Signal Transduction Antibodies 1
Anti-KCNJ8 Antibody (CAB10563)
- SKU:
- CAB10563
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-KCNJ8 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB10563 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
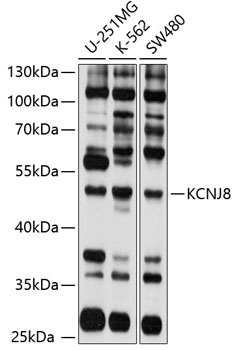
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 325-424 of human KCNJ8 (NP_004973.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:1000 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | U-251MG, K-562, SW480 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 325-424 of human KCNJ8 (NP_004973.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | VSIV TEEE GVYS VDYS KFGN TVKV AAPR CSAR ELDE KPSI LIQT LQKS ELSH QNSL RKRN SMRR NNSM RRNN SIRR NNSS LMVP KVQF MTPE GNQN TSES |
| Gene ID: | 3764 |
| Uniprot: | Q15842 |
| Cellular Location: | Membrane, Multi-pass membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 47kDa |
| Observed MW: | 48kDa |
| Synonyms: | KCNJ8, KIR6.1, uKATP-1 |
| Background: | Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. The encoded protein, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, is controlled by G-proteins. Defects in this gene may be a cause of J-wave syndromes and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). |
| UniProt Protein Function: | KCNJ8: This potassium channel is controlled by G proteins. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. Can be blocked by external barium. Defects in KCNJ8 may be associated with susceptibility to J-wave syndromes, a group of heart disorders characterized by early repolarization events as indicated by abnormal J-wave manifestation on electrocardiogram (ECG). The J point denotes the junction of the QRS complex and the ST segment on the ECG, marking the end of depolarization and the beginning of repolarization. An abnormal J wave is a deflection with a dome or hump morphology immediately following the QRS complex of the surface ECG. Examples of J-wave disorders are arrhythmias associated with an early repolarization pattern in the inferior or mid to lateral precordial leads, Brugada syndrome, some cases of idiopathic ventricular fibrillation (VF) with an early repolarization pattern in the inferior, inferolateral or global leads, as well as arrhythmias associated with hypothermia. Defects in KCNJ8 may be a cause of susceptibility to sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). SIDS is the sudden death of an infant younger than 1 year that remains unexplained after a thorough case investigation, including performance of a complete autopsy, examination of the death scene, and review of clinical history. Pathophysiologic mechanisms for SIDS may include respiratory dysfunction, cardiac dysrhythmias, cardiorespiratory instability, and inborn errors of metabolism, but definitive pathogenic mechanisms precipitating an infant sudden death remain elusive. Belongs to the inward rectifier-type potassium channel (TC 1.A.2.1) family. KCNJ8 subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Channel, potassium; Membrane protein, integral; Membrane protein, multi-pass Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12p12.1 Cellular Component: plasma membrane; voltage-gated potassium channel complex Molecular Function:ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity; inward rectifier potassium channel activity Biological Process: potassium ion transport |
| NCBI Summary: | Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. The encoded protein, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, is controlled by G-proteins. Defects in this gene may be a cause of J-wave syndromes and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). [provided by RefSeq, May 2012] |
| UniProt Code: | Q15842 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 2493600 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3764 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q15842.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q15842,O00657, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q15842 |
| Molecular Weight: | 48kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 8 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily J member 8 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | KCNJ8 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | KIR6.1; uKATP-1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 8 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 8 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir6.1; Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 8; uKATP-1 |
| Protein Family: | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel |
| UniProt Gene Name: | KCNJ8 |
View AllClose