Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 3
Anti-HNF1A Antibody (CAB3092)
- SKU:
- CAB3092
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-HNF1A Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB3092 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
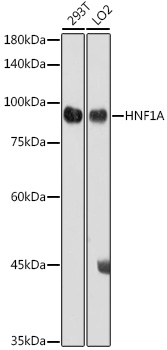
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human HNF1A |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | 293T, LO2 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human HNF1A |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 6927 |
| Uniprot: | P20823 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 12kDa/27kDa/30kDa/43kDa/55-70kDa |
| Observed MW: | 81KDa |
| Synonyms: | HNF1A, HNF-1A, HNF1, IDDM20, LFB1, MODY3, TCF-1, TCF1 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor required for the expression of several liver-specific genes. The encoded protein functions as a homodimer and binds to the inverted palindrome 5'-GTTAATNATTAAC-3'. Defects in this gene are a cause of maturity onset diabetes of the young type 3 (MODY3) and also can result in the appearance of hepatic adenomas. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HNF1A: Transcriptional activator that regulates the tissue specific expression of multiple genes, especially in pancreatic islet cells and in liver. Required for the expression of several liver specific genes. Binds to the inverted palindrome 5'- GTTAATNATTAAC-3'. Defects in HNF1A are a cause of hepatic adenomas familial (HEPAF). Hepatic adenomas are rare benign liver tumors of presumable epithelial origin that develop in an otherwise normal liver. Hepatic adenomas may be single or multiple. They consist of sheets of well-differentiated hepatocytes that contain fat and glycogen and can produce bile. Bile ducts or portal areas are absent. Kupffer cells, if present, are reduced in number and are non-functional. Conditions associated with adenomas are insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and glycogen storage diseases (types 1 and 3). Bi-allelic inactivation of HNF1A, whether sporadic or associated with MODY3, may be an early step in the developmant of some hepatocellular carcinomas. Defects in HNF1A are the cause of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 (MODY3); also symbolized MODY-3. MODY is a form of diabetes that is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset in childhood or early adulthood (usually before 25 years of age), a primary defect in insulin secretion and frequent insulin-independence at the beginning of the disease. Defects in HNF1A are the cause of susceptibility to diabetes mellitus insulin-dependent type 20 (IDDM20). IDDM20 is a multifactorial disorder of glucose homeostasis that is characterized by susceptibility to ketoacidosis in the absence of insulin therapy. Clinical fetaures are polydipsia, polyphagia and polyuria which result from hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis and secondary thirst. These features can result in long-term complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels. Belongs to the HNF1 homeobox family. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12q24.2 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; protein complex; cytoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:protein dimerization activity; protein binding; protein homodimerization activity; DNA binding; protein heterodimerization activity; transcription factor activity Biological Process: regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; transcription, DNA-dependent; insulin secretion; glucose import; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; glucose homeostasis Disease: Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin-dependent, 20; Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin-dependent; Hepatic Adenomas, Familial; Maturity-onset Diabetes Of The Young, Type 3; Renal Cell Carcinoma, Nonpapillary; Diabetes Mellitus, Noninsulin-dependent |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor required for the expression of several liver-specific genes. The encoded protein functions as a homodimer and binds to the inverted palindrome 5'-GTTAATNATTAAC-3'. Defects in this gene are a cause of maturity onset diabetes of the young type 3 (MODY3) and also can result in the appearance of hepatic adenomas. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P20823 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 51338763 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6927 |
| NCBI Accession: | P20823.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P20823,Q2M3H2, Q99861, A5Z2R8, E0YMJ5, E0YMK0, E0YMK1 E2I9R4, E2I9R5, F5H5U3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P20823 |
| Molecular Weight: | 12,491 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-alpha |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | HNF1 homeobox A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HNF1A |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HNF1; LFB1; TCF1; MODY3; TCF-1; HNF-1A; IDDM20 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-alpha |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-alpha |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1; LFB1; Transcription factor 1; TCF-1 |
| Protein Family: | Hepatocyte nuclear factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HNF1A |
| UniProt Entry Name: | HNF1A_HUMAN |