Immunology Antibodies 1
Anti-CD209 Antibody (CAB1466)
- SKU:
- CAB1466
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Immunology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CD209 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB1466 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
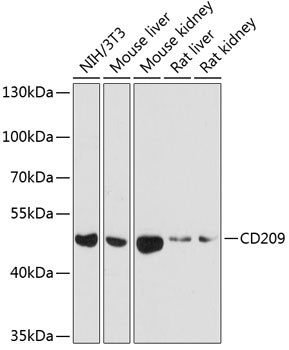
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 265-404 of human CD209 (NP_066978.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | NIH/3T3, Mouse liver, Mouse kidney, Rat liver, Rat kidney |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 265-404 of human CD209 (NP_066978.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | GNCY FMSN SQRN WHDS ITAC KEVG AQLV VIKS AEEQ NFLQ LQSS RSNR FTWM GLSD LNQE GTWQ WVDG SPLL PSFK QYWN RGEP NNVG EEDC AEFS GNGW NDDK CNLA KFWI CKKS AASC SRDE EQFL SPAP ATPN PPPA |
| Gene ID: | 30835 |
| Uniprot: | Q9NNX6 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Secreted, Single-pass type II membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 4kDa/18kDa/30-45kDa |
| Observed MW: | 46kDa |
| Synonyms: | CD209, CDSIGN, CLEC4L, DC-SIGN, DC-SIGN1 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor and is often referred to as DC-SIGN because of its expression on the surface of dendritic cells and macrophages. The encoded protein is involved in the innate immune system and recognizes numerous evolutionarily divergent pathogens ranging from parasites to viruses with a large impact on public health. The protein is organized into three distinct domains: an N-terminal transmembrane domain, a tandem-repeat neck domain and C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. The extracellular region consisting of the C-type lectin and neck domains has a dual function as a pathogen recognition receptor and a cell adhesion receptor by binding carbohydrate ligands on the surface of microbes and endogenous cells. The neck region is important for homo-oligomerization which allows the receptor to bind multivalent ligands with high avidity. Variations in the number of 23 amino acid repeats in the neck domain of this protein are rare but have a significant impact on ligand binding ability. This gene is closely related in terms of both sequence and function to a neighboring gene (GeneID 10332; often referred to as L-SIGN). DC-SIGN and L-SIGN differ in their ligand-binding properties and distribution. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CD209: Pathogen-recognition receptor expressed on the surface of immature dendritic cells (DCs) and involved in initiation of primary immune response. Thought to mediate the endocytosis of pathogens which are subsequently degraded in lysosomal compartments. The receptor returns to the cell membrane surface and the pathogen-derived antigens are presented to resting T-cells via MHC class II proteins to initiate the adaptive immune response. Probably recognizes in a calcium-dependent manner high mannose N-linked oligosaccharides in a variety of pathogen antigens, including HIV-1 gp120, HIV-2 gp120, SIV gp120, ebolavirus glycoproteins, cytomegalovirus gB, HCV E2, dengue virus gE, Leishmania pifanoi LPG, Lewis-x antigen in Helicobacter pylori LPS, mannose in Klebsiella pneumonae LPS, di-mannose and tri- mannose in Mycobacterium tuberculosis ManLAM and Lewis-x antigen in Schistosoma mansoni SEA. Homotetramer. Binds to many viral surface glycoproteins such as HIV-1 gp120, HIV-2 gp120, SIV gp120, ebolavirus envelope glycoproteins, cytomegalovirus gB, HCV E2 and dengue virus major envelope protein E. Predominantly expressed in dendritic cells and in DC-residing tissues. Also found in placental macrophages, endothelial cells of placental vascular channels, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and THP-1 monocytes. 13 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 19p13 Cellular Component: cell surface; membrane; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; integral to membrane Molecular Function:mannose binding; protein binding; peptide antigen binding; metal ion binding; virion binding; carbohydrate binding Biological Process: cell-cell recognition; heterophilic cell adhesion; antigen processing and presentation; leukocyte adhesion; virus-host interaction; regulation of T cell proliferation; innate immune response; endocytosis; peptide antigen transport; viral genome replication; virion attachment to host cell surface receptor Disease: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, Susceptibility To; Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1, Susceptibility To |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor and is often referred to as DC-SIGN because of its expression on the surface of dendritic cells and macrophages. The encoded protein is involved in the innate immune system and recognizes numerous evolutionarily divergent pathogens ranging from parasites to viruses with a large impact on public health. The protein is organized into three distinct domains: an N-terminal transmembrane domain, a tandem-repeat neck domain and C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. The extracellular region consisting of the C-type lectin and neck domains has a dual function as a pathogen recognition receptor and a cell adhesion receptor by binding carbohydrate ligands on the surface of microbes and endogenous cells. The neck region is important for homo-oligomerization which allows the receptor to bind multivalent ligands with high avidity. Variations in the number of 23 amino acid repeats in the neck domain of this protein are rare but have a significant impact on ligand binding ability. This gene is closely related in terms of both sequence and function to a neighboring gene (GeneID 10332; often referred to as L-SIGN). DC-SIGN and L-SIGN differ in their ligand-binding properties and distribution. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9NNX6 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 46396012 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 30835 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9NNX6.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9NNX6,Q2TB19, Q96QP7, Q96QP8, Q96QP9, Q96QQ0, Q96QQ1 Q96QQ2, Q96QQ3, A8KAM4, A8MVQ9, G5E9C4, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9NNX6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 33,874 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | CD209 antigen |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | CD209 molecule |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CD209 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CDSIGN; CLEC4L; DC-SIGN; DC-SIGN1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | CD209 antigen; HIV gpl20-binding protein; C-type lectin domain family 4 member L; C-type lectin domain family 4, member L; dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin 1; dendritic cell-specific intracellular adhesion molecules (ICAM)-3 grabbing non-integrin |
| UniProt Protein Name: | CD209 antigen |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | C-type lectin domain family 4 member L; Dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin 1; DC-SIGN; DC-SIGN1; CD_antigen: CD209 |
| Protein Family: | CD209 antigen |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CD209 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CD209_HUMAN |
View AllClose