Cell Biology Antibodies 6
Anti-KIF7 Antibody (CAB15581)
- SKU:
- CAB15581
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-KIF7 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB15581 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
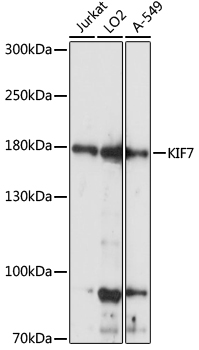
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1044-1343 of human KIF7 (NP_940927.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:200 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | Jurkat, LO2, A-549 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1044-1343 of human KIF7 (NP_940927.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | QLDE AIEA LDAA IEYK NEAI TCRQ RVLR ASAS LLSQ CEMN LMAK LSYL SSSE TRAL LCKY FDKV VTLR EEQH QQQI AFSE LEMQ LEEQ QRLV YWLE VALE RQRL EMDR QLTL QQKE HEQN MQLL LQQS RDHL GEGL ADSR RQYE ARIQ ALEK ELGR YMWI NQEL KQKL GGVN AVGH SRGG EKRS LCSE GRQA PGNE DELH LAPE LLWL SPLT EGAP RTRE ETRD LVHA PLPL TWKR SSLC GEEQ GSPE ELRQ REAA EPLV GRVL PVGE AGLP WNFG PLSK PRRE LRRA SPGM IDVR KNPL |
| Gene ID: | 374654 |
| Uniprot: | Q2M1P5 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell projection, cilium |
| Calculated MW: | 150kDa |
| Observed MW: | 150kDa |
| Synonyms: | KIF7, ACLS, AGBK, HLS2, JBTS12, UNQ340 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a cilia-associated protein belonging to the kinesin family. This protein plays a role in the sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway through the regulation of GLI transcription factors. It functions as a negative regulator of the SHH pathway by preventing inappropriate activation of GLI2 in the absence of ligand, and as a positive regulator by preventing the processing of GLI3 into its repressor form. Mutations in this gene have been associated with various ciliopathies. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | KIF7: Acts as both a negative and positive regulator of sonic hedgehog (Shh) pathway, acting downstream of SMO. Negatively regulates the pathway by preventing inappropriate activation of the transcriptional activator GLI2 in the absence of ligand. Positively regulates the pathway by preventing the processing of the transcription factor GLI3 into its repressor form. Required for efficient localization of GLI3 to cilia in response to Shh. Affects microtubular dynamics and acts as a ciliary motor. Ciliary dysfunction leads to a broad spectrum of disorders, collectively termed ciliopathies. The ciliopathy range of diseases includes Meckel-Gruber syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome, Joubert syndrome, and hydrolethalus syndrome among others. Single-locus allelism is insufficient to explain the variable penetrance and expressivity of such disorders, leading to the suggestion that variations across multiple sites of the ciliary proteome influence the clinical outcome. Primary ciliopathy loci can be modulated by pathogenic lesions in other ciliary genes to either exacerbate overall severity or induce specific endophenotypes. KIF7 may be causally associated with diverse ciliopathies, and also acts as a modifier gene across the ciliopathy spectrum. Defects in KIF7 may be a cause of Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS). A syndrome characterized by usually severe pigmentary retinopathy, early-onset obesity, polydactyly, hypogenitalism, renal malformation and mental retardation. Secondary features include diabetes mellitus, hypertension and congenital heart disease. Bardet-Biedl syndrome inheritance is autosomal recessive, but three mutated alleles (two at one locus, and a third at a second locus) may be required for clinical manifestation of some forms of the disease. Heterozygous missense mutations in KIF7 may genetically interact with other BBS genes and contribute to disease manifestation and severity. Defects in KIF7 are the cause of hydrolethalus syndrome type 2 (HLS2). HLS2 is an embryonic lethal disorder characterized by hydrocephaly or anencephaly, postaxial polydactyly of the upper limbs, and pre- or postaxial polydactyly of the lower limbs. Duplication of the hallux is a common finding. Defects in KIF7 are the cause of acrocallosal syndrome (ACLS). ACLS is a syndrome that is characterized by postaxial polydactyly, hallux duplication, macrocephaly and absence of the corpus callosum, usually with severe developmental delay. Defects in KIF7 are the cause of Joubert syndrome type 12 (JBTS12). JBTS12 is a disorder presenting with cerebellar ataxia, oculomotor apraxia, hypotonia, neonatal breathing abnormalities and psychomotor delay. Neuroradiologically, it is characterized by cerebellar vermian hypoplasia/aplasia, thickened and reoriented superior cerebellar peduncles, and an abnormally large interpeduncular fossa, giving the appearance of a molar tooth on transaxial slices (molar tooth sign). Additional variable features include retinal dystrophy and renal disease. Defects in KIF7 may be a cause of Pallister-Hall syndrome (PHS). An autosomal dominant disorder characterized by a wide range of clinical manifestations. Clinical features include hypothalamic hamartoma, pituitary dysfunction, central or postaxial polydactyly, and syndactyly. Malformations are frequent in the viscera, e.g. anal atresia, bifid uvula, congenital heart malformations, pulmonary or renal dysplasia. Belongs to the kinesin-like protein family. KIF27 subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motor; Microtubule-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 15q26.1 Cellular Component: kinesin complex; cilium Molecular Function:protein binding; microtubule binding; ATPase activity; microtubule motor activity; ATP binding Biological Process: smoothened signaling pathway; ventricular system development; metabolic process; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway; microtubule-based movement Disease: Acrocallosal Syndrome; Hydrolethalus Syndrome 2 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a cilia-associated protein belonging to the kinesin family. This protein plays a role in the sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway through the regulation of GLI transcription factors. It functions as a negative regulator of the SHH pathway by preventing inappropriate activation of GLI2 in the absence of ligand, and as a positive regulator by preventing the processing of GLI3 into its repressor form. Mutations in this gene have been associated with various ciliopathies. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | Q2M1P5 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 203096856 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 374654 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_940927.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q2M1P5,Q3SXY0, Q6UXE9, Q8IW72, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q2M1P5 |
| Molecular Weight: | 150,587 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | kinesin-like protein KIF7 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | kinesin family member 7 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | KIF7 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ACLS; HLS2; JBTS12; UNQ340 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | kinesin-like protein KIF7 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Kinesin-like protein KIF7 |
| Protein Family: | Kinesin-like protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | KIF7 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | KIF7_HUMAN |
View AllClose