Cardiovascular Antibodies
Anti-FAK Antibody (CAB0024)
- SKU:
- CAB0024
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cardiovascular
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-FAK Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB0024 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human FAK |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
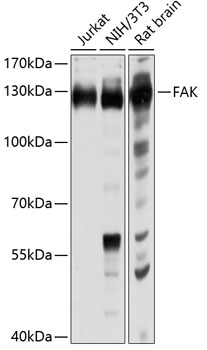
| Positive Samples: | Jurkat, NIH/3T3, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human FAK |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 5747 |
| Uniprot: | Q05397 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell junction, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Cytoplasmic side, Nucleus, Peripheral membrane protein, cell cortex, centrosome, cytoskeleton, focal adhesion, microtubule organizing center |
| Calculated MW: | 39kDa/48kDa/63kDa/99kDa/114kDa/119kDa/120kDa |
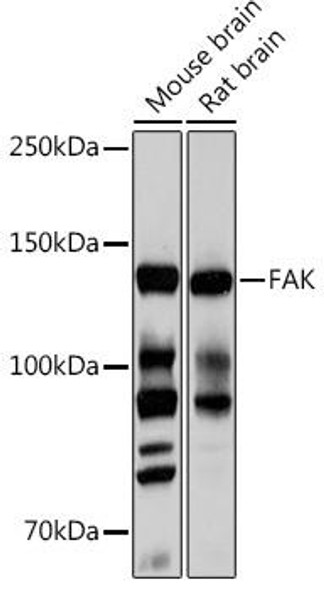
| Observed MW: | 130kDa |
| Synonyms: | FADK, FAK, FAK1, FRNK, PPP1R71, p125FAK, pp125FAK, PTK2 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase which is found concentrated in the focal adhesions that form between cells growing in the presence of extracellular matrix constituents. The encoded protein is a member of the FAK subfamily of protein tyrosine kinases but lacks significant sequence similarity to kinases from other subfamilies. Activation of this gene may be an important early step in cell growth and intracellular signal transduction pathways triggered in response to certain neural peptides or to cell interactions with the extracellular matrix. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | FAK: a tyrosine kinase of the FAK family required for cell migration and contact-dependent survival signaling. Activated by tyrosine-phosphorylation in response to either integrin clustering induced by cell adhesion or antibody cross-linking, or via G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) occupancy by ligands such as bombesin or lysophosphatidic acid, or via LDL receptor occupancy. Downstream of integrins and Src, upstream of Ras/MAPK. Localizes to focal adhesions that form between cells growing in the presence of extracellular matrix constituents. Interacts with CAS family members and with GIT1, SORBS1 and BCAR3. Interacts with Shb. Required for full Ras transformation of fibroblasts. Increased expression in breast and other cancers, related to chromosome 8q amplification. Overexpression and activation associated with increased migration, invasion and progression of ovarian cancer, and with progression in hepatocellular carcinoma, thyroid cancer, and acute myelogenous leukemia. siRNA increases chemosensitivity of pancreatic adenocarcinoma xenografts. Inhibitor: ISI15421 (antisense). Four splice-variant isoforms have been observed. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Kinase, protein; Protein kinase, tyrosine (non-receptor); EC 2.7.10.2; Protein kinase, TK; TK group; Fak family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8q24.3 Cellular Component: extrinsic to internal side of plasma membrane; cytoskeleton; focal adhesion; lamellipodium; apical plasma membrane; cytoplasm; stress fiber; plasma membrane; microtubule organizing center; cell cortex; cytosol; nucleus Molecular Function:JUN kinase binding; signal transducer activity; protein binding; protein-tyrosine kinase activity; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity; SH2 domain binding; actin binding; protein kinase binding; ATP binding; protein kinase activity; receptor binding Biological Process: heart morphogenesis; axon guidance; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; establishment of nucleus localization; apoptosis; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; neuron migration; cell motility involved in cell locomotion; negative regulation of synaptogenesis; regulation of cell shape; regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of cell proliferation; ephrin receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of axonogenesis; angiogenesis; vasculogenesis; placenta development; cell structure disassembly during apoptosis; integrin-mediated signaling pathway; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; platelet activation; central nervous system neuron axonogenesis; regulation of osteoblast differentiation; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity; signal complex assembly; cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; microtubule cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; negative regulation of organ growth; regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; embryonic development; establishment of cell polarity; positive regulation of protein kinase activity; regulation of focal adhesion formation; endothelial cell migration; innate immune response; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion; blood coagulation; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; regulation of cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; negative regulation of apoptosis; positive regulation of cell migration |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase which is found concentrated in the focal adhesions that form between cells growing in the presence of extracellular matrix constituents. The encoded protein is a member of the FAK subfamily of protein tyrosine kinases but lacks significant sequence similarity to kinases from other subfamilies. Activation of this gene may be an important early step in cell growth and intracellular signal transduction pathways triggered in response to certain neural peptides or to cell interactions with the extracellular matrix. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene, but the full-length natures of only three of them have been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | Q05397 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 3183518 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5747 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q05397.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q05397,Q14291, Q8IYN9, Q9UD85, B4E2N6, F5H4S4, J3QT16 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q05397 |
| Molecular Weight: | 1052 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Focal adhesion kinase 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | protein tyrosine kinase 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PTK2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FAK; FADK; FAK1; FRNK; PPP1R71; p125FAK; pp125FAK |
| NCBI Protein Information: | focal adhesion kinase 1; FADK 1; PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2; FAK-related non-kinase polypeptide; focal adhesion kinase isoform FAK-Del33; focal adhesion kinase-related nonkinase; protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 71; protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 71 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Focal adhesion kinase 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Focal adhesion kinase-related nonkinase; FRNK; Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 71; PPP1R71; Protein-tyrosine kinase 2; p125FAK; pp125FAK |
| Protein Family: | Focal adhesion kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PTK2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FAK1_HUMAN |