Cell Biology Antibodies 12
Anti-B4GALT1 Antibody (CAB8546)
- SKU:
- CAB8546
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Applications:
- IHC
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-B4GALT1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB8546 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
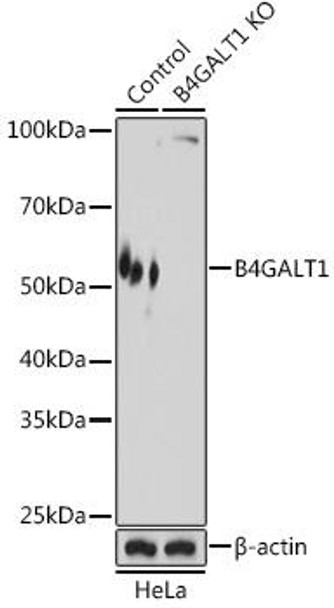
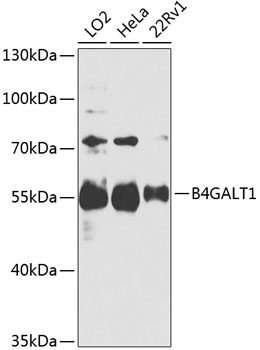
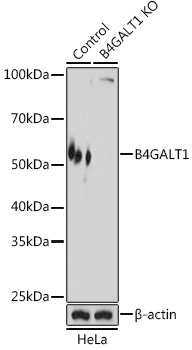
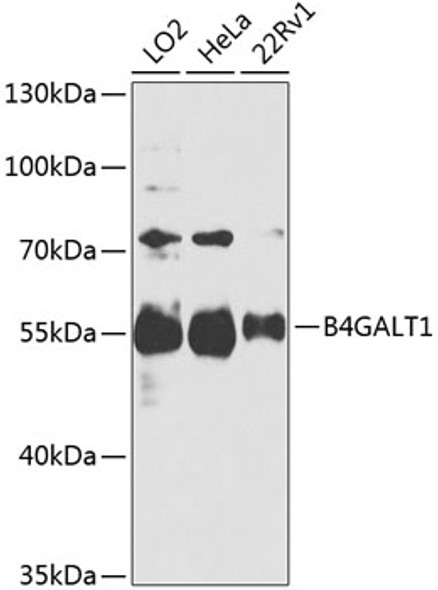
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 50-215 of human B4GALT1 (NP_001488.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | LO2, HeLa, 22Rv1 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 50-215 of human B4GALT1 (NP_001488.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | LPQL VGVS TPLQ GGSN SAAA IGQS SGEL RTGG ARPP PPLG ASSQ PRPG GDSS PVVD SGPG PASN LTSV PVPH TTAL SLPA CPEE SPLL VGPM LIEF NMPV DLEL VAKQ NPNV KMGG RYAP RDCV SPHK VAII IPFR NRQE HLKY WLYY LHPV LQRQ QLDY GIYV IN |
| Gene ID: | 2683 |
| Uniprot: | P15291 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Cell projection, Cell surface, Golgi apparatus, Golgi stack membrane, Secreted, Single-pass type II membrane protein, filopodium |
| Calculated MW: | 42kDa/43kDa |
| Observed MW: | 55kDa |
| Synonyms: | B4GALT1, B4GAL-T1, CDG2D, GGTB2, GT1, GTB, beta4Gal-T1, beta-1 |
| Background: | This gene is one of seven beta-1, 4-galactosyltransferase (beta4GalT) genes. They encode type II membrane-bound glycoproteins that appear to have exclusive specificity for the donor substrate UDP-galactose; all transfer galactose in a beta1, 4 linkage to similar acceptor sugars: GlcNAc, Glc, and Xyl. Each beta4GalT has a distinct function in the biosynthesis of different glycoconjugates and saccharide structures. As type II membrane proteins, they have an N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence that directs the protein to the Golgi apparatus and which then remains uncleaved to function as a transmembrane anchor. By sequence similarity, the beta4GalTs form four groups: beta4GalT1 and beta4GalT2, beta4GalT3 and beta4GalT4, beta4GalT5 and beta4GalT6, and beta4GalT7. This gene is unique among the beta4GalT genes because it encodes an enzyme that participates both in glycoconjugate and lactose biosynthesis. For the first activity, the enzyme adds galactose to N-acetylglucosamine residues that are either monosaccharides or the nonreducing ends of glycoprotein carbohydrate chains. The second activity is restricted to lactating mammary tissues where the enzyme forms a heterodimer with alpha-lactalbumin to catalyze UDP-galactose + D-glucose <=> UDP + lactose. The two enzymatic forms result from alternate transcription initiation sites and post-translational processing. Two transcripts, which differ only at the 5' end, with approximate lengths of 4.1 kb and 3.9 kb encode the same protein. The longer transcript encodes the type II membrane-bound, trans-Golgi resident protein involved in glycoconjugate biosynthesis. The shorter transcript encodes a protein which is cleaved to form the soluble lactose synthase. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | B4GALT1: The Golgi complex form catalyzes the production of lactose in the lactating mammary gland and could also be responsible for the synthesis of complex-type N-linked oligosaccharides in many glycoproteins as well as the carbohydrate moieties of glycolipids. Defects in B4GALT1 are the cause of congenital disorder of glycosylation type 2D (CDG2D). CDGs are a family of severe inherited diseases caused by a defect in protein N- glycosylation. They are characterized by under-glycosylated serum proteins. These multisystem disorders present with a wide variety of clinical features, such as disorders of the nervous system development, psychomotor retardation, dysmorphic features, hypotonia, coagulation disorders, and immunodeficiency. The broad spectrum of features reflects the critical role of N-glycoproteins during embryonic development, differentiation, and maintenance of cell functions. Belongs to the glycosyltransferase 7 family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative initiation. