Signal Transduction Antibodies 2
Anti-GSTM3 Antibody (CAB3905)
- SKU:
- CAB3905
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-GSTM3 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB3905 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 101-225 of human GSTM3 (NP_000840.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
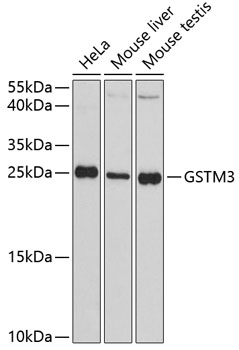
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, Mouse liver, Mouse testis |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 101-225 of human GSTM3 (NP_000840.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | VDII ENQV MDFR TQLI RLCY SSDH EKLK PQYL EELP GQLK QFSM FLGK FSWF AGEK LTFV DFLT YDIL DQNR IFDP KCLD EFPN LKAF MCRF EALE KIAA YLQS DQFC KMPI NNKM AQWG NKPV C |
| Gene ID: | 2947 |
| Uniprot: | P21266 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm |
| Calculated MW: | 26kDa |
| Observed MW: | 25kDa |
| Synonyms: | GSTM3, GST5, GSTB, GSTM3-3, GTM3 |
| Background: | Cytosolic and membrane-bound forms of glutathione S-transferase are encoded by two distinct supergene families. At present, eight distinct classes of the soluble cytoplasmic mammalian glutathione S-transferases have been identified: alpha, kappa, mu, omega, pi, sigma, theta and zeta. This gene encodes a glutathione S-transferase that belongs to the mu class. The mu class of enzymes functions in the detoxification of electrophilic compounds, including carcinogens, therapeutic drugs, environmental toxins and products of oxidative stress, by conjugation with glutathione. The genes encoding the mu class of enzymes are organized in a gene cluster on chromosome 1p13.3 and are known to be highly polymorphic. These genetic variations can change an individual's susceptibility to carcinogens and toxins as well as affect the toxicity and efficacy of certain drugs. Mutations of this class mu gene have been linked with a slight increase in a number of cancers, likely due to exposure with environmental toxins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | GSTM3: Conjugation of reduced glutathione to a wide number of exogenous and endogenous hydrophobic electrophiles. May govern uptake and detoxification of both endogenous compounds and xenobiotics at the testis and brain blood barriers. Belongs to the GST superfamily. Mu family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Transferase; Other Amino Acids Metabolism - glutathione; Xenobiotic Metabolism - drug metabolism - cytochrome P450; Cell development/differentiation; Xenobiotic Metabolism - metabolism by cytochrome P450; EC 2.5.1.18 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p13.3 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; cytosol; nucleus Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein homodimerization activity; enzyme binding; glutathione binding; glutathione transferase activity Biological Process: glutathione metabolic process; establishment of blood-nerve barrier; nitrobenzene metabolic process; response to estrogen stimulus; xenobiotic metabolic process; xenobiotic catabolic process |
| NCBI Summary: | Cytosolic and membrane-bound forms of glutathione S-transferase are encoded by two distinct supergene families. At present, eight distinct classes of the soluble cytoplasmic mammalian glutathione S-transferases have been identified: alpha, kappa, mu, omega, pi, sigma, theta and zeta. This gene encodes a glutathione S-transferase that belongs to the mu class. The mu class of enzymes functions in the detoxification of electrophilic compounds, including carcinogens, therapeutic drugs, environmental toxins and products of oxidative stress, by conjugation with glutathione. The genes encoding the mu class of enzymes are organized in a gene cluster on chromosome 1p13.3 and are known to be highly polymorphic. These genetic variations can change an individual's susceptibility to carcinogens and toxins as well as affect the toxicity and efficacy of certain drugs. Mutations of this class mu gene have been linked with a slight increase in a number of cancers, likely due to exposure with environmental toxins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P21266 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 21264423 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2947 |
| NCBI Accession: | P21266.3 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P21266 |
| Molecular Weight: | 27kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | glutathione S-transferase mu 3 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GSTM3 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | GST5; GSTB; GTM3; GSTM3-3 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | glutathione S-transferase Mu 3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 3 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | GST class-mu 3; GSTM3-3; hGSTM3-3 |
| Protein Family: | Glutathione S-transferase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GSTM3 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | GSTM3_HUMAN |
View AllClose