Cardiovascular Antibodies
Anti-ECM1 Antibody (CAB16368)
- SKU:
- CAB16368
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cardiovascular
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ECM1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16368 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
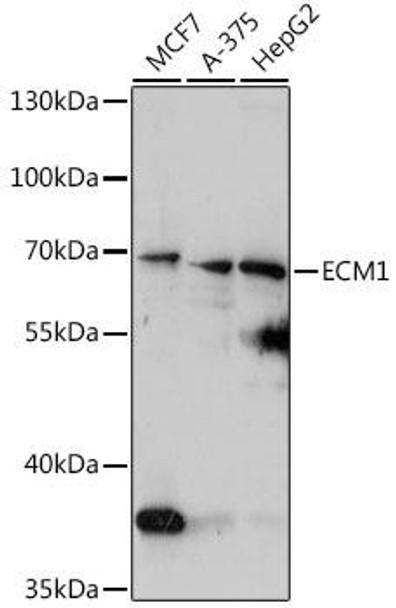
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 150-250 of human ECM1 (NP_001189787.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | MCF7, A-375, HepG2 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 150-250 of human ECM1 (NP_001189787.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | PNEQ KEGT PAPF GDQS HPEP ESWN AAQH CQQD RSQG GWGH RLDG FPPG RPSP DNLN QICL PNRQ HVVY GPWN LPQS SYSH LTRQ GETL NFLE IGYS RCCH C |
| Gene ID: | 1893 |
| Uniprot: | Q16610 |
| Cellular Location: | Secreted, extracellular matrix, extracellular space |
| Calculated MW: | 19kDa/46kDa/60kDa/63kDa |
| Observed MW: | 61kDa |
| Synonyms: | ECM1, URBWD |
| Background: | This gene encodes a soluble protein that is involved in endochondral bone formation, angiogenesis, and tumor biology. It also interacts with a variety of extracellular and structural proteins, contributing to the maintenance of skin integrity and homeostasis. Mutations in this gene are associated with lipoid proteinosis disorder (also known as hyalinosis cutis et mucosae or Urbach-Wiethe disease) that is characterized by generalized thickening of skin, mucosae and certain viscera. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ECM1: Involved in endochondral bone formation as negative regulator of bone mineralization. Stimulates the proliferation of endothelial cells and promotes angiogenesis. Inhibits MMP9 proteolytic activity. Defects in ECM1 are the cause of lipoid proteinosis (LiP); also known as lipoid proteinosis of Urbach and Wiethe or hyalinosis cutis et mucosae. LiP is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by generalized thickening of skin, mucosae and certain viscera. Classical features include beaded eyelid papules and laryngeal infiltration leading to hoarseness. Histologically, there is widespread deposition of hyaline material and disruption/reduplication of basement membrane. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted, signal peptide; Secreted Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1q21 Cellular Component: extracellular matrix; proteinaceous extracellular matrix; extracellular space Molecular Function:protein C-terminus binding; signal transducer activity; protein binding; enzyme binding; protease binding; interleukin-2 receptor binding; laminin binding Biological Process: ossification; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; negative regulation of peptidase activity; signal transduction; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of bone mineralization; positive regulation of angiogenesis; biomineral formation; negative regulation of cytokine and chemokine mediated signaling pathway; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation; angiogenesis; regulation of T-helper 2 type immune response; inflammatory response Disease: Lipoid Proteinosis Of Urbach And Wiethe |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a soluble protein that is involved in endochondral bone formation, angiogenesis, and tumor biology. It also interacts with a variety of extracellular and structural proteins, contributing to the maintenance of skin integrity and homeostasis. Mutations in this gene are associated with lipoid proteinosis disorder (also known as hyalinosis cutis et mucosae or Urbach-Wiethe disease) that is characterized by generalized thickening of skin, mucosae and certain viscera. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | Q16610 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 48429255 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1893 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q16610.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q16610,O43266, Q5T5G4, Q5T5G5, Q5T5G6, Q8IZ60, A8K8S0 B4DW49, B4DY60, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q16610 |
| Molecular Weight: | Observed MW: 55kDaCalculated MW: 19kDa, 46kDa, 60kDa, 63kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Extracellular matrix protein 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | extracellular matrix protein 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ECM1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | URBWD |
| NCBI Protein Information: | extracellular matrix protein 1; secretory component p85 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Extracellular matrix protein 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Secretory component p85 |
| Protein Family: | Extracellular matrix protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ECM1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ECM1_HUMAN |