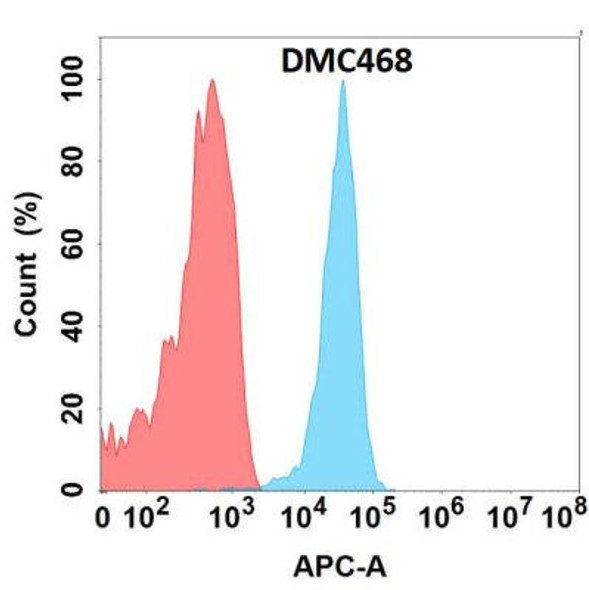
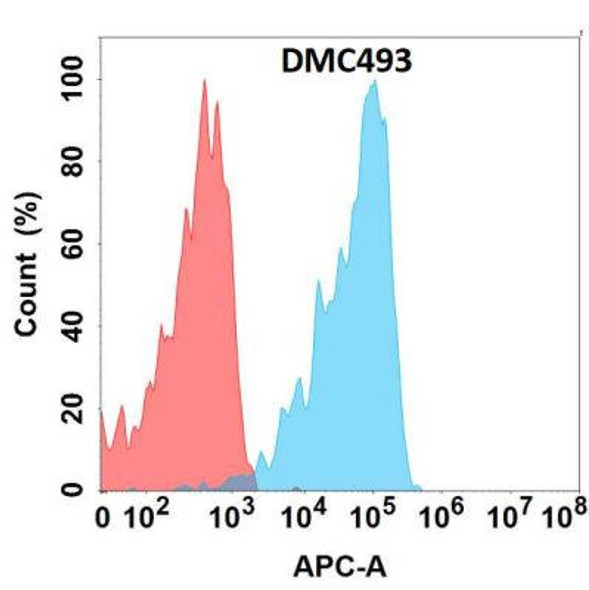
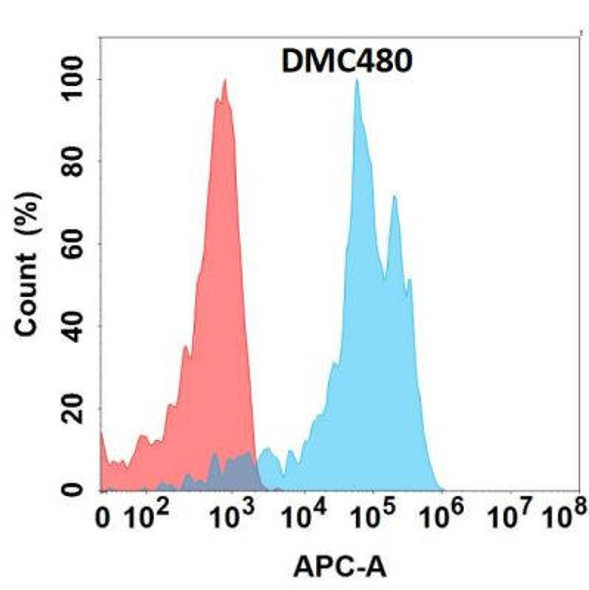
Anti-NKG2D Chimeric Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (HDAB0245)
- SKU:
- HDAB0245
- Product Type:
- Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Size:
- 100 μg
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Antibody Isotype:
- Rabbit/Human Fc chimeric IgG1
- Clone:
- DMC287
- Synonyms:
- NKG2D,CD314,KLRK1,NK cell receptor D
Description
system_update_altDatasheet
| SKU: | HDAB0245 |
| Size: | 100 µg |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal |
| Clone: | DMC287 |
| Synonyms: | NKG2D,CD314,KLRK1,NK cell receptor D |
| Applications: | Flow Cyt |
| Recommended Dilution: | Flow Cyt 1:100 |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Isotype: | Rabbit/Human Fc chimeric IgG1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Purification Method: | Purified from cell culture supernatant by affinity chromatography |
| Formulation: | Powder |
| Buffer: | 1XPBS |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C to -80°C for 12 months in lyophilized form. After reconstitution, if not intended for use within a month, aliquot and store at -80°C (Avoid repeated freezing and thawing).Lyophilized antibodies are shipped at ambient temperature. |
| Usage: | Research use only |
| Background: | Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes that can mediate lysis of certain tumor cells and virus-infected cells without previous activation. They can also regulate specific humoral and cell-mediated immunity. NK cells preferentially express several calcium-dependent (C-type) lectins, which have been implicated in the regulation of NK cell function. The NKG2 gene family is located within the NK complex, a region that contains several C-type lectin genes preferentially expressed in NK cells. This gene encodes a member of the NKG2 family. The encoded transmembrane protein is characterized by a type II membrane orientation (has an extracellular C terminus) and the presence of a C-type lectin domain. It binds to a diverse family of ligands that include MHC class I chain-related A and B proteins and UL-16 binding proteins, where ligand-receptor interactions can result in the activation of NK and T cells. The surface expression of these ligands is important for the recognition of stressed cells by the immune system, and thus this protein and its ligands are therapeutic targets for the treatment of immune diseases and cancers. Read-through transcription exists between this gene and the upstream KLRC4 (killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily C, member 4) family member in the same cluster. |