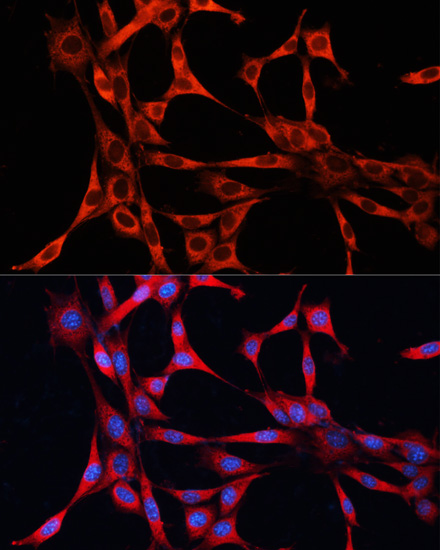
Cell Biology Antibodies 8
Anti-mTOR Antibody (CAB2445)
- SKU:
- CAB2445
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-mTOR Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB2445 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
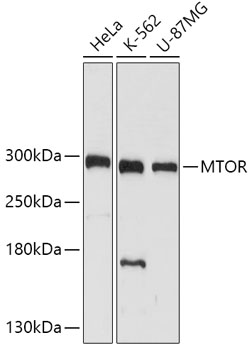
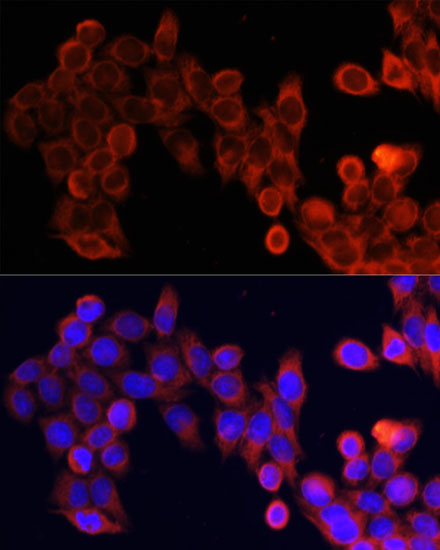
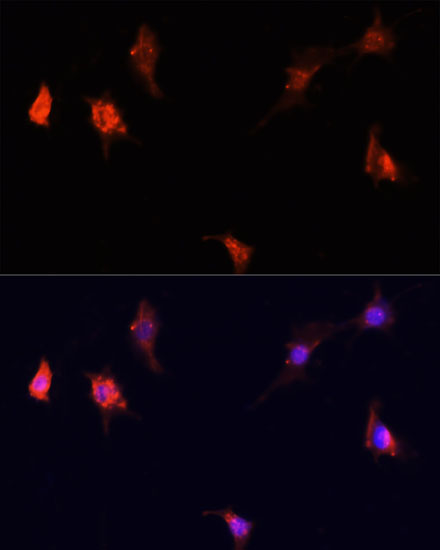
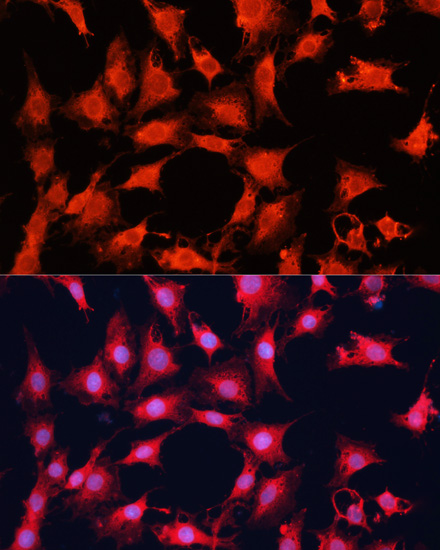
| Application: | WB IF IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-300 of human mTOR (NP_004949.1). |
| Application: | WB IF IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 IP 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, K-562, U-87MG |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-300 of human mTOR (NP_004949.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MLGT GPAA ATTA ATTS SNVS VLQQ FASG LKSR NEET RAKA AKEL QHYV TMEL REMS QEES TRFY DQLN HHIF ELVS SSDA NERK GGIL AIAS LIGV EGGN ATRI GRFA NYLR NLLP SNDP VVME MASK AIGR LAMA GDTF TAEY VEFE VKRA LEWL GADR NEGR RHAA VLVL RELA ISVP TFFF QQVQ PFFD NIFV AVWD PKQA IREG AVAA LRAC LILT TQRE PKEM QKPQ WYRH TFEE AEKG FDET LAKE KGMN RDDR IHGA LLIL NELV RISS MEGE RLRE EMEE ITQQ QLVH DKYC |
| Gene ID: | 2475 |
| Uniprot: | P42345 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Cytoplasmic side, Endoplasmic reticulum membrane, Golgi apparatus membrane, Lysosome, Mitochondrion outer membrane, Nucleus, PML body, Peripheral membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 288kDa |
| Observed MW: | 289kDa |
| Synonyms: | FRAP, FRAP1, FRAP2, RAFT1, RAPT1, SKS, mTOR, MTOR |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of phosphatidylinositol kinase-related kinases. These kinases mediate cellular responses to stresses such as DNA damage and nutrient deprivation. This protein acts as the target for the cell-cycle arrest and immunosuppressive effects of the FKBP12-rapamycin complex. The ANGPTL7 gene is located in an intron of this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | mTOR: an atypical kinase belonging to the PIKK family of kinases. Is the catalytic subunit of two protein complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2. mTORC1 activates S6K and inactivates 4E-BP1, up-regulating protein synthesis. mTORC1 contains Raptor, a positive regulatory subunit and scaffold for recruiting substrates, two negative regulators, PRAS40 and DEPTOR, and mLST8; it is a target for the cell-cycle arrest and immunosuppressive effects of the FKBP12-rapamycin complex. mTORC2, a downstream effector of PI3K, is insensitive to rapamycin and activates Akt by phosphorylating a key activation site. mTORC2 contains regulatory subunits Rictor and mSIN1, PROTOR, mLST8, and the negative regulator DEPTOR. mTORC1 suppresses PI3K activity via a strong negative feedback loop that involves S6K1. Inhibiting mTORC1 ablates this negative feedback loop and potentiates PI3K signaling. Known inhibitors of mTOR include rapamycin, temsirolimus (CCI-779). |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, atypical; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); Autophagy; EC 2.7.11.1; Kinase, protein; ATYPICAL group; PIKK family; FRAP subfamily Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p36.2 Cellular Component: cell soma; cytoplasm; cytosol; dendrite; endomembrane system; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Golgi membrane; lysosomal membrane; lysosome; membrane; mitochondrial outer membrane; nucleoplasm; phosphoinositide 3-kinase complex; PML body; TORC2 complex Molecular Function:ATP