Signal Transduction Antibodies 3
Anti-CRYAA Antibody (CAB5111)
- SKU:
- CAB5111
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CRYAA Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB5111 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IF |
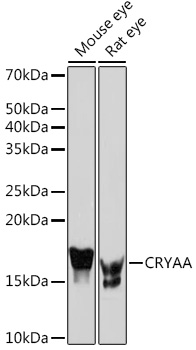
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human CRYAA |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse eye, Rat eye |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human CRYAA |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1409 |
| Uniprot: | P02489 |
| Cellular Location: | |
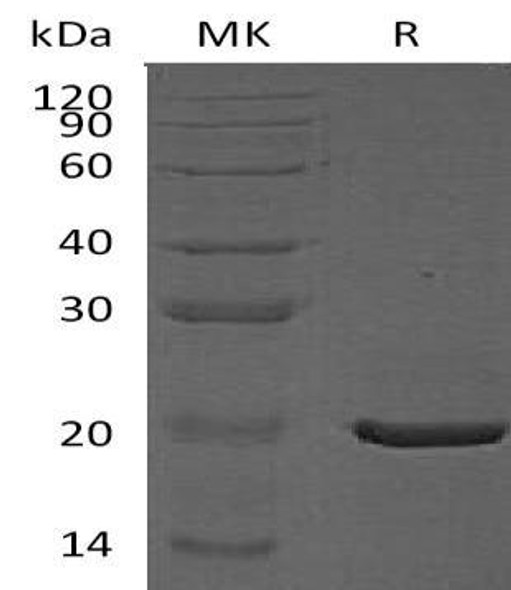
| Calculated MW: | 17kDa |
| Observed MW: | 18KDa |
| Synonyms: | CRYA1, CTRCT9, HSPB4 |
| Background: | Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families. Alpha crystallins are composed of two gene products: alpha-A and alpha-B, for acidic and basic, respectively. Alpha crystallins can be induced by heat shock and are members of the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family. They act as molecular chaperones although they do not renature proteins and release them in the fashion of a true chaperone; instead they hold them in large soluble aggregates. Post-translational modifications decrease the ability to chaperone. These heterogeneous aggregates consist of 30-40 subunits; the alpha-A and alpha-B subunits have a 3:1 ratio, respectively. Two additional functions of alpha crystallins are an autokinase activity and participation in the intracellular architecture. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. Alpha-A and alpha-B gene products are differentially expressed; alpha-A is preferentially restricted to the lens and alpha-B is expressed widely in many tissues and organs. Defects in this gene cause autosomal dominant congenital cataract (ADCC). [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CRYA1: a major structural protein of the eye lens. A member of the small heat shock protein (sHSP, also known as the HSP20) family. Alpha-A is preferentially restricted to the lens. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Heat shock protein; Chaperone Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 21q22.3 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein binding; metal ion binding; unfolded protein binding; structural constituent of eye lens Biological Process: negative regulation of intracellular transport; visual perception; response to stimulus; protein refolding; protein homooligomerization; negative regulation of apoptosis Disease: Cataract 9, Multiple Types |
| NCBI Summary: | Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families. Alpha crystallins are composed of two gene products: alpha-A and alpha-B, for acidic and basic, respectively. Alpha crystallins can be induced by heat shock and are members of the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family. They act as molecular chaperones although they do not renature proteins and release them in the fashion of a true chaperone; instead they hold them in large soluble aggregates. Post-translational modifications decrease the ability to chaperone. These heterogeneous aggregates consist of 30-40 subunits; the alpha-A and alpha-B subunits have a 3:1 ratio, respectively. Two additional functions of alpha crystallins are an autokinase activity and participation in the intracellular architecture. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. Alpha-A and alpha-B gene products are differentially expressed; alpha-A is preferentially restricted to the lens and alpha-B is expressed widely in many tissues and organs. Defects in this gene cause autosomal dominant congenital cataract (ADCC). [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | P02489 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1706112 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1409 |
| NCBI Accession: | P02489.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P02489,Q53X53, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P02489,AAB33370 |
| Molecular Weight: | 173 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Alpha-crystallin A chain |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | crystallin, alpha A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CRYAA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CRYA1; HSPB4; CTRCT9 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | alpha-crystallin A chain; crystallin, alpha-1; heat shock protein beta-4; human alphaA-crystallin (CRYA1) |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Alpha-crystallin A chain |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Heat shock protein beta-4; HspB4 |
| Protein Family: | Alpha-crystallin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CRYAA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CRYAA_HUMAN |
View AllClose


![CRYAA Monoclonal Antibody [Pc9F2AT] (CPAB0279) CRYAA Monoclonal Antibody [Pc9F2AT] (CPAB0279)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/58503/63685/cryaa-monoclonal-antibody-pc9f2at-cpab0279__15728__79029.1706535123.jpg?c=1)