Metabolism Antibodies 1
Anti-LDLR Antibody (CAB14996)
- SKU:
- CAB14996
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-LDLR Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB14996 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
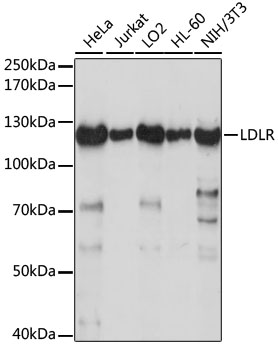
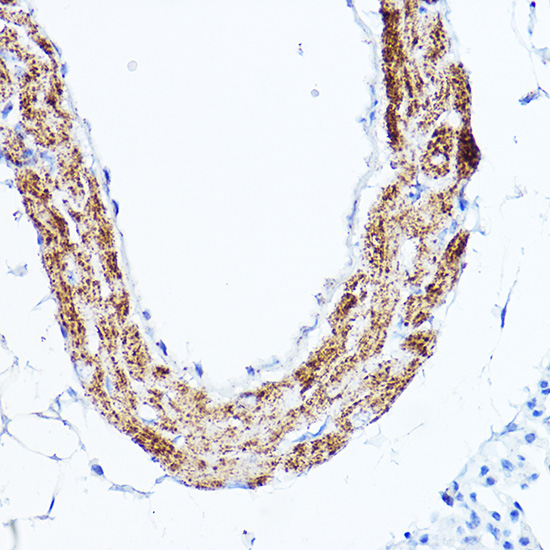
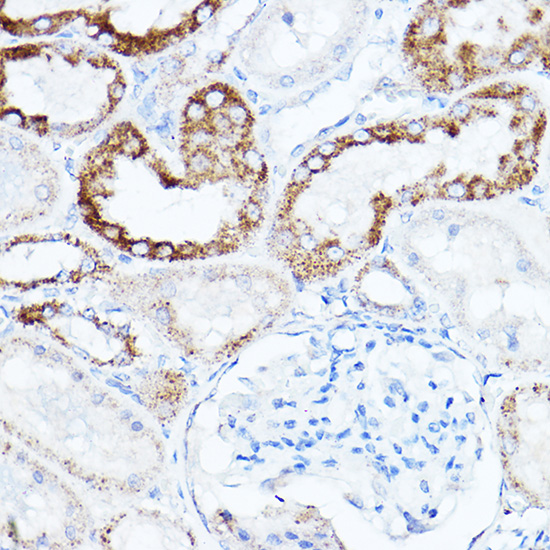
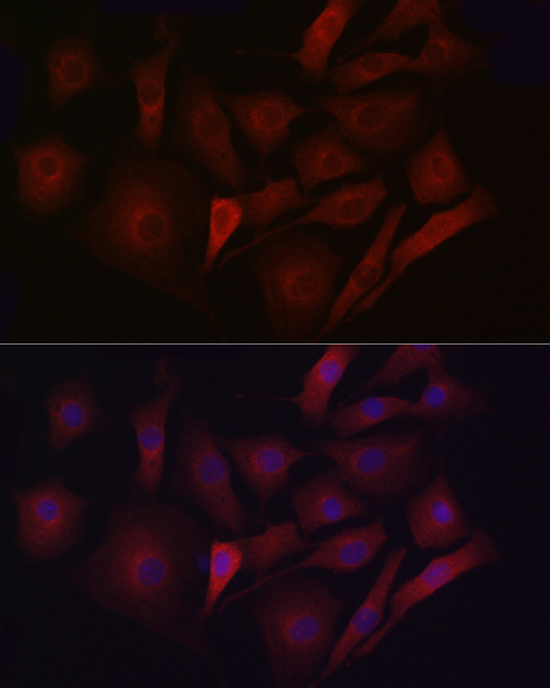
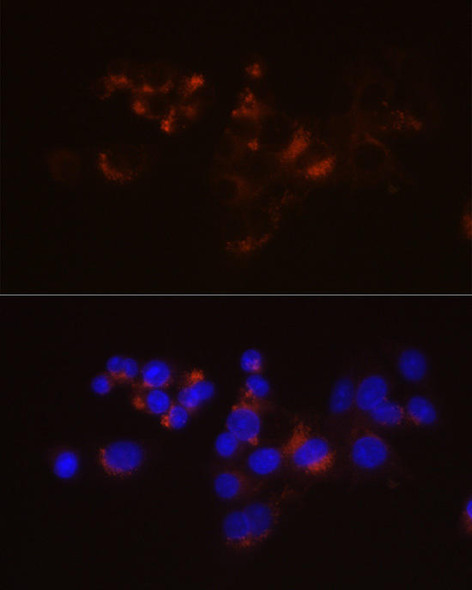
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 800 to the C-terminus of human LDLR (NP_000518.1). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, Jurkat, LO2, HL-60, NIH/3T3 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 800 to the C-terminus of human LDLR (NP_000518.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | VFLC LGVF LLWK NWRL KNIN SINF DNPV YQKT TEDE VHIC HNQD GYSY PSRQ MVSL EDDV A |
| Gene ID: | 3949 |
| Uniprot: | P01130 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Cell surface, Early endosome, Endomembrane system, Golgi apparatus, Late endosome, Lysosome, Membrane, Single-pass type I membrane protein, clathrin-coated pit |
| Calculated MW: | 75kDa/76kDa/82kDa/90kDa/95kDa |
| Observed MW: | 120kDa |
| Synonyms: | LDLR, FH, FHC, LDLCQ2 |
| Background: | The low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene family consists of cell surface proteins involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis of specific ligands. Low density lipoprotein (LDL) is normally bound at the cell membrane and taken into the cell ending up in lysosomes where the protein is degraded and the cholesterol is made available for repression of microsomal enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) reductase, the rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis. At the same time, a reciprocal stimulation of cholesterol ester synthesis takes place. Mutations in this gene cause the autosomal dominant disorder, familial hypercholesterolemia. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | LDLR: Binds LDL, the major cholesterol-carrying lipoprotein of plasma, and transports it into cells by endocytosis. In order to be internalized, the receptor-ligand complexes must first cluster into clathrin-coated pits. In case of HIV-1 infection, functions as a receptor for extracellular Tat in neurons, mediating its internalization in uninfected cells. Defects in LDLR are the cause of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH); a common autosomal semi- dominant disease that affects about 1 in 500 individuals. The receptor defect impairs the catabolism of LDL, and the resultant elevation in plasma LDL-cholesterol promotes deposition of cholesterol in the skin (xanthelasma), tendons (xanthomas), and coronary arteries (atherosclerosis). Belongs to the LDLR family. