Signal Transduction Antibodies 3
Anti-NMDAR1 Antibody (CAB11699)
- SKU:
- CAB11699
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-NMDAR1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB11699 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human NMDAR1 |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
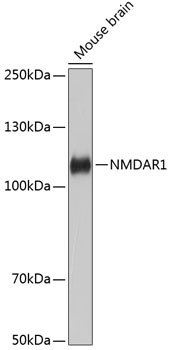
| Positive Samples: | Mouse brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human NMDAR1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 2902 |
| Uniprot: | Q05586 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 120kDa |
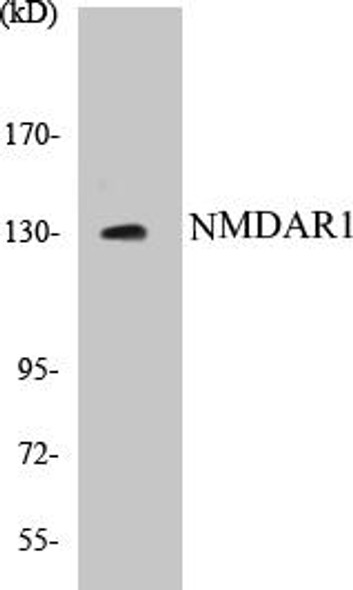
| Observed MW: | 120KDa |
| Synonyms: | GluN1, MRD8, NMD-R1, NMDA1, NMDAR1, NR1 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a critical subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, members of the glutamate receptor channel superfamily which are heteromeric protein complexes with multiple subunits arranged to form a ligand-gated ion channel. These subunits play a key role in the plasticity of synapses, which is believed to underlie memory and learning. Cell-specific factors are thought to control expression of different isoforms, possibly contributing to the functional diversity of the subunits. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NMDAR1: a subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, members of the glutamate receptor channel superfamily. Possesses high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium and is modulated by glycine. Plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. Mediates neuronal functions in glutamate neurotransmission. Three alternatively-spliced isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Channel, ligand-gated; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Membrane protein, integral; Channel, calcium Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 9q34.3 Cellular Component: neuron projection; cell surface; endoplasmic reticulum; integral to plasma membrane; postsynaptic density; dendrite; dendritic spine; terminal button; excitatory synapse; N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor complex; postsynaptic membrane; synaptic vesicle; plasma membrane; synapse; cell junction Molecular Function:voltage-gated cation channel activity; neurotransmitter binding; glutamate receptor binding; calcium channel activity; calcium ion binding; calmodulin binding; protein binding; enzyme binding; glutamate binding; extracellular-glutamate-gated ion channel activity; protein heterodimerization activity; N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor activity; glycine binding Biological Process: regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity; axon guidance; male mating behavior; prepulse inhibition; adult locomotory behavior; positive regulation of apoptosis; regulation of dendrite morphogenesis; rhythmic process; response to morphine; sensory perception of pain; regulation of axonogenesis; calcium ion homeostasis; synaptic transmission; regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange; conditioned taste aversion; ephrin receptor signaling pathway; visual learning; negative regulation of neuron apoptosis; protein tetramerization; cation transport; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic; response to amphetamine; social behavior; respiratory gaseous exchange; pons maturation; cellular calcium ion homeostasis; regulation of membrane potential; response to ethanol; regulation of synaptogenesis; olfactory learning; long-term memory; suckling behavior; propylene metabolic process; ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; cerebral cortex development; regulation of excitatory postsynaptic membrane potential; response to calcium ion Disease: Mental Retardation, Autosomal Dominant 8 |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a critical subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, members of the glutamate receptor channel superfamily which are heteromeric protein complexes with multiple subunits arranged to form a ligand-gated ion channel. These subunits play a key role in the plasticity of synapses, which is believed to underlie memory and learning. Cell-specific factors are thought to control expression of different isoforms, possibly contributing to the functional diversity of the subunits. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q05586 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 548377 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2902 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q05586.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q05586,P35437, Q12867, Q12868, Q5VSF3, Q5VSF4, Q5VSF5 Q5VSF6, Q5VSF7, A6NLK7, A6NLR1, C9K0X1, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q05586 |
| Molecular Weight: | 101,851 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GRIN1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | NR1; MRD8; GluN1; NMDA1; NMDAR1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1; NMD-R1; glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit zeta 1; glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit zeta-1; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR1; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel, subunit zeta-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit zeta-1; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR1; NMD-R1 |
| Protein Family: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GRIN1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NMDZ1_HUMAN |