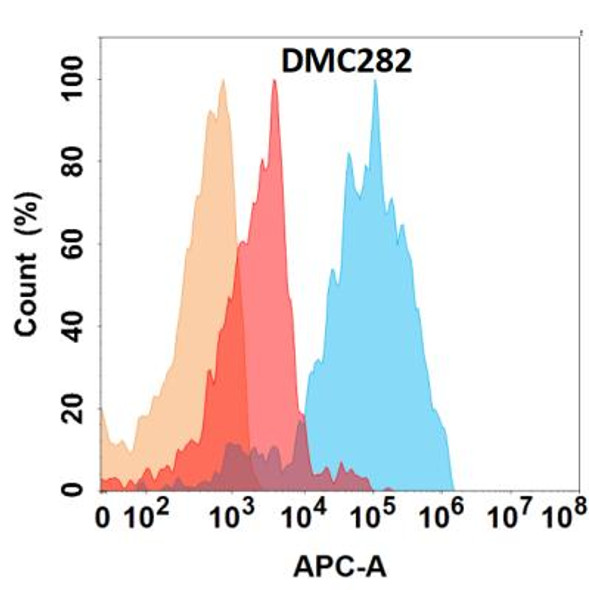
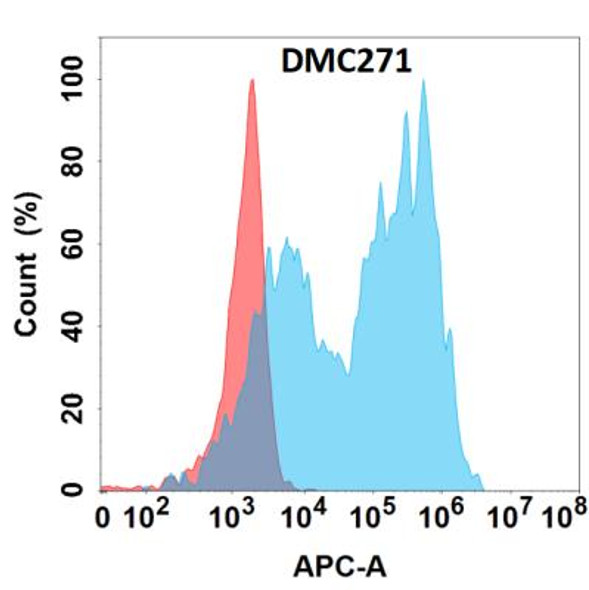
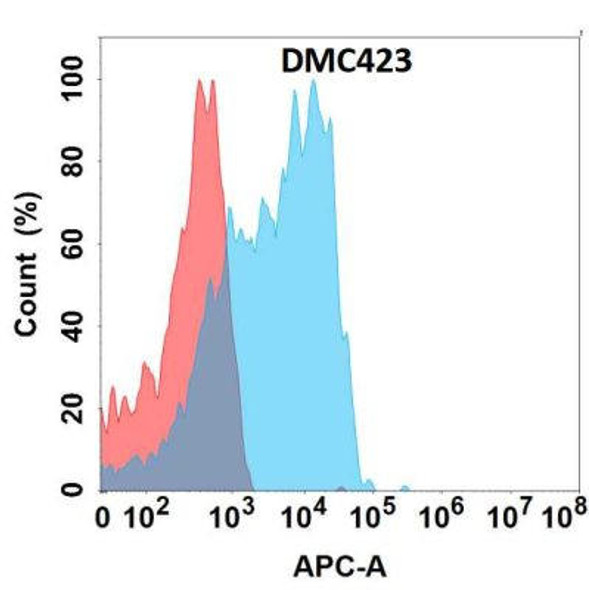
| Background: | Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to and inhibit the dipeptidyl peptidase activity of CD26, and it can induce apoptosis in certain cell types. Deletion mutations in this gene are associated with Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome, also known as Simpson dysmorphia syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009] References: Fu Ying,Urban Daniel J,Nani Roger R et al. Glypican-3-Specific Antibody Drug Conjugates Targeting Hepatocellular Carcinoma.[J] .Hepatology, 2019, 70: 563-576. Zhang Yi-Fan,Ho Mitchell,Humanization of high-affinity antibodies targeting glypican-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. |