Epigenetics & Nuclear Signaling Antibodies 1
Anti-COASY Antibody (CAB12179)
- SKU:
- CAB12179
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-COASY Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB12179 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
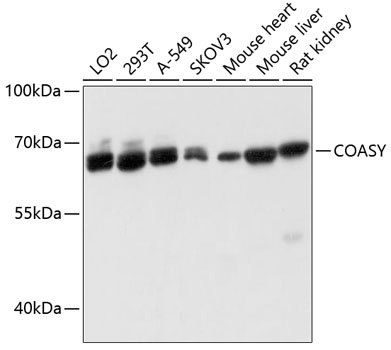
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 345-564 of human COASY (NP_079509.5). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:100 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | LO2, 293T, A-549, SKOV3, Mouse heart, Mouse liver, Rat kidney |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 345-564 of human COASY (NP_079509.5). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | LRPP YERP ELPT CLYV IGLT GISG SGKS SIAQ RLKG LGAF VIDS DHLG HRAY APGG PAYQ PVVE AFGT DILH KDGI INRK VLGS RVFG NKKQ LKIL TDIM WPII AKLA REEM DRAV AEGK RVCV IDAA VLLE AGWQ NLVH EVWT AVIP ETEA VRRI VERD GLSE AAAQ SRLQ SQMS GQQL VEQS HVVL STLW EPHI TQRQ VEKA WALL QKRI PKTH QALD |
| Gene ID: | 80347 |
| Uniprot: | Q13057 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Mitochondrion matrix |
| Calculated MW: | 62kDa/65kDa |
| Observed MW: | 62kDa |
| Synonyms: | COASY, DPCK, NBIA6, NBP, PPAT, UKR1, pOV-2 |
| Background: | Coenzyme A (CoA) functions as a carrier of acetyl and acyl groups in cells and thus plays an important role in numerous synthetic and degradative metabolic pathways in all organisms. In eukaryotes, CoA and its derivatives are also involved in membrane trafficking and signal transduction. This gene encodes the bifunctional protein coenzyme A synthase (CoAsy) which carries out the last two steps in the biosynthesis of CoA from pantothenic acid (vitamin B5). The phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase domain of this bifunctional protein catalyzes the conversion of 4'-phosphopantetheine into dephospho-coenzyme A (dpCoA) while its dephospho-CoA kinase domain completes the final step by phosphorylating dpCoA to form CoA. Mutations in this gene are associated with neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA). Alternative splicing results in multiple isoforms. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PPAT: bifunctional cytoplasmic enzyme that catalyzes the fourth and fifth sequential steps of CoA biosynthetic pathway. The fourth reaction is catalyzed by the phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase, coded by the coaD domain; the fifth reaction is catalyzed by the dephospho-CoA kinase, coded by the coaE domain. May act as a point of CoA biosynthesis regulation. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Kinase, other; EC 2.7.7.3; Transferase; EC 2.7.1.24; Cofactor and Vitamin Metabolism - pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q12-q21 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; mitochondrial outer membrane; mitochondrial matrix; cytoplasm Molecular Function:protein binding; dephospho-CoA kinase activity; pantetheine-phosphate adenylyltransferase activity; ATP binding Biological Process: coenzyme A biosynthetic process; coenzyme biosynthetic process; vitamin metabolic process; pantothenate metabolic process; phosphorylation; water-soluble vitamin metabolic process Disease: Neurodegeneration With Brain Iron Accumulation 6 |
| NCBI Summary: | Coenzyme A (CoA) functions as a carrier of acetyl and acyl groups in cells and thus plays an important role in numerous synthetic and degradative metabolic pathways in all organisms. In eukaryotes, CoA and its derivatives are also involved in membrane trafficking and signal transduction. This gene encodes the bifunctional protein coenzyme A synthase (CoAsy) which carries out the last two steps in the biosynthesis of CoA from pantothenic acid (vitamin B5). The phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase domain of this bifunctional protein catalyzes the conversion of 4'-phosphopantetheine into dephospho-coenzyme A (dpCoA) while its dephospho-CoA kinase domain completes the final step by phosphorylating dpCoA to form CoA. Mutations in this gene are associated with neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA). Alternative splicing results in multiple isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | Q13057 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 32363505 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 80347 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q13057.4 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q13057 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Bifunctional coenzyme A synthase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | Coenzyme A synthase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | COASY |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | NBP; DPCK; PPAT; UKR1; NBIA6; PCH12; pOV-2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | bifunctional coenzyme A synthase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Bifunctional coenzyme A synthase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | NBP; POV-2Including the following 2 domains:Phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase (EC:2.7.7.3)Alternative name(s):Dephospho-CoA pyrophosphorylase; Pantetheine-phosphate adenylyltransferase; PPAT |
| Protein Family: | Bifunctional coenzyme A synthase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | COASY |
| UniProt Entry Name: | COASY_HUMAN |
View AllClose