Cell Biology Antibodies 18
Anti-MT-ATP6 Antibody (CAB18315)
- SKU:
- CAB18315
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-MT-ATP6 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB18315 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
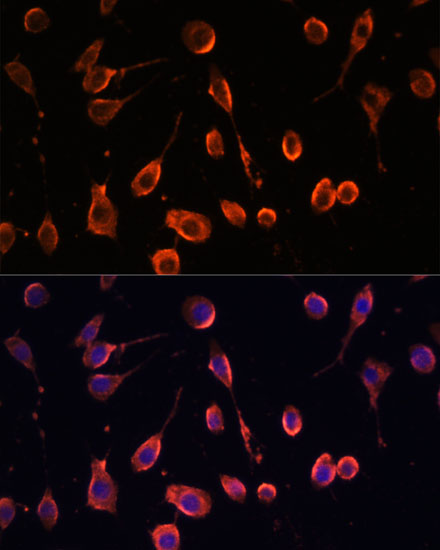
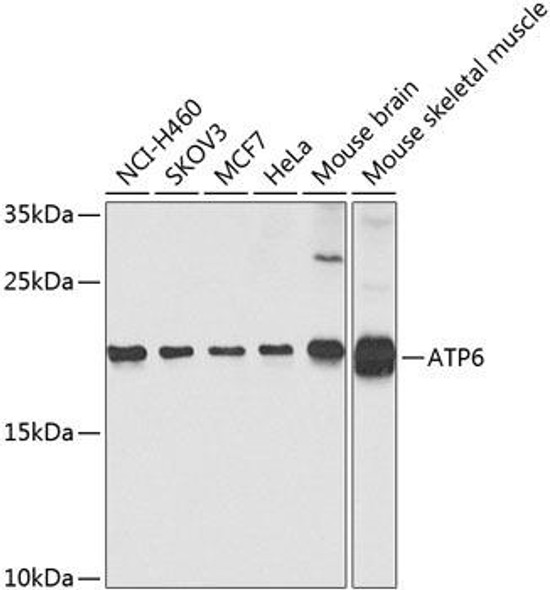
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human MT-ATP6. |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human MT-ATP6. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 4508 |
| Uniprot: | P00846 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 25kDa |
| Observed MW: |
| Synonyms: | ATPase6, MTATP6, MT-ATP6 |
| Background: |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ATP6: Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Key component of the proton channel; it may play a direct role in the translocation of protons across the membrane. Defects in MT-ATP6 are the cause of neurogenic muscle weakness, ataxia, and retinitis pigmentosa (NARP). Defects in MT-ATP6 are a cause of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON). LHON is a maternally inherited disease resulting in acute or subacute loss of central vision, due to optic nerve dysfunction. Cardiac conduction defects and neurological defects have also been described in some patients. LHON results from primary mitochondrial DNA mutations affecting the respiratory chain complexes. Defects in MT-ATP6 are a cause of Leigh syndrome (LS). LS is a severe neurological disorder characterized by bilaterally symmetrical necrotic lesions in subcortical brain regions. Defects in MT-ATP6 are a cause of mitochondrial infantile bilateral striatal necrosis (MIBSN). Bilateral striatal necrosis is a neurological disorder resembling Leigh syndrome. Belongs to the ATPase A chain family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Transporter, ion channel; Membrane protein, integral; Mitochondrial; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Transporter Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: - Disease: Neuropathy, Ataxia, And Retinitis Pigmentosa; Leber Optic Atrophy |
| UniProt Code: | P00846 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 251831112 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4508 |
| NCBI Accession: | YP_003024031.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P00846,Q34772, Q5S8W5, Q5S9E7, Q5S9I6, Q5SA31, Q6RPB7 Q6VHC0, Q6VHE0, Q6WQF4, Q7YCC1, Q7YCF8, |
| Molecular Weight: | 25kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | ATP synthase F0 subunit 6 (mitochondrion) |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | mitochondrially encoded ATP synthase 6 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MT-ATP6 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ATPase6; MTATP6; ATP6 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ATP synthase F0 subunit 6 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | ATP synthase subunit a |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | F-ATPase protein 6 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MT-ATP6 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ATP6_HUMAN |