Signal Transduction Antibodies 2
Anti-DMP1 Antibody (CAB16832)
- SKU:
- CAB16832
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-DMP1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16832 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
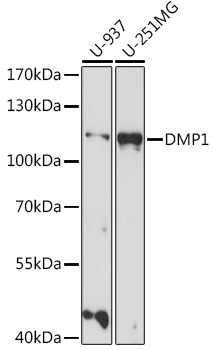
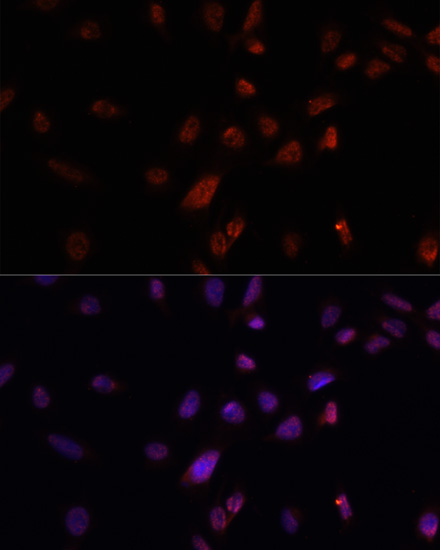
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-100 of human DMP1 (NP_004398.1). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | U-937, U-251MG |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-100 of human DMP1 (NP_004398.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MKIS ILLM FLWG LSCA LPVT RYQN NESE DSEE WKGH LAQA PTPP LESS ESSE GSKV SSEE QANE DPSD STQS EEGL GSDD HQYI YRLA GGFS RSTG KGGD |
| Gene ID: | 1758 |
| Uniprot: | Q13316 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Secreted, extracellular matrix, extracellular space |
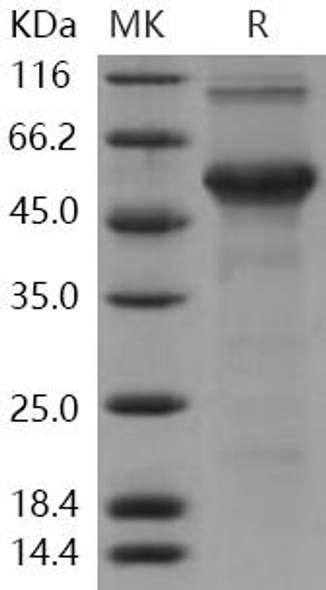
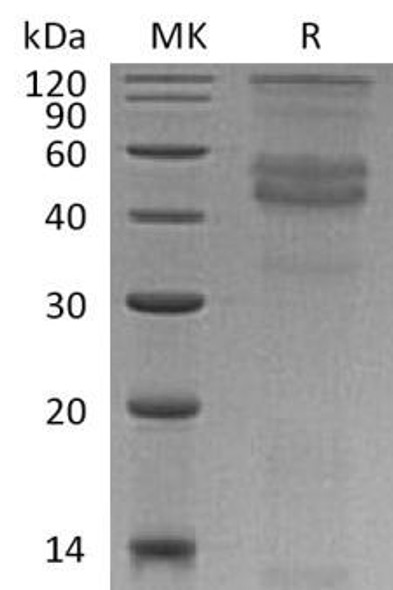
| Calculated MW: | 54kDa/55kDa |
| Observed MW: | 110kDa |
| Synonyms: | DMP1, ARHP, ARHR, DMP-1 |
| Background: | Dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein is an extracellular matrix protein and a member of the small integrin binding ligand N-linked glycoprotein family. This protein, which is critical for proper mineralization of bone and dentin, is present in diverse cells of bone and tooth tissues. The protein contains a large number of acidic domains, multiple phosphorylation sites, a functional arg-gly-asp cell attachment sequence, and a DNA binding domain. In undifferentiated osteoblasts it is primarily a nuclear protein that regulates the expression of osteoblast-specific genes. During osteoblast maturation the protein becomes phosphorylated and is exported to the extracellular matrix, where it orchestrates mineralized matrix formation. Mutations in the gene are known to cause autosomal recessive hypophosphatemia, a disease that manifests as rickets and osteomalacia. The gene structure is conserved in mammals. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | DMP1: May have a dual function during osteoblast differentiation. In the nucleus of undifferentiated osteoblasts, unphosphorylated form acts as a transcriptional component for activation of osteoblast-specific genes like osteocalcin. During the osteoblast to osteocyte transition phase it is phosphorylated and exported into the extracellular matrix, where it regulates nucleation of hydroxyapatite. Defects in DMP1 are the cause of rickets hypophosphatemic autosomal recessive type 1 (ARHR1). A hereditary form of hypophosphatemic rickets, a disorder of proximal renal tubule function that causes phosphate loss, hypophosphatemia and skeletal deformities, including rickets and osteomalacia unresponsive to vitamin D. Symptoms are bone pain, fractures and growth abnormalities. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Secreted, signal peptide Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 4q22.1 Cellular Component: extracellular region Molecular Function:calcium ion binding; integrin binding Biological Process: extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis Disease: Hypophosphatemic Rickets, Autosomal Recessive, 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | Dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein is an extracellular matrix protein and a member of the small integrin binding ligand N-linked glycoprotein family. This protein, which is critical for proper mineralization of bone and dentin, is present in diverse cells of bone and tooth tissues. The protein contains a large number of acidic domains, multiple phosphorylation sites, a functional arg-gly-asp cell attachment sequence, and a DNA binding domain. In undifferentiated osteoblasts it is primarily a nuclear protein that regulates the expression of osteoblast-specific genes. During osteoblast maturation the protein becomes phosphorylated and is exported to the extracellular matrix, where it orchestrates mineralized matrix formation. Mutations in the gene are known to cause autosomal recessive hypophosphatemia, a disease that manifests as rickets and osteomalacia. The gene structure is conserved in mammals. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q13316 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 7673998 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1758 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q13316.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q13316,O43265, A1L4L3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q13316 |
| Molecular Weight: | 56kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | DMP1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ARHP; ARHR; DMP-1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein 1 |
| Protein Family: | Dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | DMP1 |
View AllClose