Cell Death Antibodies 2
Anti-CIDEA Antibody (CAB7655)
- SKU:
- CAB7655
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Death
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CIDEA Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB7655 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 20-219 of human CIDEA (NP_001270.1). |
| Application: | IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | IF 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 20-219 of human CIDEA (NP_001270.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | SQTK RVLF TPLM HPAR PFRV SNHD RSSR RGVM ASSL QELI SKTL DALV IATG LVTL VLEE DGTV VDTE EFFQ TLGD NTHF MILE KGQK WMPG SQHV PTCS PPKR SGIA RVTF DLYR LNPK DFIG CLNV KATM YEMY SVSY DIRC TGLK GLLR SLLR FLSY SAQV TGQF LIYL GTYM LRVL DDKE ERPS LRSQ AKGR FTCG |
| Gene ID: | 1149 |
| Uniprot: | O60543 |
| Cellular Location: | Lipid droplet, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 24kDa |
| Observed MW: |
| Synonyms: | CIDEA, CIDE-A |
| Background: | This gene encodes the homolog of the mouse protein Cidea that has been shown to activate apoptosis. This activation of apoptosis is inhibited by the DNA fragmentation factor DFF45 but not by caspase inhibitors. Mice that lack functional Cidea have higher metabolic rates, higher lipolysis in brown adipose tissue and higher core body temperatures when subjected to cold. These mice are also resistant to diet-induced obesity and diabetes. This suggests that in mice this gene product plays a role in thermogenesis and lipolysis. Alternatively spliced transcripts have been identified. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CIDEA: Acts as a CEBPB coactivator in mammary epithelial cells to control the expression of a subset of CEBPB downstream target genes, including ID2, IGF1, PRLR, SOCS1, SOCS3, XDH, but not casein. By interacting with CEBPB, strengthens the association of CEBPB with the XDH promoter, increases histone acetylation and dissociates HDAC1 from the promoter. Binds to lipid droplets and regulates their enlargement, thereby restricting lipolysis and favoring storage. At focal contact sites between lipid droplets, promotes directional net neutral lipid transfer from the smaller to larger lipid droplets. The transfer direction may be driven by the internal pressure difference between the contacting lipid droplet pair and occurs at a lower rate than that promoted by CIDEC. When overexpressed, induces apoptosis. The physiological significance of its role in apoptosis is unclear. In omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese patients matched for BMI, expression levels correlate with insulin sensitivity. Expression is increased 5-6 fold in the group of patients with high insulin sensitivity, compared to the insulin- resistant group. This observation is consistent with the idea that triglyceride storage in adipocytes plays an important role in sequestering triglycerides and fatty acids away from the circulation and peripheral tissues, thus enhancing insulin sensitivity in liver and muscle. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Mitochondrial; Apoptosis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 18p11.21|18 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; lipid particle; mitochondrial envelope; mitochondrion; nucleus Molecular Function:protein homodimerization activity Biological Process: cell death; lipid metabolic process; negative regulation of cytokine secretion; negative regulation of lipid catabolic process; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production; regulation of apoptosis; sequestering of lipid; thermoregulation |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes the homolog of the mouse protein Cidea that has been shown to activate apoptosis. This activation of apoptosis is inhibited by the DNA fragmentation factor DFF45 but not by caspase inhibitors. Mice that lack functional Cidea have higher metabolic rates, higher lipolysis in brown adipose tissue and higher core body temperatures when subjected to cold. These mice are also resistant to diet-induced obesity and diabetes. This suggests that in mice this gene product plays a role in thermogenesis and lipolysis. Alternatively spliced transcripts have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | O60543 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 9087117 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1149 |
| NCBI Accession: | O60543.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O60543,Q6UPR7, B0YIY7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O60543 |
| Molecular Weight: | 24,687 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cell death activator CIDE-A |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector a |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CIDEA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CIDE-A |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cell death activator CIDE-A |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cell death activator CIDE-A |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector A |
| Protein Family: | Cell death activator |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CIDEA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CIDEA_HUMAN |
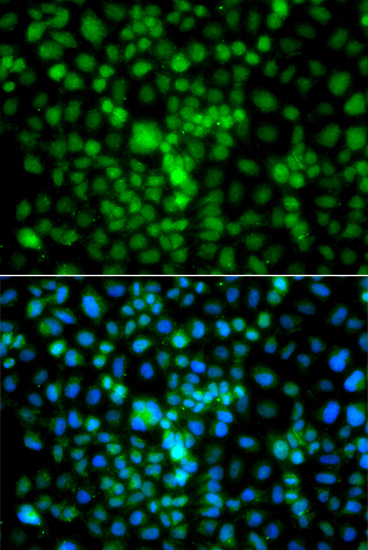 | Immunofluorescence analysis of A549 cells using CIDEA antibody (CAB7655). Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining. |
View AllClose