binding; drug binding; kinase activity; phosphoprotein binding; protein binding; protein domain specific binding; protein kinase binding; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; ribosome binding Biological Process: 'de novo' pyrimidine base biosynthetic process; brain development; cardiac muscle cell development; cardiac muscle contraction; cell aging; cell cycle arrest; cell growth; cellular response to nutrient levels; DNA repair; energy reserve metabolic process; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; gene expression; germ cell development; growth; heart morphogenesis; innate immune response; insulin receptor signaling pathway; long-term memory; macroautophagy; maternal process involved in pregnancy; mRNA stabilization; multicellular organism growth; negative regulation of autophagy; negative regulation of cell size; negative regulation of muscle atrophy; negative regulation of NFAT protein import into nucleus; negative regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; phosphorylation; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process; positive regulation of neuron maturation; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation; positive regulation of stress fiber formation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase III promoter; positive regulation of translation; post-embryonic development; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; protein amino acid phosphorylation; protein catabolic process; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; regulation of carbohydrate utilization; regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation; regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process; regulation of GTPase activity; regulation of myelination; regulation of osteoclast differentiation; regulation of protein kinase activity; regulation of response to food; response to amino acid stimulus; response to cocaine; response to morphine; response to nutrient; response to stress; ruffle organization and biogenesis; signal transduction; social behavior; spinal cord development; T cell costimulation; TOR signaling pathway; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; visual learning; voluntary musculoskeletal movement; wound healing |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of phosphatidylinositol kinase-related kinases. These kinases mediate cellular responses to stresses such as DNA damage and nutrient deprivation. This protein acts as the target for the cell-cycle arrest and immunosuppressive effects of the FKBP12-rapamycin complex. The ANGPTL7 gene is located in an intron of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P42345 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1169735 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2475 |
| NCBI Accession: | P42345.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P42345,Q4LE76, Q5TER1, Q6LE87, Q96QG3, Q9Y4I3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P42345 |
| Molecular Weight: | 288,892 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MTOR |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SKS; FRAP; FRAP1; FRAP2; RAFT1; RAPT1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin complex-associated protein 1; FKBP12-rapamycin complex-associated protein; Mammalian target of rapamycin; mTOR; Mechanistic target of rapamycin; Rapamycin and FKBP12 target 1; Rapamycin target protein 1 |
| Protein Family: | Serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MTOR |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MTOR_HUMAN |