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 2.4.1.38; Cell adhesion; EC 2.4.1.90; Cell development/differentiation; EC 2.4.1.22; Glycan Metabolism - keratan sulfate biosynthesis; Glycan Metabolism - glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - lacto and neolacto series; Carbohydrate Metabolism - galactose; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Membrane protein, integral; Glycan Metabolism - N-glycan biosynthesis; Cell surface; Transferase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 9p13 Cellular Component: basolateral plasma membrane; brush border membrane; desmosome; external side of plasma membrane; extracellular space; filopodium; glycocalyx; Golgi apparatus; Golgi membrane; Golgi trans cisterna; integral to membrane; membrane; plasma membrane Molecular Function:alpha-tubulin binding; beta-N-acetylglucosaminylglycopeptide beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase activity; beta-tubulin binding; cytoskeletal protein binding; galactosyltransferase activity; lactose synthase activity; manganese ion binding; N-acetyllactosamine synthase activity; protein homodimerization activity; protein kinase binding; UDP-galactosyltransferase activity Biological Process: acute inflammatory response; angiogenesis involved in wound healing; binding of sperm to zona pellucida; branching morphogenesis of a tube; carbohydrate metabolic process; cell adhesion; cellular protein metabolic process; development of secondary sexual characteristics; epithelial cell development; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; galactose metabolic process; glycosaminoglycan metabolic process; keratan sulfate biosynthetic process; keratan sulfate metabolic process; lactose biosynthetic process; leukocyte migration; mammary gland development; multicellular organism reproduction; negative regulation of cell proliferation; Notch signaling pathway; oligosaccharide biosynthetic process; penetration of zona pellucida; positive regulation of apoptosis involved in mammary gland involution; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in wound healing; post-translational protein modification; protein amino acid N-linked glycosylation; protein amino acid N-linked glycosylation via asparagine; regulation of acrosome reaction; regulation of cell motility; single fertilization Disease: Congenital Disorder Of Glycosylation, Type Iid |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is one of seven beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase (beta4GalT) genes. They encode type II membrane-bound glycoproteins that appear to have exclusive specificity for the donor substrate UDP-galactose; all transfer galactose in a beta1,4 linkage to similar acceptor sugars: GlcNAc, Glc, and Xyl. Each beta4GalT has a distinct function in the biosynthesis of different glycoconjugates and saccharide structures. As type II membrane proteins, they have an N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence that directs the protein to the Golgi apparatus and which then remains uncleaved to function as a transmembrane anchor. By sequence similarity, the beta4GalTs form four groups: beta4GalT1 and beta4GalT2, beta4GalT3 and beta4GalT4, beta4GalT5 and beta4GalT6, and beta4GalT7. This gene is unique among the beta4GalT genes because it encodes an enzyme that participates both in glycoconjugate and lactose biosynthesis. For the first activity, the enzyme adds galactose to N-acetylglucosamine residues that are either monosaccharides or the nonreducing ends of glycoprotein carbohydrate chains. The second activity is restricted to lactating mammary tissues where the enzyme forms a heterodimer with alpha-lactalbumin to catalyze UDP-galactose + D-glucose <=> UDP + lactose. The two enzymatic forms result from alternate transcription initiation sites and post-translational processing. Two transcripts, which differ only at the 5' end, with approximate lengths of 4.1 kb and 3.9 kb encode the same protein. The longer transcript encodes the type II membrane-bound, trans-Golgi resident protein involved in glycoconjugate biosynthesis. The shorter transcript encodes a protein which is cleaved to form the soluble lactose synthase. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P15291 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 116241264 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2683 |
| NCBI Accession: | P15291.5 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P15291,Q12909, Q12910, Q12911, Q14456, Q14509, Q14523 B2R710, D3DRL2, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P15291 |
| Molecular Weight: | 42,538 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | B4GALT1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | GT1; GTB; CDG2D; GGTB2; B4GAL-T1; beta4Gal-T1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | UDP-Gal:beta-GlcNAc beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1; UDP-galactose:beta-N-acetylglucosamine beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 |
| Protein Family: | Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | B4GALT1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | B4GT1_HUMAN |