Signal Transduction Antibodies 3
Anti-CRYBB2 Antibody (CAB5573)
- SKU:
- CAB5573
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CRYBB2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB5573 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
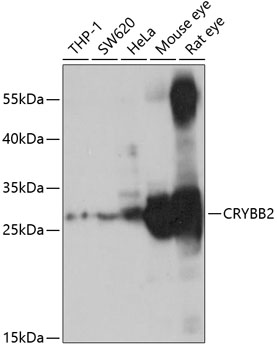
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-205 of human CRYBB2 (NP_000487.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | THP-1, SW620, HeLa, Mouse eye, Rat eye |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-205 of human CRYBB2 (NP_000487.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MASD HQTQ AGKP QSLN PKII IFEQ ENFQ GHSH ELNG PCPN LKET GVEK AGSV LVQA GPWV GYEQ ANCK GEQF VFEK GEYP RWDS WTSS RRTD SLSS LRPI KVDS QEHK IILY ENPN FTGK KMEI IDDD VPSF HAHG YQEK VSSV RVQS GTWV GYQY PGYR GLQY LLEK GDYK DSSD FGAP HPQV QSVR RIRD MQWH QRGA FHPS N |
| Gene ID: | 1415 |
| Uniprot: | P43320 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 23kDa |
| Observed MW: | 27kDa |
| Synonyms: | CRYBB2, CCA2, CRYB2, CRYB2A, CTRCT3, D22S665 |
| Background: | Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Beta-crystallins, the most heterogeneous, differ by the presence of the C-terminal extension (present in the basic group, none in the acidic group). Beta-crystallins form aggregates of different sizes and are able to self-associate to form dimers or to form heterodimers with other beta-crystallins. This gene, a beta basic group member, is part of a gene cluster with beta-A4, beta-B1, and beta-B3. A chain-terminating mutation was found to cause type 2 cerulean cataracts. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CRYBB2: a major structural protein of the eye lens. A member of the beta/gamma-crystallin family. Defects are the cause of congenital cerulean type 2 cataract, sutural cataract with punctate and cerulean opacities, and Coppock-like cataract. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 22q11.23 Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein homodimerization activity; structural molecule activity; structural constituent of eye lens Biological Process: camera-type eye development; visual perception; response to stimulus Disease: Cataract 3, Multiple Types |
| NCBI Summary: | Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Beta-crystallins, the most heterogeneous, differ by the presence of the C-terminal extension (present in the basic group, none in the acidic group). Beta-crystallins form aggregates of different sizes and are able to self-associate to form dimers or to form heterodimers with other beta-crystallins. This gene, a beta basic group member, is part of a gene cluster with beta-A4, beta-B1, and beta-B3. A chain-terminating mutation was found to cause type 2 cerulean cataracts. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P43320 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1169091 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1415 |
| NCBI Accession: | P43320.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P43320,Q9UCM8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P43320 |
| Molecular Weight: | 205 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Beta-crystallin B2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | crystallin, beta B2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CRYBB2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CCA2; CRYB2; CRYB2A; CTRCT3; D22S665 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | beta-crystallin B2; beta-B2 crystallin; beta-crystallin Bp; eye lens structural protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Beta-crystallin B2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Beta-B2 crystallin; Beta-crystallin Bp |
| Protein Family: | Beta-crystallin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CRYBB2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CRBB2_HUMAN |
View AllClose