Cell Biology Antibodies 8
Anti-BBS4 Antibody (CAB3759)
- SKU:
- CAB3759
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-BBS4 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB3759 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
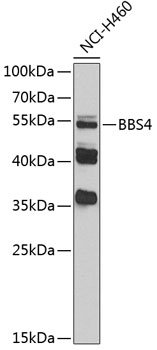
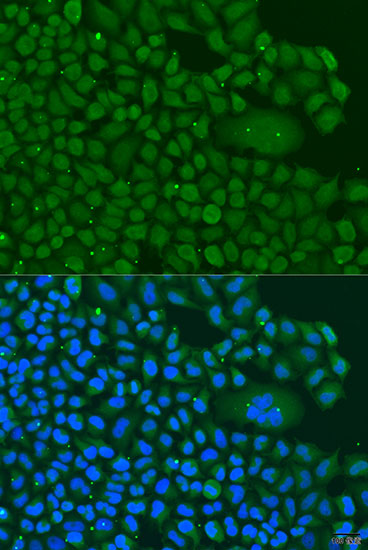
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 350-519 of human BBS4 (NP_149017.2). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | NCI-H460 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 350-519 of human BBS4 (NP_149017.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | NLED IENA KRAY AEAV HLDK CNPL VNLN YAVL LYNQ GEKK NALA QYQE MEKK VSLL KDNS SLEF DSEM VEMA QKLG AALQ VGEA LVWT KPVK DPKS KHQT TSTS KPAS FQQP LGSN QALG QAMS SAAA YRTL PSGA GGTS QFTK PPSL PLEP EPAV ESSP TETS EQIR EK |
| Gene ID: | 585 |
| Uniprot: | Q96RK4 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell projection, Cytoplasm, centriolar satellite, centrosome, cilium, cilium membrane, cytoskeleton, flagellum, microtubule organizing center |
| Calculated MW: | 38kDa/58kDa/59kDa |
| Observed MW: | 53kDa |
| Synonyms: | BBS4 |
| Background: | This gene is a member of the Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) gene family. Bardet-Biedl syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe pigmentary retinopathy, obesity, polydactyly, renal malformation and mental retardation. The proteins encoded by BBS gene family members are structurally diverse. The similar phenotypes exhibited by mutations in BBS gene family members are likely due to the protein's shared roles in cilia formation and function. Many BBS proteins localize to the basal bodies, ciliary axonemes, and pericentriolar regions of cells. BBS proteins may also be involved in intracellular trafficking via microtubule-related transport. The protein encoded by this gene has sequence similarity to O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferases in plants and archaebacteria and in human forms a multi-protein 'BBSome' complex with seven other BBS proteins. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | BBS4: May be required for the dynein-mediated transport of pericentriolar proteins to the centrosome. Required for microtubule anchoring at the centrosome but not for microtubule nucleation. The BBSome complex is required for ciliogenesis but is dispensable for centriolar satellite function. This ciliogenic function is mediated in part by the Rab8 GDP/GTP exchange factor, which localizes to the basal body and contacts the BBSome. Rab8(GTP) enters the primary cilium and promotes extension of the ciliary membrane. Firstly the BBSome associates with the ciliary membrane and binds to RAB3IP/Rabin8, the guanosyl exchange factor (GEF) for Rab8 and then the Rab8-GTP localizes to the cilium and promotes docking and fusion of carrier vesicles to the base of the ciliary membrane. Defects in BBS4 are the cause of Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 4 (BBS4). Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) is a genetically heterogeneous, autosomal recessive disorder characterized by usually severe pigmentary retinopathy, early onset obesity, polydactyly, hypogenitalism, renal malformation and mental retardation. Secondary features include diabetes mellitus, hypertension and congenital heart disease. A relatively high incidence of BBS is found in the mixed Arab populations of Kuwait and in Bedouin tribes throughout the Middle East, most likely due to the high rate of consaguinity in these populations and a founder effect. Belongs to the BBS4 family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell development/differentiation; Adaptor/scaffold; Microtubule-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 15q22.3-q23 Cellular Component: centriole; centrosome; pericentriolar material; nonmotile primary cilium; cytosol; cilium Molecular Function:protein binding; beta-tubulin binding; microtubule motor activity; alpha-tubulin binding Biological Process: fat cell differentiation; retinal rod cell development; regulation of lipid metabolic process; metabolic process; photoreceptor cell maintenance; positive regulation of multicellular organism growth; retinal homeostasis; protein transport; sensory processing; intracellular transport; visual perception; cytokinesis after mitosis; sensory cilium biogenesis; centrosome organization and biogenesis; dendrite development; brain morphogenesis; cilium biogenesis; heart looping; maintenance of protein localization in nucleus; positive regulation of flagellum biogenesis; striatum development; negative regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure; organelle organization and biogenesis; hippocampus development; sensory perception of smell; microtubule cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; regulation of cytokinesis; melanosome transport; protein localization in organelle; adult behavior; neural tube closure; cerebral cortex development; spermatid development Disease: Bardet-biedl Syndrome 4; Bardet-biedl Syndrome 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a member of the Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) gene family. Bardet-Biedl syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe pigmentary retinopathy, obesity, polydactyly, renal malformation and cognitive disability. The proteins encoded by BBS gene family members are structurally diverse. The similar phenotypes exhibited by mutations in BBS gene family members are likely due to the protein's shared roles in cilia formation and function. Many BBS proteins localize to the basal bodies, ciliary axonemes, and pericentriolar regions of cells. BBS proteins may also be involved in intracellular trafficking via microtubule-related transport. The protein encoded by this gene has sequence similarity to O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferases in plants and archaebacteria and in human forms a multi-protein "BBSome" complex with seven other BBS proteins. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016] |
| UniProt Code: | Q96RK4 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 160359000 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 585 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q96RK4.2 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q96RK4 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 4 protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | BBS4 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 4 protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 4 protein |
| Protein Family: | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 4 protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | BBS4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | BBS4_HUMAN |