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Receptor, misc.; Membrane protein, integral; Cell surface Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 19p13.2 Cellular Component: apical part of cell; basolateral plasma membrane; cell surface; coated pit; early endosome; endosome membrane; external side of plasma membrane; Golgi apparatus; integral to plasma membrane; late endosome; lysosome; membrane; plasma membrane; receptor complex Molecular Function:clathrin heavy chain binding; glycoprotein binding; identical protein binding; low-density lipoprotein receptor activity; protease binding; protein binding; receptor activity; very-low-density lipoprotein receptor activity Biological Process: cholesterol absorption; cholesterol homeostasis; cholesterol transport; endocytosis; lipid metabolic process; phospholipid transport; receptor-mediated endocytosis Disease: Hypercholesterolemia, Familial |
| NCBI Summary: | The low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene family consists of cell surface proteins involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis of specific ligands. Low density lipoprotein (LDL) is normally bound at the cell membrane and taken into the cell ending up in lysosomes where the protein is degraded and the cholesterol is made available for repression of microsomal enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) reductase, the rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis. At the same time, a reciprocal stimulation of cholesterol ester synthesis takes place. Mutations in this gene cause the autosomal dominant disorder, familial hypercholesterolemia. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P01130 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 126073 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3949 |
| NCBI Accession: | P01130.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P01130,Q53ZD9, Q59FQ1, Q9UDH7, B4DII3, B4DJZ8, B4DR00 B4DTQ3, C0JYY8, H0YLU8, H0YNT7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P01130 |
| Molecular Weight: | 82,255 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | low density lipoprotein receptor |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | LDLR |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FH; FHC; LDLCQ2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| Protein Family: | LDLR chaperone |
| UniProt Gene Name: | LDLR |
| UniProt Entry Name: | LDLR_HUMAN |