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Immunology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-NOD2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB15992 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
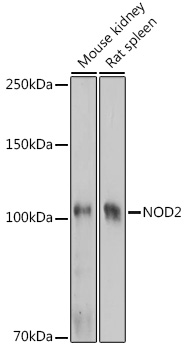
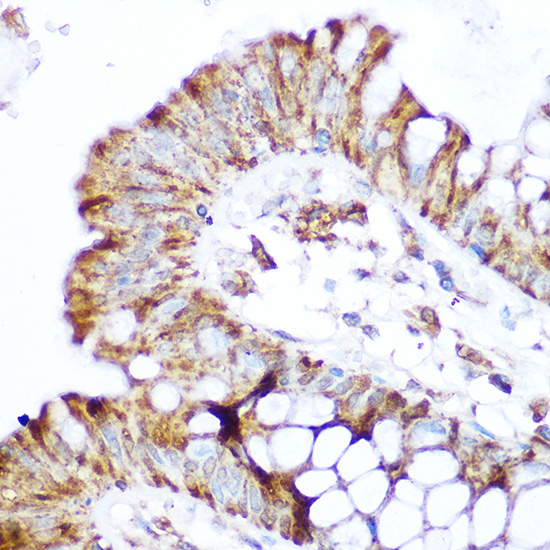
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 611-910 of human NOD2 (NP_071445.1). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse kidney, Rat spleen |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 611-910 of human NOD2 (NP_071445.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | AAFY LALS ADVP PALL RHLF NCGR PGNS PMAR LLPT MCIQ ASEG KDSS VAAL LQKA EPHN LQIT AAFL AGLL SREH WGLL AECQ TSEK ALLR RQAC ARWC LARS LRKH FHSI PPAA PGEA KSVH AMPG FIWL IRSL YEMQ EERL ARKA ARGL NVGH LKLT FCSV GPTE CAAL AFVL QHLR RPVA LQLD YNSV GDIG VEQL LPCL GVCK ALYL RDNN ISDR GICK LIEC ALHC EQLQ KLAL FNNK LTDG CAHS MAKL LACR QNFL ALRL GNNY ITAA GAQV LAEG LRGN TSLQ FLGF WGNR |
| Gene ID: | 64127 |
| Uniprot: | Q9HC29 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 22kDa/112kDa/115kDa |
| Observed MW: | 100KDa |
| Synonyms: | NOD2, ACUG, BLAU, BLAUS, CARD15, CD, CLR16.3, IBD1, NLRC2, NOD2B, PSORAS1, YAOS |
| Background: | This gene is a member of the Nod1/Apaf-1 family and encodes a protein with two caspase recruitment (CARD) domains and six leucine-rich repeats (LRRs). The protein is primarily expressed in the peripheral blood leukocytes. It plays a role in the immune response to intracellular bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) by recognizing the muramyl dipeptide (MDP) derived from them and activating the NFKB protein. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Crohn disease and Blau syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NOD2: Induces NF-kappa-B via RICK (CARDIAK, RIP2) and IKK- gamma. Confers responsiveness to intracellular bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Defects in NOD2 are the cause of Blau syndrome (BS). BS is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by early-onset granulomatous arthritis, uveitis and skin rash. Defects in NOD2 are a cause of susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease type 1 (IBD1). IBD1 is a chronic, relapsing inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract with a complex etiology. It is subdivided into Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis phenotypes. Crohn disease may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus, but most frequently it involves the terminal ileum and colon. Bowel inflammation is transmural and discontinuous; it may contain granulomas or be associated with intestinal or perianal fistulas. In contrast, in ulcerative colitis, the inflammation is continuous and limited to rectal and colonic mucosal layers; fistulas and granulomas are not observed. Both diseases include extraintestinal inflammation of the skin, eyes, or joints. Defects in NOD2 are the cause of sarcoidosis early-onset (EOS). EOS is a form of sarcoidosis manifesting in children younger than 4 years of age. Sarcoidosis is an idiopathic, systemic, inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of immune granulomas in involved organs. Granulomas predominantly invade the lungs and the lymphatic system, but also skin, liver, spleen, eyes and other organs may be involved. Early- onset sarcoidosis is quite rare and has a distinct triad of skin, joint and eye disorders, without apparent pulmonary involvement. Compared with an asymptomatic and sometimes naturally disappearing course of the disease in older children, early-onset sarcoidosis is progressive and in many cases causes severe complications, such as blindness, joint destruction and visceral involvement. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative initiation. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 16q21 Cellular Component: signalosome; cell surface; protein complex; cytoskeleton; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; cytosol; vesicle Molecular Function:protein binding; peptidoglycan binding; enzyme binding; CARD domain binding; protein kinase binding; ATP binding; muramyl dipeptide binding Biological Process: activation of MAPK activity; positive regulation of dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation; maintenance of gastrointestinal epithelium; stress-activated MAPK cascade; response to lipopolysaccharide; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta secretion; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; negative regulation of interleukin-2 production; toll-like receptor 5 signaling pathway; positive regulation of gamma-delta T cell activation; positive regulation of phagocytosis; JNK cascade; detection of muramyl dipeptide; cytokine production during immune response; detection of biotic stimulus; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway; positive regulation of oxidoreductase activity; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production; negative regulation of interleukin-12 production; positive regulation of T-helper 2 type immune response; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; positive regulation of dendritic cell cytokine production; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production; protein oligomerization; negative regulation of interleukin-18 production; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; innate immune response in mucosa; response to muramyl dipeptide; inhibition of NF-kappaB transcription factor; positive regulation of B cell activation; defense response to bacterium; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; negative regulation of T cell mediated immunity; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process; detection of bacterium; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production; positive regulation of JNK cascade; defense response; positive regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade; toll-like receptor 10 signaling pathway; response to exogenous dsRNA; negative regulation of interferon-gamma production; negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus; positive regulation of biosynthetic process of antibacterial peptides active against Gram-positive bacteria; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway; response to nutrient; positive regulation of humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production; immunoglobulin production during immune response; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production; regulation of inflammatory response; toll-like receptor signaling pathway; innate immune response Disease: Psoriatic Arthritis, Susceptibility To; Sarcoidosis, Early-onset; Inflammatory Bowel Disease 1; Blau Syndrome |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a member of the Nod1/Apaf-1 family and encodes a protein with two caspase recruitment (CARD) domains and six leucine-rich repeats (LRRs). The protein is primarily expressed in the peripheral blood leukocytes. It plays a role in the immune response to intracellular bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) by recognizing the muramyl dipeptide (MDP) derived from them and activating the NFKB protein. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Crohn disease and Blau syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9HC29 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 20137973 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 64127 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9HC29.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9HC29,Q96RH5, Q96RH6, Q96RH8, E2JEQ6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9HC29 |
| Molecular Weight: | 22,403 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | NOD2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CD; ACUG; BLAU; IBD1; NLRC2; NOD2B; CARD15; CLR16.3; PSORAS1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2; NOD-like receptor C2; NLR family, CARD domain containing 2; inflammatory bowel disease protein 1; caspase recruitment domain protein 15; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2; caspase recruitment domain family, member 15; caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 15; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine rich repeat and CARD domain containing 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 15; Inflammatory bowel disease protein 1 |
| Protein Family: | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | NOD2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NOD2_HUMAN |