Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 1
Anti-IRF4 Antibody (CAB1052)
- SKU:
- CAB1052
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-IRF4 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB1052 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
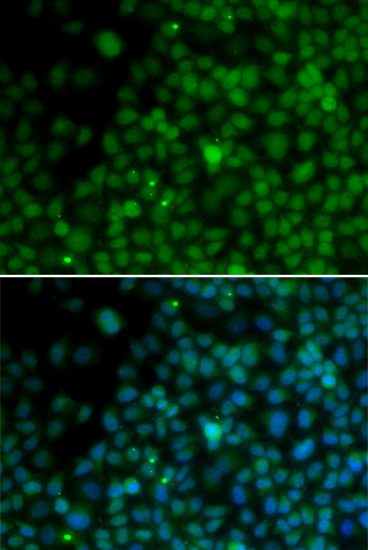
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 180-451 of human IRF4 (NP_002451.2). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
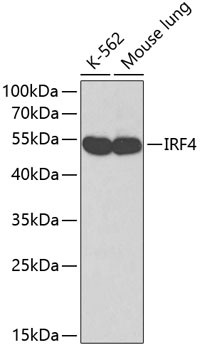
| Positive Samples: | K-562, Mouse lung |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 180-451 of human IRF4 (NP_002451.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | DYVP DQPH PEIP YQCP MTFG PRGH HWQG PACE NGCQ VTGT FYAC APPE SQAP GVPT EPSI RSAE ALAF SDCR LHIC LYYR EILV KELT TSSP EGCR ISHG HTYD ASNL DQVL FPYP EDNG QRKN IEKL LSHL ERGV VLWM APDG LYAK RLCQ SRIY WDGP LALC NDRP NKLE RDQT CKLF DTQQ FLSE LQAF AHHG RSLP RFQV TLCF GEEF PDPQ RQRK LITA HVEP LLAR QLYY FAQQ NSGH FLRG YDLP EHIS NPED YHRS IRHS SIQE |
| Gene ID: | 3662 |
| Uniprot: | Q15306 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 51kDa |
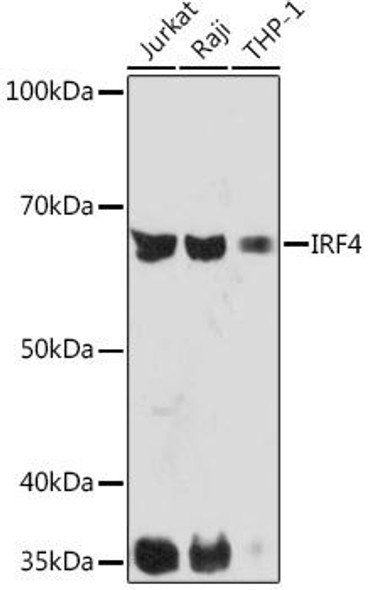
| Observed MW: | 52kDa |
| Synonyms: | IRF4, LSIRF, MUM1, NF-EM5, SHEP8, IRF-4 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the IRF (interferon regulatory factor) family of transcription factors, characterized by an unique tryptophan pentad repeat DNA-binding domain. The IRFs are important in the regulation of interferons in response to infection by virus, and in the regulation of interferon-inducible genes. This family member is lymphocyte specific and negatively regulates Toll-like-receptor (TLR) signaling that is central to the activation of innate and adaptive immune systems. A chromosomal translocation involving this gene and the IgH locus, t(6;14)(p25;q32), may be a cause of multiple myeloma. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | IRF4: Transcriptional activator. Binds to the interferon- stimulated response element (ISRE) of the MHC class I promoter. Binds the immunoglobulin lambda light chain enhancer, together with PU.1. Probably plays a role in ISRE-targeted signal transduction mechanisms specific to lymphoid cells. Interacts with SPIB and DEF6. Not induced by interferons. Lymphoid cells. Belongs to the IRF family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor; Oncoprotein Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 6p25-p23 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; membrane; cytoplasm; cytosol; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding; sequence-specific DNA binding; protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity; transcription factor binding; transcription factor activity Biological Process: transcription, DNA-dependent; T cell activation; cytokine and chemokine mediated signaling pathway; positive regulation of interleukin-2 biosynthetic process; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; regulation of T-helper cell differentiation; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation; defense response to protozoan; peptidyl-lysine methylation; positive regulation of interleukin-10 biosynthetic process; positive regulation of interleukin-4 biosynthetic process; positive regulation of interleukin-13 biosynthetic process; negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of DNA binding Disease: Skin/hair/eye Pigmentation, Variation In, 8 |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the IRF (interferon regulatory factor) family of transcription factors, characterized by an unique tryptophan pentad repeat DNA-binding domain. The IRFs are important in the regulation of interferons in response to infection by virus, and in the regulation of interferon-inducible genes. This family member is lymphocyte specific and negatively regulates Toll-like-receptor (TLR) signaling that is central to the activation of innate and adaptive immune systems. A chromosomal translocation involving this gene and the IgH locus, t(6;14)(p25;q32), may be a cause of multiple myeloma. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | Q15306 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 2497445 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3662 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q15306.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q15306,Q5VUI7, Q99660, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q15306 |
| Molecular Weight: | 451 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Interferon regulatory factor 4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | interferon regulatory factor 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | IRF4 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | MUM1; LSIRF; SHEP8; NF-EM5 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | interferon regulatory factor 4; multiple myeloma oncogene 1; lymphocyte-specific interferon regulatory factor |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Interferon regulatory factor 4 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Lymphocyte-specific interferon regulatory factor; LSIRF; Multiple myeloma oncogene 1; NF-EM5 |
| Protein Family: | Interferon regulatory factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | IRF4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | IRF4_HUMAN |