Signal Transduction Antibodies 1
Anti-GRIN2C Antibody (CAB14241)
- SKU:
- CAB14241
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-GRIN2C Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB14241 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
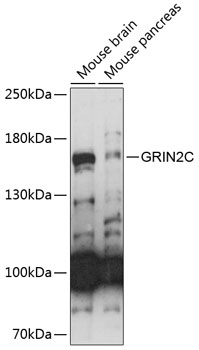
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 20-350 of human GRIN2C (NP_000826.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:1000 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse brain, Mouse pancreas |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 20-350 of human GRIN2C (NP_000826.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | GLGP GQGE QGMT VAVV FSSS GPPQ AQFR ARLT PQSF LDLP LEIQ PLTV GVNT TNPS SLLT QICG LLGA AHVH GIVF EDNV DTEA VAQI LDFI SSQT HVPI LSIS GGSA VVLT PKEP GSAF LQLG VSLE QQLQ VLFK VLEE YDWS AFAV ITSL HPGH ALFL EGVR AVAD ASHV SWRL LDVV TLEL GPGG PRAR TQRL LRQL DAPV FVAY CSRE EAEV LFAE AAQA GLVG PGHV WLVP NLAL GSTD APPA TFPV GLIS VVTE SWRL SLRQ KVRD GVAI LALG AHSY WRQH GTLP APAG DCRV HPGP VSPA REAF YRHL LNVT WEGR DFSF SPG |
| Gene ID: | 2905 |
| Uniprot: | Q14957 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell junction, Cell membrane, Multi-pass membrane protein, postsynaptic cell membrane, synapse |
| Calculated MW: | 134kDa |
| Observed MW: | 134kDa |
| Synonyms: | GRIN2C, GluN2C, NMDAR2C, NR2C, NMDA 2C |
| Background: | This gene encodes a subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, which is a subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptor. NMDA receptors are found in the central nervous system, are permeable to cations and have an important role in physiological processes such as learning, memory, and synaptic development. The receptor is a tetramer of different subunits (typically heterodimer of subunit 1 with one or more of subunits 2A-D), forming a channel that is permeable to calcium, potassium, and sodium, and whose properties are determined by subunit composition. Alterations in the subunit composition of the receptor are associated with pathophysiological conditions such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, depression, and schizophrenia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NMDAR2C: NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. Belongs to the glutamate-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.10.1) family. NR2C/GRIN2C subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, multi-pass; Membrane protein, integral; Channel, calcium; Channel, ligand-gated Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q25.1 Cellular Component: postsynaptic membrane; integral to plasma membrane; postsynaptic density; dendrite; plasma membrane; cell junction; N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor complex Molecular Function:protein binding; extracellular-glutamate-gated ion channel activity; N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor activity; protein N-terminus binding; cation channel activity; PDZ domain binding Biological Process: synaptic transmission; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic; protein localization; transport; directional locomotion; glutamate signaling pathway; ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway; response to wounding; regulation of excitatory postsynaptic membrane potential; neuromuscular process controlling balance; negative regulation of protein catabolic process |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, which is a subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptor. NMDA receptors are found in the central nervous system, are permeable to cations and have an important role in physiological processes such as learning, memory, and synaptic development. The receptor is a tetramer of different subunits (typically heterodimer of subunit 1 with one or more of subunits 2A-D), forming a channel that is permeable to calcium, potassium, and sodium, and whose properties are determined by subunit composition. Alterations in the subunit composition of the receptor are associated with pathophysiological conditions such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, depression, and schizophrenia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013] |
| UniProt Code: | Q14957 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 55770854 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2905 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_000826.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q14957,B2RTT1, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q14957 |
| Molecular Weight: | 134,209 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2C isoform 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2C |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GRIN2C |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | NR2C; GluN2C; NMDAR2C |
| NCBI Protein Information: | glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2C; N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2C; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2C; glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2C |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-3; N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2C |
| Protein Family: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GRIN2C |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NMDE3_HUMAN |