Neuroscience
Anti-CRYBA1 Antibody (CAB15267)
- SKU:
- CAB15267
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Neuroscience
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CRYBA1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB15267 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
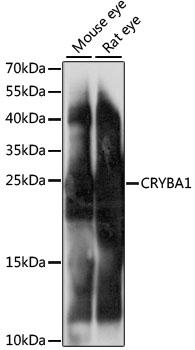
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-215 of human CRYBA1 (NP_005199.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:200 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse eye, Rat eye |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-215 of human CRYBA1 (NP_005199.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | METQ AEQQ ELET LPTT KMAQ TNPT PGSL GPWK ITIY DQEN FQGK RMEF TSSC PNVS ERSF DNVR SLKV ESGA WIGY EHTS FCGQ QFIL ERGE YPRW DAWS GSNA YHIE RLMS FRPI CSAN HKES KMTI FEKE NFIG RQWE ISDD YPSL QAMG WFNN EVGS MKIQ SGAW VCYQ YPGY RGYQ YILE CDHH GGDY KHWR EWGS HAQT SQIQ SIRR IQQ |
| Gene ID: | 1411 |
| Uniprot: | P05813 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 23kDa/25kDa |
| Observed MW: | 25kDa |
| Synonyms: | CRYBA1, CRYB1, CTRCT10 |
| Background: | Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Beta-crystallins, the most heterogeneous, differ by the presence of the C-terminal extension (present in the basic group, none in the acidic group). Beta-crystallins form aggregates of different sizes and are able to self-associate to form dimers or to form heterodimers with other beta-crystallins. This gene, a beta acidic group member, encodes two proteins (crystallin, beta A3 and crystallin, beta A1) from a single mRNA, the latter protein is 17 aa shorter than crystallin, beta A3 and is generated by use of an alternate translation initiation site. Deletion of exons 3 and 4 causes the autosomal dominant disease 'zonular cataract with sutural opacities'. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CRYBA1: a major structural protein of the eye lens. A member of the beta/gamma-crystallin family. Defects are the cause of congenital zonular cataract with sutural opacities. Two splice-variant isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q11.2 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding Biological Process: visual perception Disease: Cataract 10, Multiple Types |
| NCBI Summary: | Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Beta-crystallins, the most heterogeneous, differ by the presence of the C-terminal extension (present in the basic group, none in the acidic group). Beta-crystallins form aggregates of different sizes and are able to self-associate to form dimers or to form heterodimers with other beta-crystallins. This gene, a beta acidic group member, encodes two proteins (crystallin, beta A3 and crystallin, beta A1) from a single mRNA, the latter protein is 17 aa shorter than crystallin, beta A3 and is generated by use of an alternate translation initiation site. Deletion of exons 3 and 4 causes the autosomal dominant disease 'zonular cataract with sutural opacities'. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P05813 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 2506317 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1411 |
| NCBI Accession: | P05813.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P05813,Q13633, Q14CM9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P05813 |
| Molecular Weight: | 23,191 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Beta-crystallin A3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | crystallin beta A1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CRYBA1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CRYB1; CTRCT10 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | beta-crystallin A3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Beta-crystallin A3 |
| Protein Family: | Beta-crystallin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CRYBA1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CRBA1_HUMAN |
View AllClose