Cell Death Antibodies 2
Anti-CDK5 Antibody (CAB19029)
- SKU:
- CAB19029
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Death
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CDK5 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB19029 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
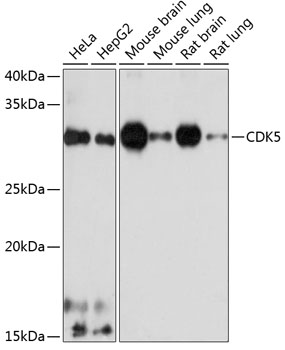
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Cdk5 |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, HepG2, Mouse brain, Mouse lung, Rat brain, Rat lung |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Cdk5 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1020 |
| Uniprot: | Q00535 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 33kDa |
| Observed MW: | 33kDa |
| Synonyms: | CDK5, LIS7, PSSALRE |
| Background: | This gene encodes a proline-directed serine/threonine kinase that is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of proteins. Unlike other members of the family, the protein encoded by this gene does not directly control cell cycle regulation. Instead the protein, which is predominantly expressed at high levels in mammalian postmitotic central nervous system neurons, functions in diverse processes such as synaptic plasticity and neuronal migration through phosphorylation of proteins required for cytoskeletal organization, endocytosis and exocytosis, and apoptosis. In humans, an allelic variant of the gene that results in undetectable levels of the protein has been associated with lethal autosomal recessive lissencephaly-7. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2015] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CDK5: a protein kinase of the CDK family. Unlike other members of this family, it is not activated by cyclins but by p35 (CDK5R1) and p39. An important regulator of neuronal positioning during brain development. May also play a role in synaptogenesis and neurotransmission. Substrates include TAU, MAP2, NF-H and -M, Nudel, PDE6, beta-catenin, amphyphysin, dynamin I, synapsin 1, Munc-18, and NMDA receptor 2A. Plays a role in myogenesis, haematopoietic cell differentiation, spermatogenesis, insulin secretion, and lens differentiation. Implicated in the pathology of neurofibrillary tangles and formation of senile plaques, hallmarks of Alzheimer?s disease. Induces tau phosphorylation and aggregation and neurofibrillary tangle deposition and neurodegeneration in in vitro and in vivo animal models. Brain samples from Alzeimer?s pateints show elevated CDK5 activity. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, CMGC; Kinase, protein; Cell cycle regulation; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); EC 2.7.11.1; CMGC group; CDK family; CDK5 subfamily; CDK/CDK5 subfamily Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 7q36 Cellular Component: axon; cell junction; cell soma; cytoplasm; cytosol; dendrite; growth cone; membrane; neuromuscular junction; nucleoplasm; nucleus; plasma membrane; postsynaptic density Molecular Function:acetylcholine receptor activator activity; cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; ErbB-2 class receptor binding; ErbB-3 class receptor binding; kinase activity; protein binding; protein kinase activity; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; tau-protein kinase activity Biological Process: axon extension; cell proliferation; negative regulation of proteolysis; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; neurite development; neuron apoptosis; neuron differentiation; neuron migration; oligodendrocyte differentiation; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; phosphorylation; positive regulation of neuron apoptosis; regulation of apoptosis; regulation of macroautophagy; regulation of synaptic plasticity; synaptic transmission; synaptic vesicle endocytosis; synaptic vesicle exocytosis; synaptogenesis Disease: Lissencephaly 7 With Cerebellar Hypoplasia |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a proline-directed serine/threonine kinase that is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of proteins. Unlike other members of the family, the protein encoded by this gene does not directly control cell cycle regulation. Instead the protein, which is predominantly expressed at high levels in mammalian postmitotic central nervous system neurons, functions in diverse processes such as synaptic plasticity and neuronal migration through phosphorylation of proteins required for cytoskeletal organization, endocytosis and exocytosis, and apoptosis. In humans, an allelic variant of the gene that results in undetectable levels of the protein has been associated with lethal autosomal recessive lissencephaly-7. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | Q00535 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 4033704 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1020 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q00535.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q00535,A1XKG3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q00535 |
| Molecular Weight: | 29,544 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cyclin-dependent-like kinase 5 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cyclin dependent kinase 5 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CDK5 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | LIS7; PSSALRE |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cyclin-dependent-like kinase 5 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cyclin-dependent-like kinase 5 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cell division protein kinase 5; Serine/threonine-protein kinase PSSALRE; Tau protein kinase II catalytic subunit; TPKII catalytic subunit |
| Protein Family: | CDK5RAP1-like protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CDK5 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CDK5_HUMAN |



![Anti-CDK5 Antibody (CAB18080)[KO Validated] Anti-CDK5 Antibody (CAB18080)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-rd6ounxcu2/images/stencil/590x590/products/55221/59964/anti-cdk5-antibody-cab18080ko-validated__91899__22815.1706529207.jpg?c=1)