Cell Biology Antibodies 12
Anti-LLGL2 Antibody (CAB8284)
- SKU:
- CAB8284
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Applications:
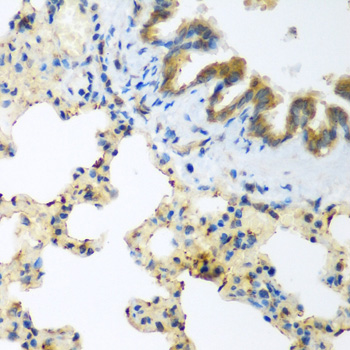
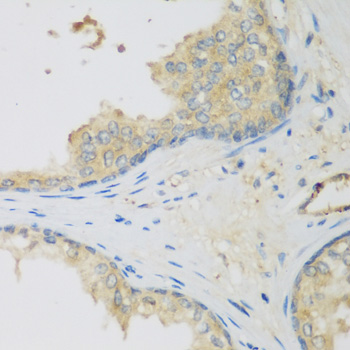
- IHC
- Applications:
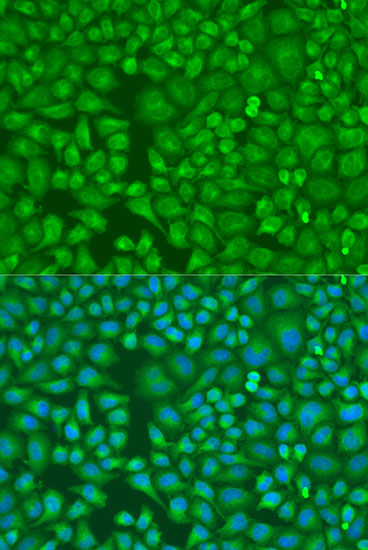
- IF
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | LLGL2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB8284 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 620-819 of mouse LLGL2 (NP_663413.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
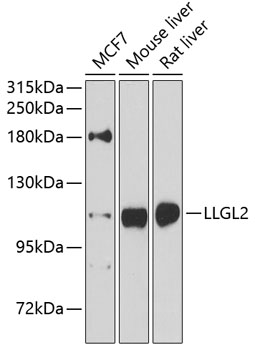
| Positive Samples: | MCF7, Mouse liver, Rat liver |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 620-819 of mouse LLGL2 (NP_663413.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | RQVF VKCT LHPS DQLA LEGP LSRV KSLK KSLR QSFR RMRR SRVS SHKR RPGG PTGE AQAQ AVNI KAER TGLQ NMEL APVQ RKIE ARSA EDSF TGFV RTLY FADT YLRD SSRH CPSL WAGT NGGT VYAF SLRV PPAE RRTD EPVR AEQA KEIQ LMHR APVV GILV LDGH NVPL PEPL EVAH DLSK SPDM QGSH QLLV VSEE |
| Gene ID: | 217325 |
| Uniprot: | |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm |
| Calculated MW: | 114kDa |
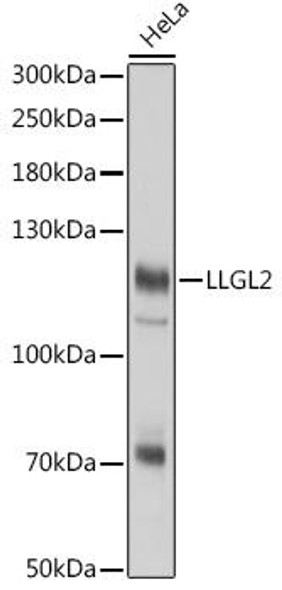
| Observed MW: | 113kDa |
| Synonyms: | LLGL2, HGL, Hugl-2, LGL2 |
| Background: | The lethal (2) giant larvae protein of Drosophila plays a role in asymmetric cell division, epithelial cell polarity, and cell migration. This human gene encodes a protein similar to lethal (2) giant larvae of Drosophila. In fly, the protein's ability to localize cell fate determinants is regulated by the atypical protein kinase C (aPKC). In human, this protein interacts with aPKC-containing complexes and is cortically localized in mitotic cells. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. |