Cell Biology Antibodies 7
Anti-c-Fos Antibody (CAB16641)
- SKU:
- CAB16641
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-c-Fos Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16641 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
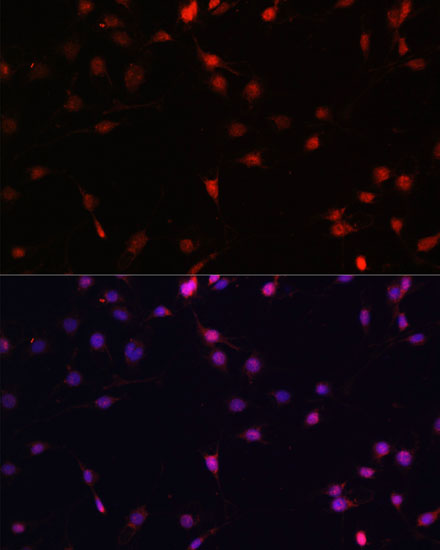
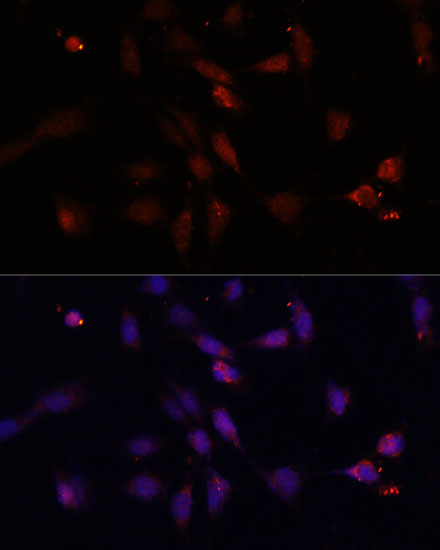
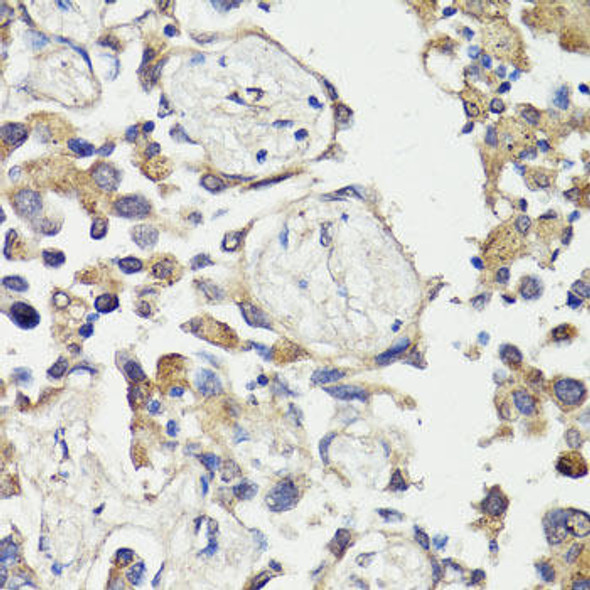
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human c-Fos |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human c-Fos |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 2353 |
| Uniprot: | P01100 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Endoplasmic reticulum, Nucleus, cytosol |
| Calculated MW: | 28kDa/36kDa/40kDa |
| Observed MW: | 55-60KDa |
| Synonyms: | FOS, AP-1, C-FOS, p55, c-Fos |
| Background: | The Fos gene family consists of 4 members: FOS, FOSB, FOSL1, and FOSL2. These genes encode leucine zipper proteins that can dimerize with proteins of the JUN family, thereby forming the transcription factor complex AP-1. As such, the FOS proteins have been implicated as regulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and transformation. In some cases, expression of the FOS gene has also been associated with apoptotic cell death. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Fos: a proto-oncogenic transcription factor of the bZIP family. Dimerizes with proteins of the JUN family, thereby forming the transcription factor complex AP-1. FOS proteins function as regulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and transformation. In some cases, expression of FOS has also been associated with apoptotic cell death. Expression increases upon a variety of stimuli, including growth factors, cytokines, neurotransmitters, polypeptide hormones, stress and cell injury. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; DNA-binding; Transcription factor; Oncoprotein Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 14q24.3 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; transcription factor complex; neuron projection; membrane; endoplasmic reticulum; nucleus; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; double-stranded DNA binding; transcription factor activity; transcription factor binding Biological Process: transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; response to gravity; response to cAMP; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; response to toxin; stress-activated MAPK cascade; response to lipopolysaccharide; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway; female pregnancy; toll-like receptor 10 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 5 signaling pathway; regulation of transcription factor activity; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; conditioned taste aversion; DNA methylation; inflammatory response; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway; aging; response to corticosterone stimulus; response to drug; response to light stimulus; nervous system development; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; sleep; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; cellular response to hormone stimulus; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; response to mechanical stimulus; response to cytokine stimulus; cellular response to extracellular stimulus; toll-like receptor signaling pathway; innate immune response; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; response to cold; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway; response to progesterone stimulus |
| NCBI Summary: | The Fos gene family consists of 4 members: FOS, FOSB, FOSL1, and FOSL2. These genes encode leucine zipper proteins that can dimerize with proteins of the JUN family, thereby forming the transcription factor complex AP-1. As such, the FOS proteins have been implicated as regulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and transformation. In some cases, expression of the FOS gene has also been associated with apoptotic cell death. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P01100 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 120470 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2353 |
| NCBI Accession: | P01100.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P01100,P18849, A8K4E2, B4DQ65, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P01100 |
| Molecular Weight: | 380 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Proto-oncogene c-Fos |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FOS |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | p55; AP-1; C-FOS |
| NCBI Protein Information: | proto-oncogene c-Fos; activator protein 1; cellular oncogene c-fos; G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 7; FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral (v-fos) oncogene homolog (oncogene FOS) |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Proto-oncogene c-Fos |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cellular oncogene fos; G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 7 |
| Protein Family: | Fos-related antigen |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FOS |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FOS_HUMAN |