Cell Biology Antibodies 16
Anti-DIAPH1 Antibody (CAB11596)
- SKU:
- CAB11596
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-DIAPH1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB11596 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human DIAPH1 |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
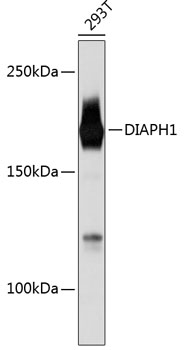
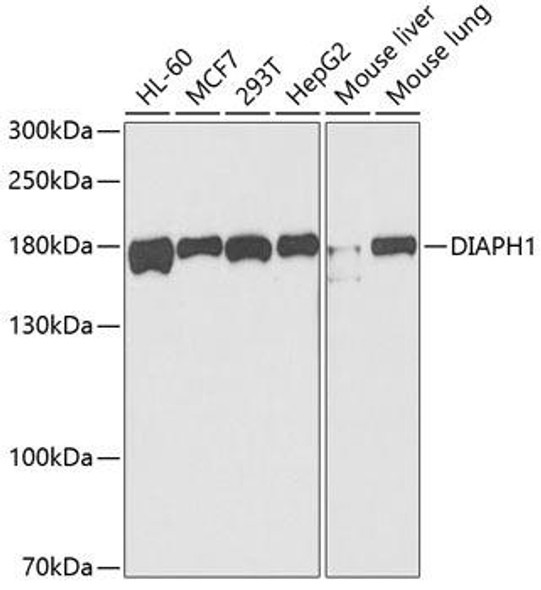
| Positive Samples: | 293T, Mouse lung, Rat testis |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human DIAPH1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1729 |
| Uniprot: | O60610 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 155kDa |
| Observed MW: | 160KDa |
| Synonyms: | DFNA1, DIA1, DRF1, LFHL1, SCBMS, hDIA1 |
| Background: | This gene is a homolog of the Drosophila diaphanous gene, and has been linked to autosomal dominant, fully penetrant, nonsyndromic sensorineural progressive low-frequency hearing loss. Actin polymerization involves proteins known to interact with diaphanous protein in Drosophila and mouse. It has therefore been speculated that this gene may have a role in the regulation of actin polymerization in hair cells of the inner ear. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Diaphanous-1: Acts in a Rho-dependent manner to recruit PFY1 to the membrane. Required for the assembly of F-actin structures, such as actin cables and stress fibers. Nucleates actin filaments. Binds to the barbed end of the actin filament and slows down actin polymerization and depolymerization. Required for cytokinesis, and transcriptional activation of the serum response factor. DFR proteins couple Rho and Src tyrosine kinase during signaling and the regulation of actin dynamics. Functions as a scaffold protein for MAPRE1 and APC to stabilize microtubules and promote cell migration. Has neurite outgrowth promoting activity. In hear cells, it may play a role in the regulation of actin polymerization in hair cells. The MEMO1-RHOA- DIAPH1 signaling pathway plays an important role in ERBB2- dependent stabilization of microtubules at the cell cortex. It controls the localization of APC and CLASP2 to the cell membrane, via the regulation of GSK3B activity. In turn, membrane-bound APC allows the localization of the MACF1 to the cell membrane, which is required for microtubule capture and stabilization. Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. Required in the control of cell shape. Homodimer. Interacts with the GTP-bound form of RHOA. Interacts with RHOC, PFY1, MAPRE1, BAIAP2 and APC. Interacts with SCAI. Interacts with DCAF7, via FH2 domain. Interacts with NCDN. Expressed in brain, heart, placenta, lung, kidney, pancreas, liver, skeletal muscle and cochlea. Belongs to the formin homology family. Diaphanous subfamily. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Actin-binding; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Adaptor/scaffold Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 5q31 Cellular Component: neuron projection; cytoplasm Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein binding; Rho GTPase binding; actin binding; profilin binding; receptor binding Biological Process: regulation of cell shape; regulation of microtubule-based process; sensory perception of sound; actin filament polymerization; cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol; neurite development; positive regulation of cell migration Disease: Deafness, Autosomal Dominant 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a homolog of the Drosophila diaphanous gene, and has been linked to autosomal dominant, fully penetrant, nonsyndromic sensorineural progressive low-frequency hearing loss. Actin polymerization involves proteins known to interact with diaphanous protein in Drosophila and mouse. It has therefore been speculated that this gene may have a role in the regulation of actin polymerization in hair cells of the inner ear. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O60610 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 215273970 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1729 |
| NCBI Accession: | O60610.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O60610,Q17RN4, Q59FH8, Q9UC76, A6NF18, B7ZKW2, E9PEZ2 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O60610 |
| Molecular Weight: | 1272 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Protein diaphanous homolog 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | diaphanous-related formin 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | DIAPH1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DIA1; DRF1; DFNA1; LFHL1; hDIA1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | protein diaphanous homolog 1; diaphanous-related formin-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Protein diaphanous homolog 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Diaphanous-related formin-1; DRF1 |
| Protein Family: | Protein diaphanous |
| UniProt Gene Name: | DIAPH1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DIAP1_HUMAN |


![Anti-DIAPH1 Antibody (CAB18081)[KO Validated] Anti-DIAPH1 Antibody (CAB18081)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/55222/59965/anti-diaph1-antibody-cab18081ko-validated__95979__33521.1706529207.jpg?c=1)


