Cell Biology Antibodies 17
Anti-Histone H1.0 Antibody (CAB4342)
- SKU:
- CAB4342
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Histone H1.0 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB4342 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Histone H1.0 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
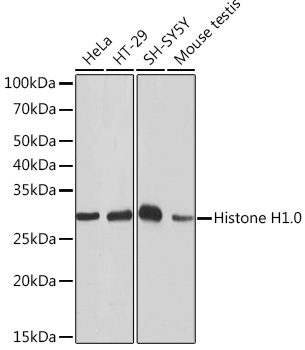
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, HT-29, SH-SY5Y, Mouse testis |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Histone H1.0 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 3005 |
| Uniprot: | P07305 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 28kDa |
| Observed MW: | 32KDa |
| Synonyms: | H10, H1FV |
| Background: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a replication-independent histone that is a member of the histone H1 family. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | H1F0: Histones H1 are necessary for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structures. The H1F0 histones are found in cells that are in terminal stages of differentiation or that have low rates of cell division. Belongs to the histone H1/H5 family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 22q13.1 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; Golgi apparatus; nuclear chromatin; nucleosome; nucleus; actin cytoskeleton Molecular Function:protein binding; chromatin DNA binding Biological Process: nucleosome assembly; apoptosis; DNA fragmentation during apoptosis; cell structure disassembly during apoptosis |
| NCBI Summary: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H1 family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P07305 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 121897 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3005 |
| NCBI Accession: | P07305.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P07305,Q6FG88, Q8N6R3, B2R6I0, B4DRD6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P07305 |
| Molecular Weight: | 194 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Histone H1.0 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | H1 histone family, member 0 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | H1F0 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | H10; H1FV |
| NCBI Protein Information: | histone H1.0; histone H1'; histone H1(0); H1.0, H1(0), H1-0 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Histone H1.0 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Histone H1'; Histone H1(0)Histone H1.0, N-terminally processed |
| Protein Family: | Histone |
| UniProt Gene Name: | H1F0 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | H10_HUMAN |
View AllClose



![Anti-Histone H1.0 Antibody (CAB3298)[KO Validated] Anti-Histone H1.0 Antibody (CAB3298)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/45366/50110/anti-histone-h1.0-antibody-cab3298ko-validated__71862__96199.1706524349.jpg?c=1)


