Signal Transduction Antibodies 3
Anti-GLUT1 Antibody (CAB11727)
- SKU:
- CAB11727
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-GLUT1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB11727 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
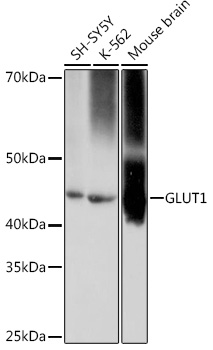
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human GLUT1 |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | SH-SY5Y, K-562, Mouse brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human GLUT1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 6513 |
| Uniprot: | P11166 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 54kDa |
| Observed MW: | 45kd |
| Synonyms: | CSE, DYT17, DYT18, DYT9, EIG12, GLUT, GLUT-1, GLUT1, GLUT1DS, HTLVR, PED, SDCHCN |
| Background: | This gene encodes a major glucose transporter in the mammalian blood-brain barrier. The encoded protein is found primarily in the cell membrane and on the cell surface, where it can also function as a receptor for human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) I and II. Mutations in this gene have been found in a family with paroxysmal exertion-induced dyskinesia. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2013] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | GLUT1: an integral membrane protein that plays an important role in the glycolytic pathway by serving as a uniporter for glucose. One of 13 members of the human equilibrative glucose transport protein family. Transports a wide range of aldoses, including both pentoses and hexoses, and dehydroascorbic acid. Shown to transport water against an osmotic gradient. A receptor for the Human T-cell Leukemia virus (HTLV). Plays a role in the constitutive or basal uptake of glucose. Expressed at highest levels in proliferating cells of the early developing embryo, cells forming the blood tissue barriers, in human erythrocytes, astrocytes and in cardiac muscle. GLUT1 and GLUT3 are both essential for normal embryonic development. Is practically the only member of the GLUT family expressed on human red blood cells, where it comprises 10 - 20% of the integral membrane protein content. Several glycolytic proteins including the transporters GLUT1 and GLUT3, as well as multiple enzymes including HK2, PFKL, LDHA, ALDOA, ALDOC, PGK1, ENO1, PKM2, CA9 and PFKFB3 are induced in cancer cells by HIF-1 alpha. Polyps from Peutz-Jeghers patients exhibit up-regulated mTORC1 signaling, HIF-1alpha, and GLUT1 levels. Defects in GLUT1 are the cause of autosomal dominant GLUT1 deficiency syndrome, a blood-brain barrier glucose transport defect characterized by infantile seizures, delayed development, and acquired microcephaly. Defects also cause dystonia type 18, an exercise-induced paroxysmal dystonia/dyskinesia. Cytochalasin B binds to its inner surface, inhibiting its glucose transport activity with an IC50 of 0.44 uM. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, integral; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Transporter; Transporter, SLC family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p34.2 Cellular Component: cortical actin cytoskeleton; Golgi membrane; integral to plasma membrane; membrane; midbody; plasma membrane Molecular Function:D-glucose transmembrane transporter activity; dehydroascorbic acid transporter activity; glucose transmembrane transporter activity; identical protein binding; protein binding; protein self-association Biological Process: glucose transport; L-ascorbic acid metabolic process; lactose biosynthetic process; protein complex assembly; regulation of insulin secretion Disease: Stomatin-deficient Cryohydrocytosis With Neurologic Defects |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a major glucose transporter in the mammalian blood-brain barrier. The encoded protein is found primarily in the cell membrane and on the cell surface, where it can also function as a receptor for human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) I and II. Mutations in this gene have been found in a family with paroxysmal exertion-induced dyskinesia. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2013] |
| UniProt Code: | P11166 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 115502394 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6513 |
| NCBI Accession: | P11166.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P11166,O75535, Q147X2, A8K9S6, B2R620, D3DPX0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P11166 |
| Molecular Weight: | 54,084 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | solute carrier family 2 member 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SLC2A1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CSE; PED; DYT9; GLUT; DYT17; DYT18; EIG12; GLUT1; HTLVR; GLUT-1; SDCHCN; GLUT1DS |
| NCBI Protein Information: | solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Glucose transporter type 1, erythrocyte/brain; GLUT-1; HepG2 glucose transporter |
| Protein Family: | Glucose transporter |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SLC2A1 |