Developmental Biology
Anti-EFNB3 Antibody (CAB2916)
- SKU:
- CAB2916
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Developmental Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-EFNB3 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB2916 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
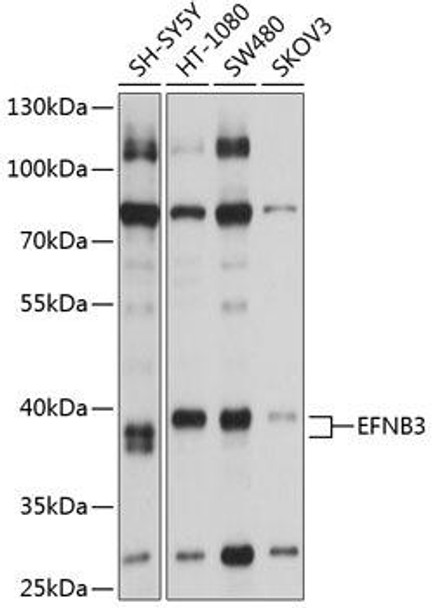
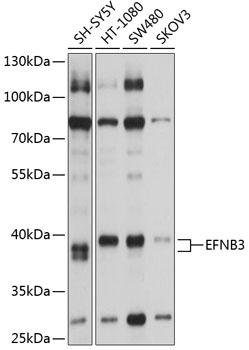
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 28-226 of human EFNB3 (NP_001397.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:1000 - 1:4000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | SH-SY5Y, HT-1080, SW480, SKOV3 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 28-226 of human EFNB3 (NP_001397.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | LSLE PVYW NSAN KRFQ AEGG YVLY PQIG DRLD LLCP RARP PGPH SSPN YEFY KLYL VGGA QGRR CEAP PAPN LLLT CDRP DLDL RFTI KFQE YSPN LWGH EFRS HHDY YIIA TSDG TREG LESL QGGV CLTR GMKV LLRV GQSP RGGA VPRK PVSE MPME RDRG AAHS LEPG KENL PGDP TSNA TSRG AEGP LPPP SMP |
| Gene ID: | 1949 |
| Uniprot: | Q15768 |
| Cellular Location: | Membrane, Single-pass type I membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 35kDa |
| Observed MW: | 36kDa |
| Synonyms: | EFNB3, EFL6, EPLG8, LERK8, ephrin-B3 |
| Background: | EFNB3, a member of the ephrin gene family, is important in brain development as well as in its maintenance. Moreover, since levels of EFNB3 expression were particularly high in several forebrain subregions compared to other brain subregions, it may play a pivotal role in forebrain function. The EPH and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. EPH Receptors typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. The ephrin ligands and receptors have been named by the Eph Nomenclature Committee (1997). Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are similarly divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | EFNB3: Cell surface transmembrane ligand for Eph receptors, a family of receptor tyrosine kinases which are crucial for migration, repulsion and adhesion during neuronal, vascular and epithelial development. Binds promiscuously Eph receptors residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. May play a pivotal role in forebrain function. Binds to, and induce the collapse of, commissural axons/growth cones in vitro. May play a role in constraining the orientation of longitudinally projecting axons. Belongs to the ephrin family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Ligand, receptor tyrosine kinase; Cell development/differentiation; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17p13.1 Cellular Component: integral to plasma membrane; plasma membrane Molecular Function:transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity; ephrin receptor binding Biological Process: axon guidance; nervous system development; viral reproduction; cell-cell signaling; axon choice point recognition; ephrin receptor signaling pathway; adult walking behavior |
| NCBI Summary: | EFNB3, a member of the ephrin gene family, is important in brain development as well as in its maintenance. Moreover, since levels of EFNB3 expression were particularly high in several forebrain subregions compared to other brain subregions, it may play a pivotal role in forebrain function. The EPH and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. EPH Receptors typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. The ephrin ligands and receptors have been named by the Eph Nomenclature Committee (1997). Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are similarly divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q15768 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 2494367 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1949 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q15768.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q15768,O00680, Q8TBH7, Q92875, B2RBW2, D3DTQ6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q15768 |
| Molecular Weight: | 340 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Ephrin-B3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ephrin-B3 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | EFNB3 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | EFL6; EPLG8; LERK8 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ephrin-B3; Ephrin B3; eph-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 8; EPH-related receptor transmembrane ligand ELK-L3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Ephrin-B3 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | EPH-related receptor transmembrane ligand ELK-L3; EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 8; LERK-8 |
| Protein Family: | Ephrin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | EFNB3 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | EFNB3_HUMAN |
View AllClose