Cell Cycle Antibodies 2
Anti-MAD1 Antibody (CAB5098)
- SKU:
- CAB5098
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Cycle
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-MAD1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB5098 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
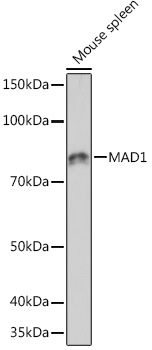
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human MAD1 |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, 294T, Mouse spleen |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human MAD1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 8379 |
| Uniprot: | Q9Y6D9 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 80kDa |
| Observed MW: | 83KDa |
| Synonyms: | MAD1, PIG9, TP53I9, TXBP181 |
| Background: | MAD1L1 is a component of the mitotic spindle-assembly checkpoint that prevents the onset of anaphase until all chromosome are properly aligned at the metaphase plate. MAD1L1 functions as a homodimer and interacts with MAD2L1. MAD1L1 may play a role in cell cycle control and tumor suppression. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | MAD1L1: a component of the spindle-assembly checkpoint that prevents the onset of anaphase until all chromosomes are properly aligned at the metaphase plate. Has a role in the correct positioning of the septum. Required for anchoring MAD2L1 to the nuclear periphery. Expressed weakly at G0/G1 and highly at late S and G2/M phase. Induced by p53. Becomes hyperphosphorylated in late S through M phases or after mitotic spindle damage. Two alternatively spliced isoforms have been described. Defects in MAD1L1 are involved in the development and/or progression of various types of cancer. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell cycle regulation; Cytoskeletal Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 7p22 Cellular Component: kinetochore; centrosome; cytoplasm; spindle; nuclear pore; nucleus; cytosol; actin cytoskeleton Molecular Function:protein binding Biological Process: mitosis; cell division; mitotic cell cycle checkpoint; mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint; mitotic cell cycle Disease: Prostate Cancer |
| NCBI Summary: | MAD1L1 is a component of the mitotic spindle-assembly checkpoint that prevents the onset of anaphase until all chromosome are properly aligned at the metaphase plate. MAD1L1 functions as a homodimer and interacts with MAD2L1. MAD1L1 may play a role in cell cycle control and tumor suppression. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9Y6D9 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 52783153 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 8379 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9Y6D9.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9Y6D9,Q13312, Q75MI0, Q86UM4, Q9UNH0, B3KR41, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9Y6D9 |
| Molecular Weight: | 718 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | MAD1 mitotic arrest deficient-like 1 (yeast) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MAD1L1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | MAD1; PIG9; TP53I9; TXBP181 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD1; MAD1-like protein 1; tax-binding protein 181; tumor protein p53 inducible protein 9; mitotic checkpoint MAD1 protein homolog; mitotic arrest deficient 1-like protein 1; mitotic-arrest deficient 1, yeast, homolog-like 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Mitotic arrest deficient 1-like protein 1; MAD1-like protein 1; Mitotic checkpoint MAD1 protein homolog; HsMAD1; hMAD1; Tax-binding protein 181 |
| Protein Family: | Mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MAD1L1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MD1L1_HUMAN |
View AllClose


![[KD Validated] MAD1/MAD1L1 Polyclonal Antibody [KD Validated] MAD1/MAD1L1 Polyclonal Antibody](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/82264/87053/A22000_1__37122__43646.1706547173.jpg?c=1)


![Anti-Smad1 Antibody [KO Validated] (CAB19113) Anti-Smad1 Antibody [KO Validated] (CAB19113)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/55871/61053/anti-smad1-antibody-ko-validated-cab19113__13713__03591.1706533697.jpg?c=1)
